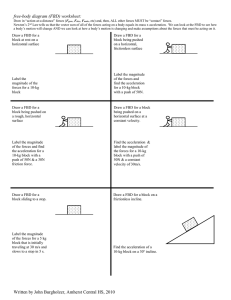
Problem 1
... weight and the curve representing the force on the scale. For calculation purposes, this area can be calculated numerically by a computer. From an eyeball examination of the graph in Figure 3.2, the elevator is not moving at t1 = 2.75 s . We are given (via a numerical integration using LabView) that ...
... weight and the curve representing the force on the scale. For calculation purposes, this area can be calculated numerically by a computer. From an eyeball examination of the graph in Figure 3.2, the elevator is not moving at t1 = 2.75 s . We are given (via a numerical integration using LabView) that ...
Scheme of work for chapter 9
... calculations are included: see ‘Try these’ p203 and the problem sets listed. The equation s = ut + ½ at2 also follows from graphical considerations of the area under a v-t graph. Three of the equations are provided on the formula sheet, the fourth, s = ½ (u+v)t, is not. This last equation is simply ...
... calculations are included: see ‘Try these’ p203 and the problem sets listed. The equation s = ut + ½ at2 also follows from graphical considerations of the area under a v-t graph. Three of the equations are provided on the formula sheet, the fourth, s = ½ (u+v)t, is not. This last equation is simply ...
RP 3P1 Force and Motion - NC Science Wiki
... molecules; the stars, planets, and moons; the earth and its surface and everything on its surface; all living things, and every part of living things. Nothing in the universe is at rest. Since everything is moving, there is no fixed reference point against which the motion of things can be described ...
... molecules; the stars, planets, and moons; the earth and its surface and everything on its surface; all living things, and every part of living things. Nothing in the universe is at rest. Since everything is moving, there is no fixed reference point against which the motion of things can be described ...
Inertia - bYTEBoss
... Inertia • Galileo developed the concept of Inertia • Inertia is a property of matter that causes it to resist changes in its velocity • Mass is a quantitative measure of inertia • As mass increases inertia increases » Double the mass---------double the inertia » Triple the mass -----------triple th ...
... Inertia • Galileo developed the concept of Inertia • Inertia is a property of matter that causes it to resist changes in its velocity • Mass is a quantitative measure of inertia • As mass increases inertia increases » Double the mass---------double the inertia » Triple the mass -----------triple th ...
Forces and Motion
... What happens if you are standing on a skateboard or a slippery floor and push against a wall? You slide in the opposite direction (away from the wall), because you pushed on the wall but the wall pushed back on you with equal and opposite force. Why does it hurt so much when you stub your toe? When ...
... What happens if you are standing on a skateboard or a slippery floor and push against a wall? You slide in the opposite direction (away from the wall), because you pushed on the wall but the wall pushed back on you with equal and opposite force. Why does it hurt so much when you stub your toe? When ...
Jeopardy
... Final Jeopardy Answer No, Inertia and the force of gravity keep the satellite in orbit ...
... Final Jeopardy Answer No, Inertia and the force of gravity keep the satellite in orbit ...
Chapter 5 Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Newton’s First Law Every object continues in its state of rest or of uniform speed in a straight line unless acted on by a nonzero net force. 1. If an object is either stationary, or moving at a constant speed in a straight line, there is no net force acting on the object. • In either case, there m ...
... Newton’s First Law Every object continues in its state of rest or of uniform speed in a straight line unless acted on by a nonzero net force. 1. If an object is either stationary, or moving at a constant speed in a straight line, there is no net force acting on the object. • In either case, there m ...
Universal Gravitation
... • Newton proposed that an attraction between bodies is universal. • Gravitational force is extremely weak between ordinary objects. • Objects with enormous mass have significant gravitational force. Creates orbits Creates tides Is known as weight for objects on the surface. ...
... • Newton proposed that an attraction between bodies is universal. • Gravitational force is extremely weak between ordinary objects. • Objects with enormous mass have significant gravitational force. Creates orbits Creates tides Is known as weight for objects on the surface. ...
Содержание учебно-методического комплекса
... He sent a beam of sunlight through the prism. It fell on a white surface. The prism separated the beam of sunlight into the colors of a rainbow. Newton believed that all these colors -- mixed together in light -- produced the color white. He proved this by letting the beam of rainbow-colored light p ...
... He sent a beam of sunlight through the prism. It fell on a white surface. The prism separated the beam of sunlight into the colors of a rainbow. Newton believed that all these colors -- mixed together in light -- produced the color white. He proved this by letting the beam of rainbow-colored light p ...
1 - Net Start Class
... 1/6-th that of Earth's? ________ Explain or show your work. 5. How much net force is required to keep a 5-kg object moving rightward with a constant velocity of 2 m/s? ________ Explain or show your work. 6. TRUE or FALSE: For an object resting upon a non-accelerating surface, the normal force is equ ...
... 1/6-th that of Earth's? ________ Explain or show your work. 5. How much net force is required to keep a 5-kg object moving rightward with a constant velocity of 2 m/s? ________ Explain or show your work. 6. TRUE or FALSE: For an object resting upon a non-accelerating surface, the normal force is equ ...
Chapter 10: Dynamics of Rotational Motion
... must obey both of the following forms of Newton's Second Law: Two following conditions should be met: 1. The axis through the center of mass must be an axis of symmetry ...
... must obey both of the following forms of Newton's Second Law: Two following conditions should be met: 1. The axis through the center of mass must be an axis of symmetry ...
Physics 121C Mechanics
... 1. Draw the particle first at its initial position and second at its final position. For convenience, the object can be represented as a dot or box. Label the initial and final positions of the object. 2. Put one or more coordinate axes on the drawing. 3. Draw arrows for the initial and final veloci ...
... 1. Draw the particle first at its initial position and second at its final position. For convenience, the object can be represented as a dot or box. Label the initial and final positions of the object. 2. Put one or more coordinate axes on the drawing. 3. Draw arrows for the initial and final veloci ...
Dynamics
... If a force acts of a body, the body will accelerate. The ratio of the applied force to the resulting acceleration is the inertia (or mass) of the body. If a torque acts on a body that can rotate freely about some axis, the body will undergo an angular acceleration. The ratio of the applied torque to ...
... If a force acts of a body, the body will accelerate. The ratio of the applied force to the resulting acceleration is the inertia (or mass) of the body. If a torque acts on a body that can rotate freely about some axis, the body will undergo an angular acceleration. The ratio of the applied torque to ...
physics space notes File
... The launch begins with the rocket producing thrust by burning fuel and expelling the resulting hot gases out one end. These hot gases have a momentum in one direction, and since the total momentum of the rocket-fuel system is zero, the rocket itself has an equal momentum in the opposite direction. T ...
... The launch begins with the rocket producing thrust by burning fuel and expelling the resulting hot gases out one end. These hot gases have a momentum in one direction, and since the total momentum of the rocket-fuel system is zero, the rocket itself has an equal momentum in the opposite direction. T ...