Document
... is already in motion. Of these two forces, (20) friction is greater. The amount of friction can be calculated using the equation (21). The constant in the equation is called the (22). The Net Force Causes Acceleration If more than one force acts on an object, the amount of acceleration can be calcul ...
... is already in motion. Of these two forces, (20) friction is greater. The amount of friction can be calculated using the equation (21). The constant in the equation is called the (22). The Net Force Causes Acceleration If more than one force acts on an object, the amount of acceleration can be calcul ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... mass—which is roughly the amount of material present in the object Mass is NOT volume, the measure of space that an object takes up Mass is NOT weight, the force of gravity on an object Mass is a measure of the inertia that an object exhibits in response to any effort made to start it, stop it ...
... mass—which is roughly the amount of material present in the object Mass is NOT volume, the measure of space that an object takes up Mass is NOT weight, the force of gravity on an object Mass is a measure of the inertia that an object exhibits in response to any effort made to start it, stop it ...
Force and Newton`s First Law
... 1st - A car will sit at a stoplight until you press the gas 2nd - It is harder to carry a box of rocks than a box of popcorn 3rd - When birds fly, they push their wings down in order to go up ...
... 1st - A car will sit at a stoplight until you press the gas 2nd - It is harder to carry a box of rocks than a box of popcorn 3rd - When birds fly, they push their wings down in order to go up ...
Q ~ ~ ~ ~ # $ ~ ( 3 0 %... 1. (5%)
... 300 K (point A in the figure). It is heated at constant volume to 3.00 atill (point B). Then, it is allowed to expand isothermally to 1.OO atm (yoint C) and at last is compressed isobarically (constant pressure) to its original state. (a) Find the number of moles in the sample. (b) Find the temperat ...
... 300 K (point A in the figure). It is heated at constant volume to 3.00 atill (point B). Then, it is allowed to expand isothermally to 1.OO atm (yoint C) and at last is compressed isobarically (constant pressure) to its original state. (a) Find the number of moles in the sample. (b) Find the temperat ...
Chapters One and Two - elementaryscienceteachers
... Acceleration (cont.) If a roller coaster is traveling at 7 m/s at its highest point, and 3 seconds later its speed has increased to 28 m/s, what is its average acceleration? ...
... Acceleration (cont.) If a roller coaster is traveling at 7 m/s at its highest point, and 3 seconds later its speed has increased to 28 m/s, what is its average acceleration? ...
Newton"s 1st
... Hypothetically Galileo reasoned that if the second ramp was removed altogether, the ball would roll down the first incline plane and roll forever and ever trying to attain the same height from where it was released. ...
... Hypothetically Galileo reasoned that if the second ramp was removed altogether, the ball would roll down the first incline plane and roll forever and ever trying to attain the same height from where it was released. ...
Part IV
... • In the absence of external forces, when viewed from an inertial reference frame, an object at rest remains at rest & an object in motion continues in motion with a constant velocity – Newton’s 1st Law describes what happens in the absence of a net force. – It also tells us that when no force acts ...
... • In the absence of external forces, when viewed from an inertial reference frame, an object at rest remains at rest & an object in motion continues in motion with a constant velocity – Newton’s 1st Law describes what happens in the absence of a net force. – It also tells us that when no force acts ...
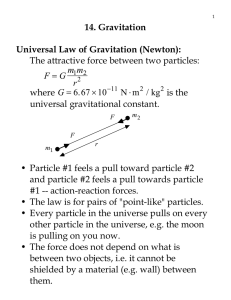
14. Gravitation Universal Law of Gravitation (Newton): G
... Calculate the gravitational force due to a hollowed sphere, assuming that the mass of the ...
... Calculate the gravitational force due to a hollowed sphere, assuming that the mass of the ...
Drag
... have to use the momentum formalism, rather than F=ma. It is also the first example of non-uniform acceleration that we will deal with using the Force Approach. On the mathematical side, it gives us more experience with differential equations than we get from simple UAM (uniformly accelerated motion) ...
... have to use the momentum formalism, rather than F=ma. It is also the first example of non-uniform acceleration that we will deal with using the Force Approach. On the mathematical side, it gives us more experience with differential equations than we get from simple UAM (uniformly accelerated motion) ...
Newtons laws notes
... acted on by an unbalanced force. u An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. u Inertia: The tendency for ...
... acted on by an unbalanced force. u An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. u Inertia: The tendency for ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
Document
... Runtime calculate the position and orientation of the camera with the sun Put textures to simulate the len’s flare ...
... Runtime calculate the position and orientation of the camera with the sun Put textures to simulate the len’s flare ...
5.1 - Mass/Spring Systems
... weight W is balanced by the restoring force F ks . Weight is defined by ____________ times ______________. _______________ can be measured in ...
... weight W is balanced by the restoring force F ks . Weight is defined by ____________ times ______________. _______________ can be measured in ...
Unit 3-Energy and Momentum Study Guide
... Vocabulary: Force, time, mass, velocity, acceleration, displacement, momentum, impulse, conservation of momentum, elastic collisions, inelastic collisions, vector, scalar, impulse momentum change theorem, Newton’s first law, Newton’s second law, Newton’s third law, work, sine, cosine, tangent, angul ...
... Vocabulary: Force, time, mass, velocity, acceleration, displacement, momentum, impulse, conservation of momentum, elastic collisions, inelastic collisions, vector, scalar, impulse momentum change theorem, Newton’s first law, Newton’s second law, Newton’s third law, work, sine, cosine, tangent, angul ...