CentripetalForce
... in two ways, a change of direction and/or a change in magnitude. As you have learned, if the net force on an object, and thus the acceleration, is perpendicular to the velocity at an instant in time then only the direction of the velocity will change and the speed will remain constant. If the net fo ...
... in two ways, a change of direction and/or a change in magnitude. As you have learned, if the net force on an object, and thus the acceleration, is perpendicular to the velocity at an instant in time then only the direction of the velocity will change and the speed will remain constant. If the net fo ...
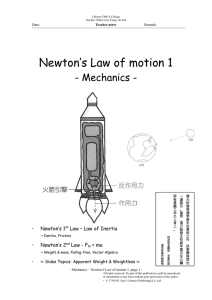
Newton`s Law of motion 1
... Gravitational mass is measured by such method, e.g. spring balance. Measuring the mass (inertia mass) Mass can be defined as the ‘ amount of matter’ in an object. But considering Newton’s 2nd Law of motion, m = FN / a, mass has a new meaning – “Inertia”. Inertia is the resistance of an object to a c ...
... Gravitational mass is measured by such method, e.g. spring balance. Measuring the mass (inertia mass) Mass can be defined as the ‘ amount of matter’ in an object. But considering Newton’s 2nd Law of motion, m = FN / a, mass has a new meaning – “Inertia”. Inertia is the resistance of an object to a c ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... Impulse and Momentum Using the Impulse-Momentum Theorem Let’s discuss the change in momentum of a baseball. The impulse that is the area under the curve is approximately 13.1 N·s. The direction of the impulse is in the direction of the force. Therefore, the change in momentum of the ball also is 13. ...
... Impulse and Momentum Using the Impulse-Momentum Theorem Let’s discuss the change in momentum of a baseball. The impulse that is the area under the curve is approximately 13.1 N·s. The direction of the impulse is in the direction of the force. Therefore, the change in momentum of the ball also is 13. ...
Energy II (ed) - Personal.psu.edu
... It follows from this similarity that this gravitational force will do work that is the negative change of a potential energy that behaves similarly to the potential energy of electrostatic attraction, i.e., Egrav = − G m1m2 / r, ...
... It follows from this similarity that this gravitational force will do work that is the negative change of a potential energy that behaves similarly to the potential energy of electrostatic attraction, i.e., Egrav = − G m1m2 / r, ...
Welcome to Physics I !!!
... L • From this, we can determine the effective “spring” constant k • And we can determine the natural frequency of the pendulum ...
... L • From this, we can determine the effective “spring” constant k • And we can determine the natural frequency of the pendulum ...
ML Forces Newton Laws from Prentice Hall
... plus your friend's force. When two forces act in the same direction, they add together. Figure 1 uses arrows to show the addition of forces. The head of each arrow points in the direction of a force. The width of each arrow tells you the strength of a force. A wider arrow shows a greater force. (Whe ...
... plus your friend's force. When two forces act in the same direction, they add together. Figure 1 uses arrows to show the addition of forces. The head of each arrow points in the direction of a force. The width of each arrow tells you the strength of a force. A wider arrow shows a greater force. (Whe ...
Using the Law of Universal Gravitation
... the Earth” experiment? Cavendish’s experiment often is called “weighing Earth,” because his experiment helped determine Earth’s mass. Once the value of G is known, not only the mass of Earth, but also the mass of the Sun can be determined. In addition, the gravitational force between any two objects ...
... the Earth” experiment? Cavendish’s experiment often is called “weighing Earth,” because his experiment helped determine Earth’s mass. Once the value of G is known, not only the mass of Earth, but also the mass of the Sun can be determined. In addition, the gravitational force between any two objects ...
PHY 1112 : PHYSICS CHAPTER 3 Newton’s Laws of Motion and
... Newton's First Law states that every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change its state by the action of an external force. This is normally taken as the definition of inertia. The key point here is that if there is no net force acting on an ...
... Newton's First Law states that every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change its state by the action of an external force. This is normally taken as the definition of inertia. The key point here is that if there is no net force acting on an ...
F - Uplift North Hills Prep
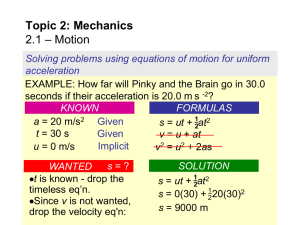
... Solving problems involving forces and resultant force EXAMPLE: A 1000-kg airplane is flying at a constant velocity of 125 m s-1. Label and determine the value of the weight W, the lift L, the drag D and the thrust F if the drag is 25000 N. L SOLUTION: D W Since the velocity is constant, Newton’s fi ...
... Solving problems involving forces and resultant force EXAMPLE: A 1000-kg airplane is flying at a constant velocity of 125 m s-1. Label and determine the value of the weight W, the lift L, the drag D and the thrust F if the drag is 25000 N. L SOLUTION: D W Since the velocity is constant, Newton’s fi ...
chapter-6-with-changes-thursday-jan-9
... projectile is the same as solving a constant velocity problem. We will be ignoring air resistance. All problems will be treated as if there is no air drag and therefore no horizontal acceleration (no horizontal net force). ...
... projectile is the same as solving a constant velocity problem. We will be ignoring air resistance. All problems will be treated as if there is no air drag and therefore no horizontal acceleration (no horizontal net force). ...
Key Learning(s) - East Pennsboro Area School District
... mathematical product of the Force acting on the rotating object and the distance away from the axis of rotation that the force is acting ...
... mathematical product of the Force acting on the rotating object and the distance away from the axis of rotation that the force is acting ...
File
... Dimensional analysis • Dimensional analysis makes use of the fact that dimensions can be treated as algebraic quantities. For example, quantities can be added or subtracted only if they have the same dimensions. • For example we can Show that the expression v = at is dimensionally correct, where v ...
... Dimensional analysis • Dimensional analysis makes use of the fact that dimensions can be treated as algebraic quantities. For example, quantities can be added or subtracted only if they have the same dimensions. • For example we can Show that the expression v = at is dimensionally correct, where v ...
4.3 Centripetal Acceleration
... your speed, the more noticeable this acceleration will become. In this section we examine the direction and magnitude of that acceleration. Figure 1 shows an object moving in a circular path at constant speed. The direction of the instantaneous velocity is shown at two points along the path. Acceler ...
... your speed, the more noticeable this acceleration will become. In this section we examine the direction and magnitude of that acceleration. Figure 1 shows an object moving in a circular path at constant speed. The direction of the instantaneous velocity is shown at two points along the path. Acceler ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.