Document
... velocity. Their inertia keeps them in one of these two natural motion states, and it requires an unbalanced, external force to “knock them out” of their preferred motion state. Many forces can act on an object at rest, but unless the forces are unbalanced, the object will not move. The same can be s ...
... velocity. Their inertia keeps them in one of these two natural motion states, and it requires an unbalanced, external force to “knock them out” of their preferred motion state. Many forces can act on an object at rest, but unless the forces are unbalanced, the object will not move. The same can be s ...
Circular Motion - juan
... Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all the real forces, those for which you can identify agents that act along the centripetal axis. ...
... Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all the real forces, those for which you can identify agents that act along the centripetal axis. ...
Lab 5
... always involve the interaction between two objects. One object always exerts a force on another object. When you push a grocery cart or a stalled car, you are exerting a force on it. On the other hand, forces don’t always give rise to motion. For example, you may push very hard on a heavy sofa and i ...
... always involve the interaction between two objects. One object always exerts a force on another object. When you push a grocery cart or a stalled car, you are exerting a force on it. On the other hand, forces don’t always give rise to motion. For example, you may push very hard on a heavy sofa and i ...
PhysicsNotes QRECT Video Version With MetaNumber Feb 19 2013.pdf
... 3.2 Projectile motion in two dimensions using vectors r(t) = (x(t) , y(t) ) and v(t) = (vx(t) , vy(t)) ............ 11 3.3 Graphical view of motion in a river or with an air current using vectors graphically ........................... 11 3.4 More complex projectile problems ........................ ...
... 3.2 Projectile motion in two dimensions using vectors r(t) = (x(t) , y(t) ) and v(t) = (vx(t) , vy(t)) ............ 11 3.3 Graphical view of motion in a river or with an air current using vectors graphically ........................... 11 3.4 More complex projectile problems ........................ ...
Chapter 10
... Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, q) where r is the distance from the origin to P and q is the measured counterclockwise from the reference line ...
... Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, q) where r is the distance from the origin to P and q is the measured counterclockwise from the reference line ...
Torque, Atwood Machines, Angular M.
... Angular Momentum is also conserved Here is what this says: IF THE NET TORQUE is equal to ZERO the CHANGE ANGULAR MOMENTUM is equal to ZERO and thus the ANGULAR MOMENTUM is CONSERVED. Here is a common example. An ice skater begins a spin with his arms out. His angular velocity at the beginning of th ...
... Angular Momentum is also conserved Here is what this says: IF THE NET TORQUE is equal to ZERO the CHANGE ANGULAR MOMENTUM is equal to ZERO and thus the ANGULAR MOMENTUM is CONSERVED. Here is a common example. An ice skater begins a spin with his arms out. His angular velocity at the beginning of th ...
$doc.title
... rest on a fricPonless air track. The force acts for a short Pme interval and gives the cart a final speed. To reach the same speed using a force that is half as big, the force must ...
... rest on a fricPonless air track. The force acts for a short Pme interval and gives the cart a final speed. To reach the same speed using a force that is half as big, the force must ...
Period 3 Activity Sheet: Motion and Forces
... 1) On the diagrams, arrows show the force of gravity acting down equally on each sheet of paper. What other force acts on each sheet of paper as it falls? ________________________ 2) Draw arrows on each diagram to show the direction and relative size of this force. ...
... 1) On the diagrams, arrows show the force of gravity acting down equally on each sheet of paper. What other force acts on each sheet of paper as it falls? ________________________ 2) Draw arrows on each diagram to show the direction and relative size of this force. ...
solns - CEMC
... We use the concept of mass to describe how much matter is inside a physical object. Anything that takes up space has matter in it. Generally, the bigger an object is, the more mass it has, but not always. If you could blow up a balloon to be the same size as an elephant, the balloon would still have ...
... We use the concept of mass to describe how much matter is inside a physical object. Anything that takes up space has matter in it. Generally, the bigger an object is, the more mass it has, but not always. If you could blow up a balloon to be the same size as an elephant, the balloon would still have ...
sy12_oct12_f11
... This occurs when the normal force goes to zero or, equivalently, when all the weight is used to achieve circular motion. Fc = mg = m v2 /r v = (gr)½ (just like an object in orbit) Note this approach can also be used to estimate the maximum walking ...
... This occurs when the normal force goes to zero or, equivalently, when all the weight is used to achieve circular motion. Fc = mg = m v2 /r v = (gr)½ (just like an object in orbit) Note this approach can also be used to estimate the maximum walking ...
PowerPoint
... “This stuff is really neat... It is fun to actually see the calculations for magnetism. However, since this is the first time I’ve really seen it, it is still a bit confusing. If you could go through different examples and go over the actual concepts more, that would be great.” “Magnets. How do they ...
... “This stuff is really neat... It is fun to actually see the calculations for magnetism. However, since this is the first time I’ve really seen it, it is still a bit confusing. If you could go through different examples and go over the actual concepts more, that would be great.” “Magnets. How do they ...
Explanation - Fort Bend ISD
... The speed of the needle is a measure of your acceleration (in a straight line). ...
... The speed of the needle is a measure of your acceleration (in a straight line). ...
Lecture13
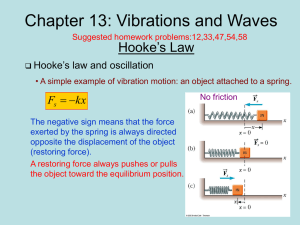
... distance of the object from its equilibrium position. –A<= x <= A. - The period T is the time it takes the object to move through one complete cycle of motion from x=A to x=-A and then back to x=A. - The frequency f is the number of complete cycles or vibrations per unit time. f=1/T. ...
... distance of the object from its equilibrium position. –A<= x <= A. - The period T is the time it takes the object to move through one complete cycle of motion from x=A to x=-A and then back to x=A. - The frequency f is the number of complete cycles or vibrations per unit time. f=1/T. ...
Windsor High School Birdsell Conceptual Physics A Windsor High
... A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B2. Explain the law of inertia B3. Calculate the net force on an object. B4. Add forces as vectors B5. ...
... A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B2. Explain the law of inertia B3. Calculate the net force on an object. B4. Add forces as vectors B5. ...
Force, Mass and Momentum
... going forward (small mass by high velocity) which equalled the momentum of the rifle going backwards (big mass by small velocity). Because they were moving in opposite directions one was positive while the other was negative so their total was again zero. The same analysis applies to a rocket ship i ...
... going forward (small mass by high velocity) which equalled the momentum of the rifle going backwards (big mass by small velocity). Because they were moving in opposite directions one was positive while the other was negative so their total was again zero. The same analysis applies to a rocket ship i ...