The Nature of Force
... Mass is the amount of matter in an object. SI unit is the kilogram. The amount of inertia an object has depends on its mass. The greater the mass the greater the inertia. ...
... Mass is the amount of matter in an object. SI unit is the kilogram. The amount of inertia an object has depends on its mass. The greater the mass the greater the inertia. ...
Course: Advanced Placement Physics B Teacher: Mr. Nathan
... projectiles fired both horizontally and at an angle ...
... projectiles fired both horizontally and at an angle ...
Newton`s Laws MC test
... directed at an angle θ below the horizontal, and the box remains a rest. The box rests on a horizontal surface that has some friction with the box. The friction force on the box due to the floor is equal to ...
... directed at an angle θ below the horizontal, and the box remains a rest. The box rests on a horizontal surface that has some friction with the box. The friction force on the box due to the floor is equal to ...
Forces and Motion
... Any change in the state of motion of an object is the result of the sum of all the forces acting on it. The result, the combination of all these forces is called the net force. ...
... Any change in the state of motion of an object is the result of the sum of all the forces acting on it. The result, the combination of all these forces is called the net force. ...
forces
... When our mass is in kg (kilograms) and our acceleration is in m/s2 (meters per second squared) then our force’s units will be: ...
... When our mass is in kg (kilograms) and our acceleration is in m/s2 (meters per second squared) then our force’s units will be: ...
Scalar A scalar quantity is a physical quantity which is completely
... to two separate motions in one dimension : resolving into horizontal and vertical and dealing with each component independently. Newtons Second Law. Newtons’ Second Law deals with the effect of forces on moving objects, and provides a means to define the unit of ...
... to two separate motions in one dimension : resolving into horizontal and vertical and dealing with each component independently. Newtons Second Law. Newtons’ Second Law deals with the effect of forces on moving objects, and provides a means to define the unit of ...
Sears_690_Content Sets_complete - Physics
... 5.1l Weight is the gravitational force with which a planet attracts a mass*. The mass of an object is independent of the gravitational field in which it is located. Set #9 5.1pThe impulse* imparted to an object causes a change in its momentum*. Set #10 5.1q According to Newton’s Third Law, forces oc ...
... 5.1l Weight is the gravitational force with which a planet attracts a mass*. The mass of an object is independent of the gravitational field in which it is located. Set #9 5.1pThe impulse* imparted to an object causes a change in its momentum*. Set #10 5.1q According to Newton’s Third Law, forces oc ...
Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2003
... This constant is not given by the theory but must be measured by experiment. This form of forces is known as an inverse-square law, because the magnitude of the force is inversely proportional to the square of the distances between the objects. Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2003 ...
... This constant is not given by the theory but must be measured by experiment. This form of forces is known as an inverse-square law, because the magnitude of the force is inversely proportional to the square of the distances between the objects. Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2003 ...
Newton intro with hover pucks
... – Applied (push or pull exerted by an outside object) • Remember we need an unbalanced forced to cause a change in motion. • The motion will not change if the forces acting on it are ZERO! • Tendency of an object to maintain its present motion or no motion is INERTIA ...
... – Applied (push or pull exerted by an outside object) • Remember we need an unbalanced forced to cause a change in motion. • The motion will not change if the forces acting on it are ZERO! • Tendency of an object to maintain its present motion or no motion is INERTIA ...
Forces and Motion
... Any change in the state of motion of an object is the result of the sum of all the forces acting on it. The result, the combination of all these forces is called the net force. ...
... Any change in the state of motion of an object is the result of the sum of all the forces acting on it. The result, the combination of all these forces is called the net force. ...
Motion
... Forces that are equal in size and opposite in direction Unbalanced Forces (Unequal Forces) Forces that are NOT equal in size or opposite in direction ALWAYS cause a change in motion ...
... Forces that are equal in size and opposite in direction Unbalanced Forces (Unequal Forces) Forces that are NOT equal in size or opposite in direction ALWAYS cause a change in motion ...
homeworklesson4.26.2012
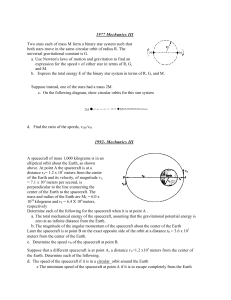
... e. Fully describe the subsequent motion of the ball from the time it reaches the center of the planet. f. Write an equation that could be used to calculate the time it takes the ball to move from point P to the center of the planet. It is not necessary to solve this equation. ...
... e. Fully describe the subsequent motion of the ball from the time it reaches the center of the planet. f. Write an equation that could be used to calculate the time it takes the ball to move from point P to the center of the planet. It is not necessary to solve this equation. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
Kreutter: Linear Dynamics 7 Newton`s Second Law: Quantitative I
... Now think about an equality . In this situation, if we increase c and keep b constant, than a will decrease. If we decrease c and keep b constant, than a will increase. Think about how this is different than if we increase or decrease b. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: We choose a particular object ( ...
... Now think about an equality . In this situation, if we increase c and keep b constant, than a will decrease. If we decrease c and keep b constant, than a will increase. Think about how this is different than if we increase or decrease b. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: We choose a particular object ( ...