Circular Motion
... probably because it could be divided up so many different ways, i.e. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 12, 24 and 30. This got picked up by the Babylonians and passed on to the Egyptians. And from there to us. The circle has 6 × 60, or 360 parts. It’s popularity may also be related to fact that it is close to th ...
... probably because it could be divided up so many different ways, i.e. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 12, 24 and 30. This got picked up by the Babylonians and passed on to the Egyptians. And from there to us. The circle has 6 × 60, or 360 parts. It’s popularity may also be related to fact that it is close to th ...
Document
... length of chain and swing: 4.5 m distance from center of rotation to chain attachment: 6.7 m 1. Draw a FBD of a rider and the swing 2nd Law Equations. 2. What is the source of the centripetal force acting on a rider and the swing? 3. Which will ride higher: an empty swing or one with someone in it? ...
... length of chain and swing: 4.5 m distance from center of rotation to chain attachment: 6.7 m 1. Draw a FBD of a rider and the swing 2nd Law Equations. 2. What is the source of the centripetal force acting on a rider and the swing? 3. Which will ride higher: an empty swing or one with someone in it? ...
Part II
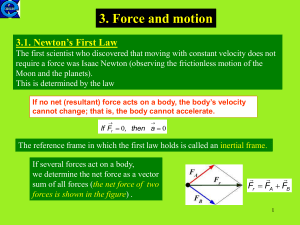
... – Any reference frame moving with uniform (nonaccelerated) motion with respect to an “absolute” frame “fixed” with respect to the stars. ...
... – Any reference frame moving with uniform (nonaccelerated) motion with respect to an “absolute” frame “fixed” with respect to the stars. ...
80 Revision Motion
... minutes? (A) 3m (B) 33m (C) 333m (D) 3333m 5. How long does it take for a car traveling at 85m/s to cover a distance of 15km? (A) 6s (B) 1275s (C) 176s (D) 221s 6. A dragster accelerates at a constant rate from rest to 55.56m/s in 12s. What was their acceleration? (A) 2400m/s/s (B) 16.6m/s/s (C) 9.8 ...
... minutes? (A) 3m (B) 33m (C) 333m (D) 3333m 5. How long does it take for a car traveling at 85m/s to cover a distance of 15km? (A) 6s (B) 1275s (C) 176s (D) 221s 6. A dragster accelerates at a constant rate from rest to 55.56m/s in 12s. What was their acceleration? (A) 2400m/s/s (B) 16.6m/s/s (C) 9.8 ...
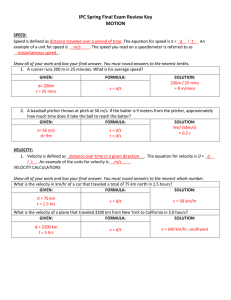
Chapter 2 Review WS Name ______Answer Key Date ______
... 1. Compare and Contrast the following pairs of vocabulary words. a. Speed and velocity -Both tell how distance changes with time. -Velocity includes the direction b. Distance and displacement -Displacement is distance and direction from a starting point, distance is how far an object is from somethi ...
... 1. Compare and Contrast the following pairs of vocabulary words. a. Speed and velocity -Both tell how distance changes with time. -Velocity includes the direction b. Distance and displacement -Displacement is distance and direction from a starting point, distance is how far an object is from somethi ...
Motion and Forces ppt.
... according to the inverse-square law. The force of gravity weakens as the distance squared. Ex: If you were three times farther from the center of the Earth as you are now, your weight would be 1/9 of what it is now. ...
... according to the inverse-square law. The force of gravity weakens as the distance squared. Ex: If you were three times farther from the center of the Earth as you are now, your weight would be 1/9 of what it is now. ...
Section V
... plate; the bullet ricochets along the path CD with a velocity of 500 m/s. Knowing that the bullet caused a 50-mm scratch on the surface of the plate, determine the average impulsive force exerted on the bullet during its contact with the plate. (Hint Assume an average speed of 550 m/s during contact ...
... plate; the bullet ricochets along the path CD with a velocity of 500 m/s. Knowing that the bullet caused a 50-mm scratch on the surface of the plate, determine the average impulsive force exerted on the bullet during its contact with the plate. (Hint Assume an average speed of 550 m/s during contact ...
Set 5
... 6) The principal moments of inertia of a uniform plate are I1, I2>I1, and I3=I1+I2. Choose a coordinate system with the origin at the cm of the plate. The plate rotates with an angular velocity ω about an axis that makes an angle α with the plane of the plate such that at time t=0, ω1(t=0)=ωcos α, ...
... 6) The principal moments of inertia of a uniform plate are I1, I2>I1, and I3=I1+I2. Choose a coordinate system with the origin at the cm of the plate. The plate rotates with an angular velocity ω about an axis that makes an angle α with the plane of the plate such that at time t=0, ω1(t=0)=ωcos α, ...
Work is a force that moves through a distance
... 5. 1N equals 1kgm/s2. What is a Dyne equal to? 6 How much force is required to accelerate a 1800kg car at 3.00m/s/s? 7. What is the weight of the 1800kg car in question G? 8. What is the difference between mass and weight? 9. What unit is weight measured in? 10. What is inertia? 11. What do automobi ...
... 5. 1N equals 1kgm/s2. What is a Dyne equal to? 6 How much force is required to accelerate a 1800kg car at 3.00m/s/s? 7. What is the weight of the 1800kg car in question G? 8. What is the difference between mass and weight? 9. What unit is weight measured in? 10. What is inertia? 11. What do automobi ...
Name: Date:______ Period:_____ Chapter 19 Honors Study Guide
... 2. What is acceleration? Negative acceleration? The measure of how quickly the velocity of an object changes; when an object’s initial velocity is greater than its final velocity 3. Define speed? The distance an object moves divided by the time it took to move that distance 4. What is the difference ...
... 2. What is acceleration? Negative acceleration? The measure of how quickly the velocity of an object changes; when an object’s initial velocity is greater than its final velocity 3. Define speed? The distance an object moves divided by the time it took to move that distance 4. What is the difference ...
EFFECT OF CENTRIFUGAL AND CORIOLIS FORCES DUE TO
... with constant angular velocity ω about its polar axis, then: ...
... with constant angular velocity ω about its polar axis, then: ...