STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... H. Problems Involving Energy and Momentum I. Angular Momentum of a Particle J. Angular Momentum of a System of Particles K. Generalized Principle of Impulse and Momentum L. Conservation of Angular Momentum M. Application to Space Mechanics VI. Kinematics of Rigid Bodies ...
... H. Problems Involving Energy and Momentum I. Angular Momentum of a Particle J. Angular Momentum of a System of Particles K. Generalized Principle of Impulse and Momentum L. Conservation of Angular Momentum M. Application to Space Mechanics VI. Kinematics of Rigid Bodies ...
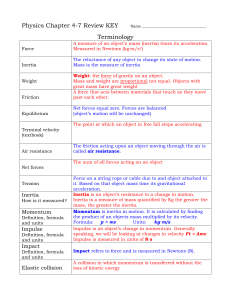
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... • Mass: measures the difficulty in accelerating an object • Newton’s first law: if the net force on an object is zero, its velocity is constant • Inertial frame of reference: one in which the first law holds • Newton’s second law: • Free-body diagram: a sketch showing all the forces on an object ...
... • Mass: measures the difficulty in accelerating an object • Newton’s first law: if the net force on an object is zero, its velocity is constant • Inertial frame of reference: one in which the first law holds • Newton’s second law: • Free-body diagram: a sketch showing all the forces on an object ...
Physics 102 Introduction to Physics
... All vectors (force, velocity, acceleration, etc) add the same way. The 30N and 40N forces add to get a resultant force of 50N. The DIRECTION of the resultant 50N force is given by the diagonal of the “parallelagram” (The Parallelagram Rule) ...
... All vectors (force, velocity, acceleration, etc) add the same way. The 30N and 40N forces add to get a resultant force of 50N. The DIRECTION of the resultant 50N force is given by the diagonal of the “parallelagram” (The Parallelagram Rule) ...
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 4
... mph. The airplane accounts for the wind (by pointing the plane somewhat into the wind) and flies directly east relative to the ground. What is the plane’s resulting ground speed? In what direction is the nose of the plane pointed? 193.6 mph 14.5 deg. north of east ...
... mph. The airplane accounts for the wind (by pointing the plane somewhat into the wind) and flies directly east relative to the ground. What is the plane’s resulting ground speed? In what direction is the nose of the plane pointed? 193.6 mph 14.5 deg. north of east ...
Lecture 16 - Circular Motion
... Newton knew that at the surface of the earth bodies (apples) fall 5 m in the first second, and that this acceleration is due to earth’s gravity. He showed that the gravity force is the same as if all earth’s mass were at its center, 4000 mi from the surface. (This required inventing Calculus). He wo ...
... Newton knew that at the surface of the earth bodies (apples) fall 5 m in the first second, and that this acceleration is due to earth’s gravity. He showed that the gravity force is the same as if all earth’s mass were at its center, 4000 mi from the surface. (This required inventing Calculus). He wo ...
Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion
... between two objects – When objects are touching they naturally cause a resistance in motion – Friction occurs because microwelds form ...
... between two objects – When objects are touching they naturally cause a resistance in motion – Friction occurs because microwelds form ...
Introduction Worksheet 1
... a) What power was used to move the mass? b) The mass is now pulled from rest by a horizontal force of 0.80 N for 12 s What kinetic energy will it gain? Hint: first find the acceleration of the mass. c) Referring to (b), what power was used to accelerate the mass? ...
... a) What power was used to move the mass? b) The mass is now pulled from rest by a horizontal force of 0.80 N for 12 s What kinetic energy will it gain? Hint: first find the acceleration of the mass. c) Referring to (b), what power was used to accelerate the mass? ...
Torque on Current Loop
... v⊥ = v sinφ contributes to circular motion v|| = v cosφ is unchanged ...
... v⊥ = v sinφ contributes to circular motion v|| = v cosφ is unchanged ...
Motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field
... Our derivation above shows that the quantum mechanical Hamiltonian of a charged particle is defined in terms of the vector potential, A. Since the latter is defined only up to some gauge choice, this suggests that the wavefunction is not a gauge invariant object. Indeed, it is only the observables a ...
... Our derivation above shows that the quantum mechanical Hamiltonian of a charged particle is defined in terms of the vector potential, A. Since the latter is defined only up to some gauge choice, this suggests that the wavefunction is not a gauge invariant object. Indeed, it is only the observables a ...
Newton`s 2nd power point
... acted upon by an unbalanced force will accelerate in the direction of the force. • If you kick the ball, it starts moving. • The ball accelerates only while your foot is in contact with the ball. ...
... acted upon by an unbalanced force will accelerate in the direction of the force. • If you kick the ball, it starts moving. • The ball accelerates only while your foot is in contact with the ball. ...
Chapter5Class3 - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Banking the curve can help keep cars from skidding. In fact, for every banked curve, there is one speed at which the entire centripetal force is supplied by the ...
... Banking the curve can help keep cars from skidding. In fact, for every banked curve, there is one speed at which the entire centripetal force is supplied by the ...
1 Dot Product and Cross Products • For two vectors, the dot product
... • When a wheel is rolling is without slipping the point at the bottom of the wheel is instanteously not moving (it has non zero acceleration however). Thus what actually keeps a tire from slipping is the coefficient of static and not kinetic friction. If a an object is rolling without slipping we h ...
... • When a wheel is rolling is without slipping the point at the bottom of the wheel is instanteously not moving (it has non zero acceleration however). Thus what actually keeps a tire from slipping is the coefficient of static and not kinetic friction. If a an object is rolling without slipping we h ...