Solution
... The collision of a proton and antiproton to produce one particle can written as: p + p −→ X where X is the particles that is produced with MX c2 = 91.2 × 103 M eV . Doing this reaction with a minimum incoming momentum means that particle X is produced at rest. (a) Doing this reaction in the center o ...
... The collision of a proton and antiproton to produce one particle can written as: p + p −→ X where X is the particles that is produced with MX c2 = 91.2 × 103 M eV . Doing this reaction with a minimum incoming momentum means that particle X is produced at rest. (a) Doing this reaction in the center o ...
V - USU Physics
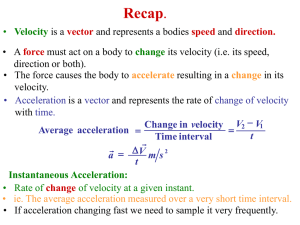
... • Velocity is a vector and represents a bodies speed and direction. • A force must act on a body to change its velocity (i.e. its speed, direction or both). • The force causes the body to accelerate resulting in a change in its velocity. • Acceleration is a vector and represents the rate of change o ...
... • Velocity is a vector and represents a bodies speed and direction. • A force must act on a body to change its velocity (i.e. its speed, direction or both). • The force causes the body to accelerate resulting in a change in its velocity. • Acceleration is a vector and represents the rate of change o ...
Dynamics Notes
... constant speed but constantly changed direction as it orbited the sun. From his data, Kepler was able to form his three laws that all heavenly bodies seemed to follow, irrespective of their identity. Yet planets do not orbit exactly at constant speed, nor exactly in a circular path. Kepler's 1st Law ...
... constant speed but constantly changed direction as it orbited the sun. From his data, Kepler was able to form his three laws that all heavenly bodies seemed to follow, irrespective of their identity. Yet planets do not orbit exactly at constant speed, nor exactly in a circular path. Kepler's 1st Law ...
Dimensional Analysis and Hydraulic Similitude
... the flow are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. If m is volume flow rate emanating from the line of the source, U is the uniform velocity, determine; (a) Location of stagnation point ‘b’ (b) Radial and tangential velocity at a point ‘P’ downstream of the flow as shown in the figure ...
... the flow are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. If m is volume flow rate emanating from the line of the source, U is the uniform velocity, determine; (a) Location of stagnation point ‘b’ (b) Radial and tangential velocity at a point ‘P’ downstream of the flow as shown in the figure ...