3.2 The Momentum Principles
... Momentum is a measure of the tendency of an object to keep moving once it is set in motion. Consider first the particle of rigid body dynamics: the (linear) momentum p is defined to be its mass times velocity, p = mv . The rate of change of momentum p& is ...
... Momentum is a measure of the tendency of an object to keep moving once it is set in motion. Consider first the particle of rigid body dynamics: the (linear) momentum p is defined to be its mass times velocity, p = mv . The rate of change of momentum p& is ...
Classical mechanics
... mechanics. Second, recent developments in classical mechanics, mainly associated with the growth of chaos theory, have spawned whole new branches of physics and mathematics and have changed our understanding of the notion of causality. It is these new ideas that have attracted some of the best minds ...
... mechanics. Second, recent developments in classical mechanics, mainly associated with the growth of chaos theory, have spawned whole new branches of physics and mathematics and have changed our understanding of the notion of causality. It is these new ideas that have attracted some of the best minds ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Newton`s Laws of Motion
... the club, the unbalanced force, makes contact with it. ...
... the club, the unbalanced force, makes contact with it. ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... Using Newton’s Laws • Newton’s Second Law • Tells about an object’s acceleration • Looks at forces acting on one object • Accounts for all the forces acting on the object ...
... Using Newton’s Laws • Newton’s Second Law • Tells about an object’s acceleration • Looks at forces acting on one object • Accounts for all the forces acting on the object ...
Chapter 13 Lecture
... energy will be in the form of kinetic energy of the particles when they are at infinite separation. ...
... energy will be in the form of kinetic energy of the particles when they are at infinite separation. ...
Lesson Plans 6th Grade Science
... Trick! - tell student only partial directions when giving their position based on reference point. Student will invariably ask, “wait… how far?” or “wait… which direction?” thus emphasizing that position involves both distance and direction. Used the game of tubes to come up with speed graphs for av ...
... Trick! - tell student only partial directions when giving their position based on reference point. Student will invariably ask, “wait… how far?” or “wait… which direction?” thus emphasizing that position involves both distance and direction. Used the game of tubes to come up with speed graphs for av ...
Force and Motion Section 6.1
... direction and magnitude of the force. • Because forces are vectors, the total force on an object is the vector sum of all forces exerted on the object. • You are looking for the net force on the object. ...
... direction and magnitude of the force. • Because forces are vectors, the total force on an object is the vector sum of all forces exerted on the object. • You are looking for the net force on the object. ...
A2_Unit4_03_Momentum_02
... The impulse of a force is defined as the product of the force and the time which the force acts for The impulse = Ft = mv The impulse of the force acting upon an object is equal to the change of momentum for the force ...
... The impulse of a force is defined as the product of the force and the time which the force acts for The impulse = Ft = mv The impulse of the force acting upon an object is equal to the change of momentum for the force ...
January 2000
... Problem If one pitches a penny into a large magnet, eddy currents are induced in the penny, and their interaction with the magnetic field results in a repulsive force, according to Lenz’ law. Estimate the minimum velocity needed for a penny to enter a long, solenoid magnet with central field B = 1 T ...
... Problem If one pitches a penny into a large magnet, eddy currents are induced in the penny, and their interaction with the magnetic field results in a repulsive force, according to Lenz’ law. Estimate the minimum velocity needed for a penny to enter a long, solenoid magnet with central field B = 1 T ...
4.1. INTERACTION OF LIGHT WITH MATTER
... Equation (4.45) is an expression for the absorption spectrum since the rate of transitions can be related to the power absorbed from the field. More generally we would express the absorption spectrum in terms of a sum over all initial and final states, the eigenstates of H0: ...
... Equation (4.45) is an expression for the absorption spectrum since the rate of transitions can be related to the power absorbed from the field. More generally we would express the absorption spectrum in terms of a sum over all initial and final states, the eigenstates of H0: ...
Kepler - ClassNet
... Isaac Newton • Kepler's Laws were a revolution in regards to understanding planetary motion, but there was no explanation why they worked • That explanation would have to wait until Isaac Newton formulated his laws of motion and the concept of gravity • Newton's discoveries were important because t ...
... Isaac Newton • Kepler's Laws were a revolution in regards to understanding planetary motion, but there was no explanation why they worked • That explanation would have to wait until Isaac Newton formulated his laws of motion and the concept of gravity • Newton's discoveries were important because t ...
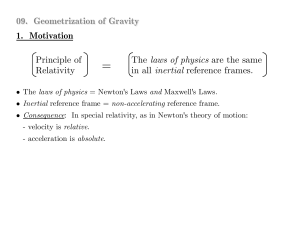
09. General Relativity: Geometrization of Gravity
... Einstein's motivations for general relativity: (I) Can we extend the Principle of Relativity to accelerated reference frames? (Can acceleration be made relative?) (II) Can we incorporate gravity into Special Relativity? (Can we extend the "laws of physics" in the Principle of Relativity to include N ...
... Einstein's motivations for general relativity: (I) Can we extend the Principle of Relativity to accelerated reference frames? (Can acceleration be made relative?) (II) Can we incorporate gravity into Special Relativity? (Can we extend the "laws of physics" in the Principle of Relativity to include N ...