Lab 8 - Ballistic pendulum
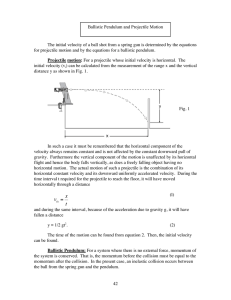
... time interval t required for the projectile to reach the floor, it will have moved horizontally through a distance ...
... time interval t required for the projectile to reach the floor, it will have moved horizontally through a distance ...
Work/Energy
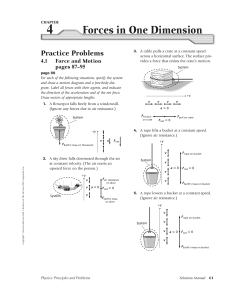
... A 0.40 kg block is pushed up against a spring (with spring constant 270 N/m ) on a frictionless surface so that the spring is compressed 0.20 m. When the block is released, it slides across the surface and collides with the 0.60 kg bob of a pendulum. The bob is made of clay and the block sticks to i ...
... A 0.40 kg block is pushed up against a spring (with spring constant 270 N/m ) on a frictionless surface so that the spring is compressed 0.20 m. When the block is released, it slides across the surface and collides with the 0.60 kg bob of a pendulum. The bob is made of clay and the block sticks to i ...
College Physics
... values of the coefficients of friction can vary greatly. In situations like this, where an object of mass m slides down a slope that makes an angle ...
... values of the coefficients of friction can vary greatly. In situations like this, where an object of mass m slides down a slope that makes an angle ...
lab #4 - Physics Department, Princeton University
... What happens when you roll a ball, a hollow "pipe," or a solid circular cylinder down the ramp? If you roll two of them down side by side, which one gets to the bottom first? Is mechanical energy conserved here? If not, where is it going? If time permits, make movies of a couple of these objects rol ...
... What happens when you roll a ball, a hollow "pipe," or a solid circular cylinder down the ramp? If you roll two of them down side by side, which one gets to the bottom first? Is mechanical energy conserved here? If not, where is it going? If time permits, make movies of a couple of these objects rol ...
rev1 - UConn Physics
... A fighter pilot flying in a circular turn will pass out if the centripetal acceleration he experiences is more than about 9 times the acceleration of gravity g. If his F18 is moving with a speed of 300 m/s, what is the approximate diameter of the tightest turn this pilot can make and survive to tell ...
... A fighter pilot flying in a circular turn will pass out if the centripetal acceleration he experiences is more than about 9 times the acceleration of gravity g. If his F18 is moving with a speed of 300 m/s, what is the approximate diameter of the tightest turn this pilot can make and survive to tell ...
Experimental determination of natural frequency and damping ratio
... weight of the suspended mass), so the above equation becomes ...
... weight of the suspended mass), so the above equation becomes ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.