rotation ppt
... Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net force to produce the centripetal acceleration. The centripetal force is the name given to the net force required to keep an object moving on a circular path. The direction of the centripetal force always points toward the center of the circle and ...
... Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net force to produce the centripetal acceleration. The centripetal force is the name given to the net force required to keep an object moving on a circular path. The direction of the centripetal force always points toward the center of the circle and ...
Document
... Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net force to produce the centripetal acceleration. The centripetal force is the name given to the net force required to keep an object moving on a circular path. The direction of the centripetal force always points toward the center of the circle and ...
... Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net force to produce the centripetal acceleration. The centripetal force is the name given to the net force required to keep an object moving on a circular path. The direction of the centripetal force always points toward the center of the circle and ...
Rotational Motion
... Every point in a body rotating about a fixed axis moves in a circle whose center is on the axis and whose radius is r, the perpendicular distance of that point from the axis of rotation. A perpendicular line drawn from the axis to any point sweeps out the same angle in the same time. Position of t ...
... Every point in a body rotating about a fixed axis moves in a circle whose center is on the axis and whose radius is r, the perpendicular distance of that point from the axis of rotation. A perpendicular line drawn from the axis to any point sweeps out the same angle in the same time. Position of t ...
CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM
... ! Can you compute a linear impulse? An angular impulse? ! When angular momentum is constant, what is the effect of changing moment of inertia? ! What influences the moment of inertia of the human body? ! Can you compute moment of inertia? ! Can you apply the parallel axis theorem? ! Can you apply th ...
... ! Can you compute a linear impulse? An angular impulse? ! When angular momentum is constant, what is the effect of changing moment of inertia? ! What influences the moment of inertia of the human body? ! Can you compute moment of inertia? ! Can you apply the parallel axis theorem? ! Can you apply th ...
05.TE.Newton`s Second Law
... 3. calculate the percentage error between the experimental result and the accepted value for a mass. Newton’s second law of motion states the relationship that can be used to predict the change of motion (acceleration) of an object when an unbalanced force is applied. The acceleration is directly pr ...
... 3. calculate the percentage error between the experimental result and the accepted value for a mass. Newton’s second law of motion states the relationship that can be used to predict the change of motion (acceleration) of an object when an unbalanced force is applied. The acceleration is directly pr ...
PHYS 1111 Introductory Physics – Mechanics, Waves
... 6. Solve as many end-of-chapter problems as possible. 7. Concepts first. Do NOT plug-and-chug. 8. Use a buddy system: find a friend with whom to discuss physics. 9. Think about physics on a regular basis. 10. If everything fails, consider dropping the class before the deadline and re-taking it at a ...
... 6. Solve as many end-of-chapter problems as possible. 7. Concepts first. Do NOT plug-and-chug. 8. Use a buddy system: find a friend with whom to discuss physics. 9. Think about physics on a regular basis. 10. If everything fails, consider dropping the class before the deadline and re-taking it at a ...
Physics 2414, Spring 2005 Group Exercise 10, Apr 28, 2005 ns
... (b) Write down the x-component of eqn. (6) and thus get an expression relating Nh and Ff . +Nh + 0+0 − Ff + 0 = 0 Nh = Ff ...
... (b) Write down the x-component of eqn. (6) and thus get an expression relating Nh and Ff . +Nh + 0+0 − Ff + 0 = 0 Nh = Ff ...
Science-M3-Force-and..
... When two forces act in opposite directions they also add together. But the adding is the same as adding a positive and a negative number. If one force is greater than the other force, the overall force is in the direction of the greater force. In any situation, the overall force on an object after a ...
... When two forces act in opposite directions they also add together. But the adding is the same as adding a positive and a negative number. If one force is greater than the other force, the overall force is in the direction of the greater force. In any situation, the overall force on an object after a ...
lectures 2014
... rather than algebraically. However, you usually give yourself a big advantage if you delay substitution of numerical values until the last line as it enables you to check dimensions at every stage, and quantities often cancel before the last line. An exception to this rule arises where some terms ar ...
... rather than algebraically. However, you usually give yourself a big advantage if you delay substitution of numerical values until the last line as it enables you to check dimensions at every stage, and quantities often cancel before the last line. An exception to this rule arises where some terms ar ...
Forces notes from class 16-17
... -A force is a “push” or “pull” that is applied to an object. Where are forces located? -A force occurs at a point of contact between the object and some identifiable agent that exerts the force. -A force can be exerted by an animate or inanimate agent. Give an example of a force you have experienced ...
... -A force is a “push” or “pull” that is applied to an object. Where are forces located? -A force occurs at a point of contact between the object and some identifiable agent that exerts the force. -A force can be exerted by an animate or inanimate agent. Give an example of a force you have experienced ...
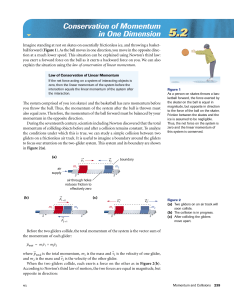
Lecture 8.2
... (i.e., different amounts of time, accelerations, and final speeds), there is a quantity that is the same for both at the end of the motion. It is (1/2) mv2 and is called the (final) kinetic energy of the carts. ...
... (i.e., different amounts of time, accelerations, and final speeds), there is a quantity that is the same for both at the end of the motion. It is (1/2) mv2 and is called the (final) kinetic energy of the carts. ...
Physics 235 Chapter 10 Motion in a Non-Inertial Reference Frame
... This acceleration is certainly not equal to F/m, but the previous relations can be used to express the acceleration in the rotating reference frame in terms of the acceleration in the fixed reference frame: ⎛ dV ⎞ ar = a f − ⎜ − 2ω × vr − ω × r − ω × {ω × r } ⎝ dt ⎟⎠ fixed ...
... This acceleration is certainly not equal to F/m, but the previous relations can be used to express the acceleration in the rotating reference frame in terms of the acceleration in the fixed reference frame: ⎛ dV ⎞ ar = a f − ⎜ − 2ω × vr − ω × r − ω × {ω × r } ⎝ dt ⎟⎠ fixed ...