Which way does the normal force on the block point?
... objects moving at constant velocity tend to continue at this velocity UNLESS acted on by a net force and ...
... objects moving at constant velocity tend to continue at this velocity UNLESS acted on by a net force and ...
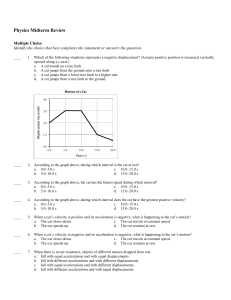
Physics Midterm Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... 70. What is the magnitude of the resultant displacement of a dog looking for its bone in the yard if the dog first heads 57.0 north of west for 10.3 m and then turns and heads west for 4.00 m? 71. A stone is thrown at an angle of 30.0 above the horizontal from the top edge of a cliff with an init ...
... 70. What is the magnitude of the resultant displacement of a dog looking for its bone in the yard if the dog first heads 57.0 north of west for 10.3 m and then turns and heads west for 4.00 m? 71. A stone is thrown at an angle of 30.0 above the horizontal from the top edge of a cliff with an init ...
Content Area: Communication Arts
... A. The motion of an object is described as a change in position, direction, and speed relative to another object (frame of reference) (FM1A) B. An object that is accelerating is speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction (FM1B) C. Every object exerts a gravitational force on every other object ...
... A. The motion of an object is described as a change in position, direction, and speed relative to another object (frame of reference) (FM1A) B. An object that is accelerating is speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction (FM1B) C. Every object exerts a gravitational force on every other object ...
AP Physics 1
... examine how a force exerted on an object or system does work on the object or system as it moves through a distance. [SP 4.2, 5.1] The student is able to make claims, analyze, discuss, and predict and calculate the energy transfer to (i.e., the work done on) an object or system from information abou ...
... examine how a force exerted on an object or system does work on the object or system as it moves through a distance. [SP 4.2, 5.1] The student is able to make claims, analyze, discuss, and predict and calculate the energy transfer to (i.e., the work done on) an object or system from information abou ...
AP Physics I - Pompton Lakes School
... The motion of an object can be described by its position and velocity as functions of time and by its average speed and average acceleration during intervals of time. Objects undergo different kinds of motion (translational, rotational, and vibrational). ...
... The motion of an object can be described by its position and velocity as functions of time and by its average speed and average acceleration during intervals of time. Objects undergo different kinds of motion (translational, rotational, and vibrational). ...
Lecture #11 - the GMU ECE Department
... • First law an object at rest remains at rest if no unbalanced forces acting on it an object in motion with a constant velocity, and if there are no unbalanced forces acting on it, the object will continue to move with the same velocity ...
... • First law an object at rest remains at rest if no unbalanced forces acting on it an object in motion with a constant velocity, and if there are no unbalanced forces acting on it, the object will continue to move with the same velocity ...
Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr Srinivasan
... Coulomb damping offers damping force generated because of friction between two surfaces. Now you may wonder where the surfaces are coming in, can I have friction between the liquid surface and the solid surface? Interestingly let us take up a structure or a leg which is connected by a specific joint ...
... Coulomb damping offers damping force generated because of friction between two surfaces. Now you may wonder where the surfaces are coming in, can I have friction between the liquid surface and the solid surface? Interestingly let us take up a structure or a leg which is connected by a specific joint ...
Chapter 11 Equilibrium - Farmingdale State College
... Hence, bodies in equilibrium are nothing more than a special case of Newton’s second law. In fact we have already solved some of these problems in chapters 5 and 6 without specifically saying that they were bodies in equilibrium. Remember that if the acceleration is zero, then there is no change of ...
... Hence, bodies in equilibrium are nothing more than a special case of Newton’s second law. In fact we have already solved some of these problems in chapters 5 and 6 without specifically saying that they were bodies in equilibrium. Remember that if the acceleration is zero, then there is no change of ...
Slide 1
... 13. In the tractor pull competition, the trailer is set up so that as the tractor pulls the trailer, the trailer shifts its mass forward, increasing the drag, and thus increasing the force required to pull. If ur not sure what I’m referring to, Youtube it! A graph of the Force required vs distance ...
... 13. In the tractor pull competition, the trailer is set up so that as the tractor pulls the trailer, the trailer shifts its mass forward, increasing the drag, and thus increasing the force required to pull. If ur not sure what I’m referring to, Youtube it! A graph of the Force required vs distance ...
Roller Coaster (AP) Physics
... scientists say the rock is in a “1 g” environment, [1 g = 9.8 m/s2 = 22 mph/s]. Any time an object experiences the pull equal to the force of gravity, it is said to be in a “one g” environment. We live in a 1 g environment. If a rock whose weight on the Earth is 100 lbs was moved to a 2 g environmen ...
... scientists say the rock is in a “1 g” environment, [1 g = 9.8 m/s2 = 22 mph/s]. Any time an object experiences the pull equal to the force of gravity, it is said to be in a “one g” environment. We live in a 1 g environment. If a rock whose weight on the Earth is 100 lbs was moved to a 2 g environmen ...
Forces - Ateneonline
... •Draw an idealization of the body in question (a dot, a box,…). You will need one free body diagram for each body in the problem that will provide useful information for you to solve the given problem. •Indicate only the forces acting on the body. Label the forces appropriately. Do not include the f ...
... •Draw an idealization of the body in question (a dot, a box,…). You will need one free body diagram for each body in the problem that will provide useful information for you to solve the given problem. •Indicate only the forces acting on the body. Label the forces appropriately. Do not include the f ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.