Exam 1 Solutions Kinematics and Newton’s laws of motion
... C) The car travels westward and slows down. D) The car travels eastward and slows down. E) The car starts from rest and moves toward the east. In C) What if you choose west as negative? ...
... C) The car travels westward and slows down. D) The car travels eastward and slows down. E) The car starts from rest and moves toward the east. In C) What if you choose west as negative? ...
click - Uplift Education
... ▪ When the drag force reaches the magnitude of the gravitational force, the falling object will stop accelerating and fall at a constant velocity. This is called the terminal velocity/speed. ...
... ▪ When the drag force reaches the magnitude of the gravitational force, the falling object will stop accelerating and fall at a constant velocity. This is called the terminal velocity/speed. ...
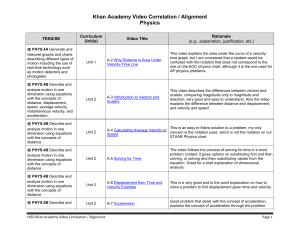
Khan Academy Video Correlation / Alignment Physics
... of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and the distance between their centers. Ⓡ PHYS.5B Describe and calculate how the magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and the distance between ...
... of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and the distance between their centers. Ⓡ PHYS.5B Describe and calculate how the magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and the distance between ...
Jeopardy
... Speedy the snail accelerates from 2 m/s to 15 m/s at a constant acceleration of 5 m/s2. This is the distance Speedy covers as he accelerates. ...
... Speedy the snail accelerates from 2 m/s to 15 m/s at a constant acceleration of 5 m/s2. This is the distance Speedy covers as he accelerates. ...
Ch 7: Momentum Conservation
... always conserved! Explain. 6. An astronaut is using a drill to fix the gyroscopes on the Hubble telescope. Suddenly, she loses her footing and floats away from the telescope. What should she do to save herself? 7. You look up one morning and see that a 30 kg chunk of asbestos from your ceiling is fa ...
... always conserved! Explain. 6. An astronaut is using a drill to fix the gyroscopes on the Hubble telescope. Suddenly, she loses her footing and floats away from the telescope. What should she do to save herself? 7. You look up one morning and see that a 30 kg chunk of asbestos from your ceiling is fa ...
Grade 12 Physics ISU independent study unit new book Word
... 1. Read p320 to321 What subatomic particles are the basic units of charge? What is the law of electric charges? What does +e and -e stand for? P320 If an object has equal numbers of protons and electrons, what is its total charge? If an object has too many or an excess of electrons to balance the #p ...
... 1. Read p320 to321 What subatomic particles are the basic units of charge? What is the law of electric charges? What does +e and -e stand for? P320 If an object has equal numbers of protons and electrons, what is its total charge? If an object has too many or an excess of electrons to balance the #p ...
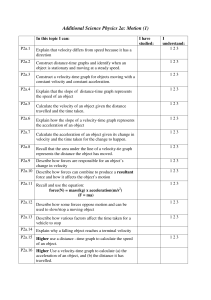
Summary of Chapters 1-3 Equations of motion for a uniformly accelerating object
... the gravity force pulling the mass down the ramp? As you slowly put the mass on the ramp, the ramp compresses & stretches along the ramp as gravity tries to slide the mass down the ramp. When you let go, the ramp has stretched enough to push on the mass with EXACTLY the right amount of force up the ...
... the gravity force pulling the mass down the ramp? As you slowly put the mass on the ramp, the ramp compresses & stretches along the ramp as gravity tries to slide the mass down the ramp. When you let go, the ramp has stretched enough to push on the mass with EXACTLY the right amount of force up the ...
What is a force? - iGCSE Science Courses
... • Describe the ways in which a force may change the motion of a body • Find the resultant of two or more forces acting along the same line • Recognise that if there is no resultant force on a body it either remains at rest or continues at constant speed in a straight line • Understand friction as th ...
... • Describe the ways in which a force may change the motion of a body • Find the resultant of two or more forces acting along the same line • Recognise that if there is no resultant force on a body it either remains at rest or continues at constant speed in a straight line • Understand friction as th ...
Exam 2 solutions - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Problem 9. The amount of potential energy possessed by an object that has been lifted up is equal to: a. the distance the object is lifted b. the force used to lift the object c. the object’s acceleration due to gravity d. the weight of the object e. the work done in lifting the object 9. Potential ...
... Problem 9. The amount of potential energy possessed by an object that has been lifted up is equal to: a. the distance the object is lifted b. the force used to lift the object c. the object’s acceleration due to gravity d. the weight of the object e. the work done in lifting the object 9. Potential ...
Rotation: Moment of Inertia and Torque
... that is free to rotate in all planes, as shown in Fig. 10, then the wheel will fall and oscillate like a pendulum. However, if the wheel is spinning sufficiently fast, it will rotate in a horizontal plane and will not swing like a pendulum. This motion is called precession. In Fig. 10, the red line ...
... that is free to rotate in all planes, as shown in Fig. 10, then the wheel will fall and oscillate like a pendulum. However, if the wheel is spinning sufficiently fast, it will rotate in a horizontal plane and will not swing like a pendulum. This motion is called precession. In Fig. 10, the red line ...