Physics as Spacetime Geometry
... One can call t0 time, but then must necessarily, in connection with this, define space by the manifold of three parameters x0 , y, z in which the laws of physics would then have exactly the same expressions by means of x0 , y, z, t0 as by means of x, y, z, t. Hereafter we would then have in the wor ...
... One can call t0 time, but then must necessarily, in connection with this, define space by the manifold of three parameters x0 , y, z in which the laws of physics would then have exactly the same expressions by means of x0 , y, z, t0 as by means of x, y, z, t. Hereafter we would then have in the wor ...
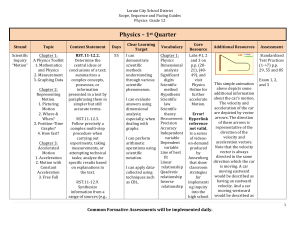
Physics – 1st Quarter
... In earlier grades, Newton’s laws of motion were introduced; gravitational forces and fields were described conceptually; the gravitational force (weight) acting on objects near Earth’s surface was calculated; fricti ...
... In earlier grades, Newton’s laws of motion were introduced; gravitational forces and fields were described conceptually; the gravitational force (weight) acting on objects near Earth’s surface was calculated; fricti ...
Rigid Body Simulation
... a clearly unstable arrangement of five identical bricks, however it is not immediately apparent how this stack will fall down. As difficult as it is, it has many useful applications. Some of the more notable examples are those in 3D animations, engineering, haptic displays in robotics, and computer ...
... a clearly unstable arrangement of five identical bricks, however it is not immediately apparent how this stack will fall down. As difficult as it is, it has many useful applications. Some of the more notable examples are those in 3D animations, engineering, haptic displays in robotics, and computer ...
Lecture 9
... times a week. • Helpdesk has hours everyday and is free. – Hours are posted on my website ...
... times a week. • Helpdesk has hours everyday and is free. – Hours are posted on my website ...
Engineering Mechanics
... this phase should enable us to obtain the right solutions and make the right decisions from the beginning. This requires good design, analysis and synthesis methods and tools, as well as good simulation techniques including computational prototyping and digital mock-ups".1 Modelling, however, is an ...
... this phase should enable us to obtain the right solutions and make the right decisions from the beginning. This requires good design, analysis and synthesis methods and tools, as well as good simulation techniques including computational prototyping and digital mock-ups".1 Modelling, however, is an ...
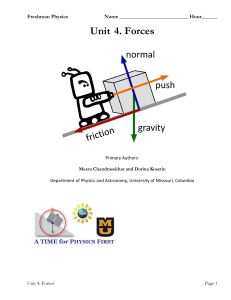
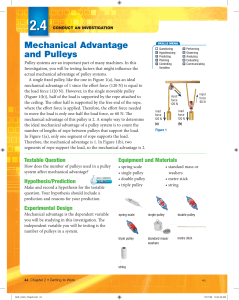
Unit 4. Forces - Perry County School District 32
... original form when the force is removed are called elastic. A force is called elastic force if once removed allows the object to recover its original form, length, shape. This can happen to things other than springs, for example, a tree branch can be pulled down and it retracts to its original posit ...
... original form when the force is removed are called elastic. A force is called elastic force if once removed allows the object to recover its original form, length, shape. This can happen to things other than springs, for example, a tree branch can be pulled down and it retracts to its original posit ...
gen physics pdf
... 007 10.0 points John and Mary Smith plan to put a wooden fence around their yard in order to keep the mean cats away from their dog Fido. There is a gate that is 3.27 m long which is not included as part of the length of the fence. What total length of fence is required to enclose a rectangular yard ...
... 007 10.0 points John and Mary Smith plan to put a wooden fence around their yard in order to keep the mean cats away from their dog Fido. There is a gate that is 3.27 m long which is not included as part of the length of the fence. What total length of fence is required to enclose a rectangular yard ...
4 Physics 6A Newton`s Laws Examples
... How does Newton’s 3rd law apply here? Does each force in our diagram have an ‘equal and opposite’ reaction force? Ok, last one – what is the reaction that corresponds to the normal force? First identify which 2 objects are interacting. This time it is the eraser and the chalk rail, but in the vertic ...
... How does Newton’s 3rd law apply here? Does each force in our diagram have an ‘equal and opposite’ reaction force? Ok, last one – what is the reaction that corresponds to the normal force? First identify which 2 objects are interacting. This time it is the eraser and the chalk rail, but in the vertic ...
Pearson Physics Level 20 Unit IV Oscillatory Motion and Mechanical
... potential energy and the points at their equilibrium position will have the greatest kinetic energy. 14. When a circular wave is reflected from a straight barrier, the shape of the wave is not affected; only its direction of motion changes. 15. The energy stored in a pulse depends on the amplitude o ...
... potential energy and the points at their equilibrium position will have the greatest kinetic energy. 14. When a circular wave is reflected from a straight barrier, the shape of the wave is not affected; only its direction of motion changes. 15. The energy stored in a pulse depends on the amplitude o ...
preview as pdf - Pearson Higher Education
... A collision is a short-duration interaction between two objects. The collision between a tennis ball and a racket, or a baseball and a bat, may seem instantaneous to your eye, but that is a limitation of your perception. A high-speed photograph reveals that the side of the ball is significantly flat ...
... A collision is a short-duration interaction between two objects. The collision between a tennis ball and a racket, or a baseball and a bat, may seem instantaneous to your eye, but that is a limitation of your perception. A high-speed photograph reveals that the side of the ball is significantly flat ...
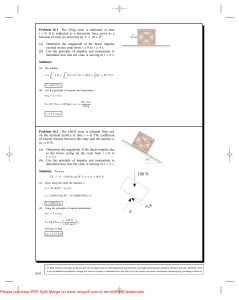
Problem 16.1 The 20-kg crate is stationary at time t = 0. It is
... Problem 16.6 A bioengineer models the force generated by the wings of the 0.2-kg snow petrel by an equation of the form F = F0 (1 + sin ωt), where F0 and ω are constants. From video measurements of a bird taking off, he estimates that ω = 18 and determines that the bird requires 1.42 s to take off ...
... Problem 16.6 A bioengineer models the force generated by the wings of the 0.2-kg snow petrel by an equation of the form F = F0 (1 + sin ωt), where F0 and ω are constants. From video measurements of a bird taking off, he estimates that ω = 18 and determines that the bird requires 1.42 s to take off ...
Conservation of Momentum
... where the subscript ‘1’ refers to properties of Ball 1, the subscript ‘2’ refers to properties of Ball 2, the unprimed velocities correspond to values before the collision takes place and the primed velocities to those after the collision occurs. Careful attention must be paid to ! both the magnitud ...
... where the subscript ‘1’ refers to properties of Ball 1, the subscript ‘2’ refers to properties of Ball 2, the unprimed velocities correspond to values before the collision takes place and the primed velocities to those after the collision occurs. Careful attention must be paid to ! both the magnitud ...
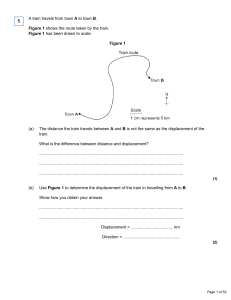
A train travels from town A to town B. Figure 1 shows the route taken
... The bus travels at 5 m/s between points A and B. The bus and passengers have a total mass of 16 000 kg. Use the equation in the box to calculate the momentum of the bus and passengers between points A and B. momentum = mass x velocity ...
... The bus travels at 5 m/s between points A and B. The bus and passengers have a total mass of 16 000 kg. Use the equation in the box to calculate the momentum of the bus and passengers between points A and B. momentum = mass x velocity ...
PHYS 1211 (as of Jan. 05)
... and re-taking it at a later time. Tutors are available either for free through the UGA Tutoring Program at Tutors: Milledge Hall, http://tutor.uga.edu, or for pay through the Physics Department, http://www.physast.uga.edu/tutors. NOTE: In physics, learning can be frustrating and nonlinear. Often you ...
... and re-taking it at a later time. Tutors are available either for free through the UGA Tutoring Program at Tutors: Milledge Hall, http://tutor.uga.edu, or for pay through the Physics Department, http://www.physast.uga.edu/tutors. NOTE: In physics, learning can be frustrating and nonlinear. Often you ...
Table of Contents
... 08. Sketch what the velocity vs. time graph would look like for this trip. 09. Sketch what the acceleration vs. time graph would look like for this trip. ...
... 08. Sketch what the velocity vs. time graph would look like for this trip. 09. Sketch what the acceleration vs. time graph would look like for this trip. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.