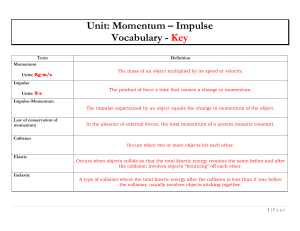
Circular Motion - Manchester HEP
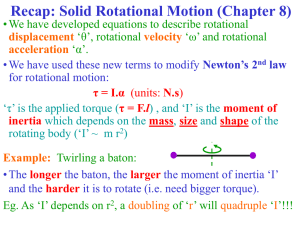
... This is now analogous to collisions between balls of different masses. Angular momentum is still conserved, but the moment of inertia of the two masses is no longer equal. When the lighter (lower I) object hits the heavier (higher I) one it bounces off reversing the direction of its angular velocity ...
... This is now analogous to collisions between balls of different masses. Angular momentum is still conserved, but the moment of inertia of the two masses is no longer equal. When the lighter (lower I) object hits the heavier (higher I) one it bounces off reversing the direction of its angular velocity ...
Dynamics 1
... Recognize the significance of Newton’s second law of motion and use it to solve motion ...
... Recognize the significance of Newton’s second law of motion and use it to solve motion ...
DimensionsUnits
... position) acceleration (rate of change of an object’s velocity with respect to time) force (“push” or “pull” that can change an object’s motion) (Note that weight is just a ...
... position) acceleration (rate of change of an object’s velocity with respect to time) force (“push” or “pull” that can change an object’s motion) (Note that weight is just a ...
Lec8
... implied that the object is contained entirely within a point. In the next part of this course, we will be interested in the forward model. That is, if we know the forces on the particle, what should the resulting motion be? The reason I call this a forward model is because the classification of diff ...
... implied that the object is contained entirely within a point. In the next part of this course, we will be interested in the forward model. That is, if we know the forces on the particle, what should the resulting motion be? The reason I call this a forward model is because the classification of diff ...
NewtonsLawsPacket
... any force, the net force is a vector and has a direction. Being the vector sum of all the forces, there may be some negative signs present in the net force equation to indicate that one force is opposite in direction to another force. According to Newton's second law, the net force is related to mas ...
... any force, the net force is a vector and has a direction. Being the vector sum of all the forces, there may be some negative signs present in the net force equation to indicate that one force is opposite in direction to another force. According to Newton's second law, the net force is related to mas ...
1-D ForcesDocument(94-5)
... any force, the net force is a vector and has a direction. Being the vector sum of all the forces, there may be some negative signs present in the net force equation to indicate that one force is opposite in direction to another force. According to Newton's second law, the net force is related to mas ...
... any force, the net force is a vector and has a direction. Being the vector sum of all the forces, there may be some negative signs present in the net force equation to indicate that one force is opposite in direction to another force. According to Newton's second law, the net force is related to mas ...
Advanced Placement C Physics – Course Guide
... (1) Draw a well-labeled diagram showing all real forces that act on the body. (2) Write down the vector equation that results from applying Newton's Second Law to the body, and take components of this equation along appropriate axes. c. Students should be able to analyze situations in which a body m ...
... (1) Draw a well-labeled diagram showing all real forces that act on the body. (2) Write down the vector equation that results from applying Newton's Second Law to the body, and take components of this equation along appropriate axes. c. Students should be able to analyze situations in which a body m ...
A force is a push or pull. An object at rest needs a force to get it
... A)Find the force pushing the wagon downhill .(that is the x-component of the weight !) B) The force pushing the wagon into the surface (that will be the y-component of the weight !!) C) if the wagon is moving at a constant speed Find the normal force N (recoil force from ground) and the pulling forc ...
... A)Find the force pushing the wagon downhill .(that is the x-component of the weight !) B) The force pushing the wagon into the surface (that will be the y-component of the weight !!) C) if the wagon is moving at a constant speed Find the normal force N (recoil force from ground) and the pulling forc ...
S - Nuffield Foundation
... Note that we often use the same letter for a vector and its magnitude, but the vector is written either in bold or is underlined. ...
... Note that we often use the same letter for a vector and its magnitude, but the vector is written either in bold or is underlined. ...