Chapter 8- Rotational Motion
... horizontal axis. (c) About which axis would it be harder to accelerate this array? ...
... horizontal axis. (c) About which axis would it be harder to accelerate this array? ...
Centripetal force
... We usually think of acceleration as a change in speed. Because velocity includes both speed and direction, acceleration can also be a change in the direction of motion. ...
... We usually think of acceleration as a change in speed. Because velocity includes both speed and direction, acceleration can also be a change in the direction of motion. ...
Physics, Chapter 10: Momentum and Impulse
... The impact between two isolated bodies in space may be most easily understood in terms of the principle of conservation of momentum. In addition, many problems of propulsion may be most easily understood in terms of momentum conservation. Consider the problem of an airplane moving through the air. W ...
... The impact between two isolated bodies in space may be most easily understood in terms of the principle of conservation of momentum. In addition, many problems of propulsion may be most easily understood in terms of momentum conservation. Consider the problem of an airplane moving through the air. W ...
File
... A 0.25 kg ball is traveling 40 m/s to the right when it is hit with a force of 3,000 N for 0.005 seconds. What is its final velocity? ...
... A 0.25 kg ball is traveling 40 m/s to the right when it is hit with a force of 3,000 N for 0.005 seconds. What is its final velocity? ...
Solutions to Assigned Problems Chapter 4
... showing only the horizontal forces. FT1 is the tension in the coupling between the locomotive and the first car, and it pulls to the right on the first car. FT2 is the tension in the coupling between the first car an the second car. It pulls to the right on car 2, labeled FT2R and to the left on car ...
... showing only the horizontal forces. FT1 is the tension in the coupling between the locomotive and the first car, and it pulls to the right on the first car. FT2 is the tension in the coupling between the first car an the second car. It pulls to the right on car 2, labeled FT2R and to the left on car ...
ENGR-36_Lec - Chabot College
... • 1 lb Is The Force Required To Give A Mass Of 1 Slug An Acceleration Of 1 ft/s² • 1 lb Is The Force Required To Give A Mass Of 1/32.2 Slug An Acceleration Of 32.2 ft/s² Engineering-36: Vector Mechanics - Statics ...
... • 1 lb Is The Force Required To Give A Mass Of 1 Slug An Acceleration Of 1 ft/s² • 1 lb Is The Force Required To Give A Mass Of 1/32.2 Slug An Acceleration Of 32.2 ft/s² Engineering-36: Vector Mechanics - Statics ...
Dynamics Review Outline
... force to be constantly applied to keep it moving at a constant velocity. If a force of 10.25 newtons were applied to the same block the result would be a net force of 8.0 newtons and an acceleration of 0.53 meters per second2. If 40 newtons of force are required to make a 3.0 kilogram object acceler ...
... force to be constantly applied to keep it moving at a constant velocity. If a force of 10.25 newtons were applied to the same block the result would be a net force of 8.0 newtons and an acceleration of 0.53 meters per second2. If 40 newtons of force are required to make a 3.0 kilogram object acceler ...
Kinetic Energy and Work
... A glider attached to both springs is located between them. When the glider is in equilibrium, spring 1 is stretched by extension xi1 to the right of its unstretched length and spring 2 is stretched by xi2 to the left. Now a horizontal force Fapp is applied to the glider to move it a distance xa to t ...
... A glider attached to both springs is located between them. When the glider is in equilibrium, spring 1 is stretched by extension xi1 to the right of its unstretched length and spring 2 is stretched by xi2 to the left. Now a horizontal force Fapp is applied to the glider to move it a distance xa to t ...
PHYSICS 11 – General Physics
... turntable until a rate of 58 rpm is reached, at which point the coin slides off. What is the coefficient of static friction between the coin and the turntable? 8. Calculate the force of gravity on a spacecraft 12,800 km above the earth’s surface if its mass is 850 kg. 9. What minimum speed must a ro ...
... turntable until a rate of 58 rpm is reached, at which point the coin slides off. What is the coefficient of static friction between the coin and the turntable? 8. Calculate the force of gravity on a spacecraft 12,800 km above the earth’s surface if its mass is 850 kg. 9. What minimum speed must a ro ...
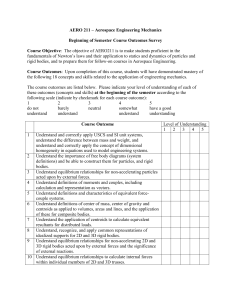
Outcomes Survey Begi.. - Aerospace Engineering Courses page
... bodies, and be able to develop diagrams and equations modeling motion in Cartesian, polar and path coordinate systems. Recognize that these equations are differential, even though students may not have the capability of solving these equations. 15 Understand the fundamental definition of work. 16 Un ...
... bodies, and be able to develop diagrams and equations modeling motion in Cartesian, polar and path coordinate systems. Recognize that these equations are differential, even though students may not have the capability of solving these equations. 15 Understand the fundamental definition of work. 16 Un ...
Exam 1 Solutions Kinematics and Newton’s laws of motion
... C) The car travels westward and slows down. D) The car travels eastward and slows down. E) The car starts from rest and moves toward the east. In C) What if you choose west as negative? ...
... C) The car travels westward and slows down. D) The car travels eastward and slows down. E) The car starts from rest and moves toward the east. In C) What if you choose west as negative? ...