Chapter 7 Study Guide: Forces Focus on the highlighted terms and
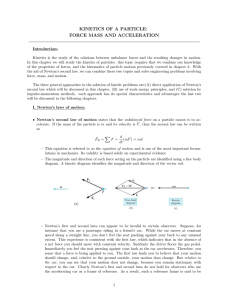
... *Newton’s First Law of Motion: Objects at rest will remain at rest and objects moving at a constant velocity will continue moving at a constant velocity unless they are acted upon by nonzero net forces. It is also called the law of inertia. inertia-the resistance to changes in motion Ex: what you fe ...
... *Newton’s First Law of Motion: Objects at rest will remain at rest and objects moving at a constant velocity will continue moving at a constant velocity unless they are acted upon by nonzero net forces. It is also called the law of inertia. inertia-the resistance to changes in motion Ex: what you fe ...
ppt - Faculty Web Sites at the University of Virginia
... An object at rest remains at rest unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
... An object at rest remains at rest unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
P4: Explaining Motion
... If we increase the time over which the force acts then the resultant force will be smaller (the change in momentum is unchanged!) • This is the principle used in crash helmets, air bags, seat belts, climbing ropes and crumple zones on cars ...
... If we increase the time over which the force acts then the resultant force will be smaller (the change in momentum is unchanged!) • This is the principle used in crash helmets, air bags, seat belts, climbing ropes and crumple zones on cars ...
Physics_100_chapt_3
... Newton’3rd Law: action-reaction Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal in magnitude but opposite in direction force on the first. ...
... Newton’3rd Law: action-reaction Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal in magnitude but opposite in direction force on the first. ...
motion
... Hint- Newton’s 3rd Law. The action force is the kick, while the equal and opposite reaction is the body of the person who’s being kicked pushing back on the kicker. ...
... Hint- Newton’s 3rd Law. The action force is the kick, while the equal and opposite reaction is the body of the person who’s being kicked pushing back on the kicker. ...
Forces
... which a force is acting depends on the amount of net force being applied and on the mass of the object. Law 3: For every force, there is an equal and opposite counter-force. (Forces come in pairs). ...
... which a force is acting depends on the amount of net force being applied and on the mass of the object. Law 3: For every force, there is an equal and opposite counter-force. (Forces come in pairs). ...
Impulse and Momentum
... Before he can move, a tackler, running at a velocity of +4.8 m/s, grabs him. The tackler holds onto the receiver, and the two move off together with a velocity of +2.6 m/s. The mass of the tackler is 116 kg. Assuming that momentum is conserved, find the mass of the receiver. ...
... Before he can move, a tackler, running at a velocity of +4.8 m/s, grabs him. The tackler holds onto the receiver, and the two move off together with a velocity of +2.6 m/s. The mass of the tackler is 116 kg. Assuming that momentum is conserved, find the mass of the receiver. ...
Self Assessment
... Identify which Law of Motion each is by placing a 1, 2 or 3 in the blank 19. _______ You’re in a car that slams on the brakes and you go flying forward 20. _______ When you hit a nail with a hammer, they both feel the same force 21. _______ The nail in #2 moves more than the hammer does. 22. _______ ...
... Identify which Law of Motion each is by placing a 1, 2 or 3 in the blank 19. _______ You’re in a car that slams on the brakes and you go flying forward 20. _______ When you hit a nail with a hammer, they both feel the same force 21. _______ The nail in #2 moves more than the hammer does. 22. _______ ...
PPT_W07D1_mac
... Total Force on a System of N Particles is the External Force The total force on a system of particles is the sum of the total external and total internal forces. Since the total internal force is zero ...
... Total Force on a System of N Particles is the External Force The total force on a system of particles is the sum of the total external and total internal forces. Since the total internal force is zero ...
Chapter 4
... force acting on an object of mass m near the Earth’s surface is called the weight w of the object ...
... force acting on an object of mass m near the Earth’s surface is called the weight w of the object ...
Chapter 5.3-6.3 Equilibrium and Newton`s Laws
... Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion: Newton’s Third Law (action-reaction) ...
... Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion: Newton’s Third Law (action-reaction) ...
Day 1 Notes: Dealing with projectiles in two dimensions. There are
... lines x and y axis. Then, the original horizontal and vertical line will become diagonal line. From then, everything is the same as the mothod introduced in D. ...
... lines x and y axis. Then, the original horizontal and vertical line will become diagonal line. From then, everything is the same as the mothod introduced in D. ...
Basic Physics Topics For Today`s Class Newton`s Laws of Motion (1
... Work and Energy Energy • Ability of a body to do work • Work due to motion is called Kinetic Energy (KE) KE = ½ x mass x velocity2 measured in Joules – Example: If a 1 kg object fall from a height of 1 m with a velocity of 4.43 m/s KE = ½ x 1kg x (1 m/s)2 = 9.8 J ...
... Work and Energy Energy • Ability of a body to do work • Work due to motion is called Kinetic Energy (KE) KE = ½ x mass x velocity2 measured in Joules – Example: If a 1 kg object fall from a height of 1 m with a velocity of 4.43 m/s KE = ½ x 1kg x (1 m/s)2 = 9.8 J ...