Forces and Motion
... and opposite force on the first object • Momentum – Product of an object’s mass and its velocity – Objects momentum at rest is zero – Unit kg m/s ...
... and opposite force on the first object • Momentum – Product of an object’s mass and its velocity – Objects momentum at rest is zero – Unit kg m/s ...
Practice exam 2, Mechanics ch. 0-9
... 4 A sailor is driving a cart across the deck of an aircraft carrier. The aircraft carrier, A, is sailing at 22 m/s relative to the ocean, O, in the direction 17 degrees counterclockwise from east. The cart, C, is moving relative to the ship at 14 m/s, 11 degrees clockwise from east. The sailor tosse ...
... 4 A sailor is driving a cart across the deck of an aircraft carrier. The aircraft carrier, A, is sailing at 22 m/s relative to the ocean, O, in the direction 17 degrees counterclockwise from east. The cart, C, is moving relative to the ship at 14 m/s, 11 degrees clockwise from east. The sailor tosse ...
Newton`s second law
... light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. 2) The interacting bodies are on the scale of the atomic structure Quantum mechanics ...
... light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. 2) The interacting bodies are on the scale of the atomic structure Quantum mechanics ...
1 EXPERIMENT 5 CONSERVATION OF LINEAR MOMENTUM
... where M is the total mass of the system and v is the speed of the center of mass. The total momentum of a system of n particles is equal to the multiplication of the total mass of the system and the speed of the center of mass. So long as the net force on the entire system is zero, the total momentu ...
... where M is the total mass of the system and v is the speed of the center of mass. The total momentum of a system of n particles is equal to the multiplication of the total mass of the system and the speed of the center of mass. So long as the net force on the entire system is zero, the total momentu ...
File
... • A push or pull that causes an object to move, stop, or change direction • A force will cause an object with mass to accelerate. ...
... • A push or pull that causes an object to move, stop, or change direction • A force will cause an object with mass to accelerate. ...
Newton`s 2nd Law Note
... In the previous unit a variety of ways by which motion can be described (words, graphs, diagrams, numbers, etc.) were discussed. In this unit (Newton's Laws of Motion), the ways in which motion can be explained will be discussed. Isaac Newton (a 17th century scientist) put forth a variety of laws wh ...
... In the previous unit a variety of ways by which motion can be described (words, graphs, diagrams, numbers, etc.) were discussed. In this unit (Newton's Laws of Motion), the ways in which motion can be explained will be discussed. Isaac Newton (a 17th century scientist) put forth a variety of laws wh ...
Newton`sLaws - Redwood High School
... That Professor Goddard…does not know the relation of action to reaction, and of the need to have something better than a vacuum against which to react - to say that would be absurd. Of course, he only seems to lack the knowledge ladled out daily in high schools. The New York Times, January 13, 1920 ...
... That Professor Goddard…does not know the relation of action to reaction, and of the need to have something better than a vacuum against which to react - to say that would be absurd. Of course, he only seems to lack the knowledge ladled out daily in high schools. The New York Times, January 13, 1920 ...
Powerpoint for today
... held by the parking brake, what is the magnitude of the frictional force that holds your car in place? B. The coefficient of static friction between your car's wheels and the road when wet is 0.30. What is the largest angle slope on which you can park your car in the rain so that it will not slide d ...
... held by the parking brake, what is the magnitude of the frictional force that holds your car in place? B. The coefficient of static friction between your car's wheels and the road when wet is 0.30. What is the largest angle slope on which you can park your car in the rain so that it will not slide d ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... equivalent to that of a particle.) (b) What maximum height is reached? (7.94 m; 0.722 m) 9) A stone is thrown horizontally at a speed of 5.0 m/s from the top of a cliff that is 78.4 m high. (a) How long does it take the stone to reach the bottom of the cliff? (b) How far from the base of the cliff ...
... equivalent to that of a particle.) (b) What maximum height is reached? (7.94 m; 0.722 m) 9) A stone is thrown horizontally at a speed of 5.0 m/s from the top of a cliff that is 78.4 m high. (a) How long does it take the stone to reach the bottom of the cliff? (b) How far from the base of the cliff ...
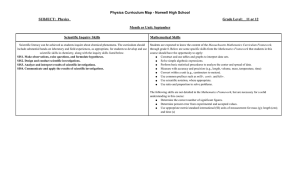
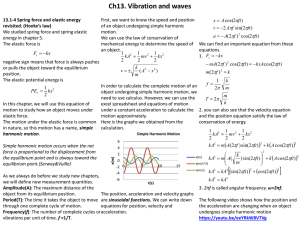
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... object from its equilibrium position. The position, acceleration and velocity graphs Period(T): The time it takes the object to move are sinusoidal functions. We can write down through one complete cycle of motion. equations for position, velocity and Frequency(f): The number of complete cycles or a ...
... object from its equilibrium position. The position, acceleration and velocity graphs Period(T): The time it takes the object to move are sinusoidal functions. We can write down through one complete cycle of motion. equations for position, velocity and Frequency(f): The number of complete cycles or a ...
Interpret The Graph Below
... Segment O-A: The bus is _____. Its speed changes from 0 to 10 m/s in 5 seconds. Segment A-B: The bus is moving at a _____ of 10 m/s for 5 seconds. Segment B-C: The bus is _____. It is slowing down from 10 m/s to rest in 3 seconds. Segment C-D: The bus is _____. It has stopped. Segment D-E: The bus i ...
... Segment O-A: The bus is _____. Its speed changes from 0 to 10 m/s in 5 seconds. Segment A-B: The bus is moving at a _____ of 10 m/s for 5 seconds. Segment B-C: The bus is _____. It is slowing down from 10 m/s to rest in 3 seconds. Segment C-D: The bus is _____. It has stopped. Segment D-E: The bus i ...
1. When an object is moving - what effect will a balanced force have
... (accelerate) D. The object will accelerate and decelerate. ...
... (accelerate) D. The object will accelerate and decelerate. ...
Underline your strong TEKS and circle your weak TEKS
... Did the student accelerate during the ride home? ©2014 Science Teaching Junkie, Inc. ...
... Did the student accelerate during the ride home? ©2014 Science Teaching Junkie, Inc. ...