d = 0.5 gt 2
... falling under the sole influence of gravity. ► That is to say that any object which is moving and being acted upon only be the force of gravity is said to be "in a state of free fall." ► This definition of free fall leads to two important characteristics about a freefalling object: Free-falling ob ...
... falling under the sole influence of gravity. ► That is to say that any object which is moving and being acted upon only be the force of gravity is said to be "in a state of free fall." ► This definition of free fall leads to two important characteristics about a freefalling object: Free-falling ob ...
EOCT Review (Extra Credit)
... 2. Describe energy transfer if you touch something and it feels cold to you, AND if you touch another object and it feels hot. 3. Describe the following: kinetic energy, thermal energy, temperature, and thermometer. 4. Differentiate between the three methods of energy transfer. 5. Explain in detail ...
... 2. Describe energy transfer if you touch something and it feels cold to you, AND if you touch another object and it feels hot. 3. Describe the following: kinetic energy, thermal energy, temperature, and thermometer. 4. Differentiate between the three methods of energy transfer. 5. Explain in detail ...
Gr 11 Physical Sciences P1 Eng
... An object attracts another with a gravitational force F. If the distance between the centres of the two objects is now decreased to a third (⅓) of the original distance, the force of attraction that the one object would exert on the other would become ... ...
... An object attracts another with a gravitational force F. If the distance between the centres of the two objects is now decreased to a third (⅓) of the original distance, the force of attraction that the one object would exert on the other would become ... ...
solns - CEMC
... If instead the object is moving, it will be doing so with constant speed and in the same direction throughout its movement. If you want to do any of the following things to it, you must push it or pull it: 1. Make it go faster 2. Make it go slower 3. Make it change direction By this logic, if you o ...
... If instead the object is moving, it will be doing so with constant speed and in the same direction throughout its movement. If you want to do any of the following things to it, you must push it or pull it: 1. Make it go faster 2. Make it go slower 3. Make it change direction By this logic, if you o ...
force
... to keep an object moving at a constant speed • Galileo studied how gravity produces constant acceleration. He concluded that objects not subjected friction or any other force would continue to move indefinitely • Newton built off the work of Galileo and later published his work in a book entitled Pr ...
... to keep an object moving at a constant speed • Galileo studied how gravity produces constant acceleration. He concluded that objects not subjected friction or any other force would continue to move indefinitely • Newton built off the work of Galileo and later published his work in a book entitled Pr ...
Conservation of Energy and Momentum Elastic Collisions Inelastic
... external impulse is zero, and system momentum is exactly conserved. It also says that if for some reason the net external impulse can be approximated by zero, then system momentum is approximately conserved (and the approximation may be extremely accurate). ...
... external impulse is zero, and system momentum is exactly conserved. It also says that if for some reason the net external impulse can be approximated by zero, then system momentum is approximately conserved (and the approximation may be extremely accurate). ...
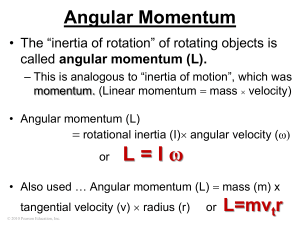
V p
... not change the system momentum. The particles may be gyrating wildly around each other, but the system momentum remains constant. ...
... not change the system momentum. The particles may be gyrating wildly around each other, but the system momentum remains constant. ...
Lecture notes - University of Oxford
... Newtonian mechanics, as first developed by Galileo and Newton in the 17th century, is an extraordinarily successful theory. Its laws are clear and relatively simple to state, but are applicable to an enormous array of dynamical problems. They are also valid over a vast range of scales. For example, ...
... Newtonian mechanics, as first developed by Galileo and Newton in the 17th century, is an extraordinarily successful theory. Its laws are clear and relatively simple to state, but are applicable to an enormous array of dynamical problems. They are also valid over a vast range of scales. For example, ...
K-1 Speed©! “Feel the Physics!”
... At the starting line of a race you are at rest, therefore you tend to stay at rest. But when you get the green light, you accelerate as fast as you can go, and feel as though you are ...
... At the starting line of a race you are at rest, therefore you tend to stay at rest. But when you get the green light, you accelerate as fast as you can go, and feel as though you are ...
Holt Ch 4 Presentation
... – Depends on location • ag varies slightly with location on Earth. • ag is different on other planets. ...
... – Depends on location • ag varies slightly with location on Earth. • ag is different on other planets. ...
Dynamics - Slides - Chapter15 - GearTeam
... This equation is referred to as the conservation of linear momentum. Conservation of linear momentum is often applied when particles collide or interact. When particles impact, only impulsive forces cause a change of linear momentum. The sledgehammer applies an impulsive force to the stake. The weig ...
... This equation is referred to as the conservation of linear momentum. Conservation of linear momentum is often applied when particles collide or interact. When particles impact, only impulsive forces cause a change of linear momentum. The sledgehammer applies an impulsive force to the stake. The weig ...
Wednesday, February 13, 2008
... Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forc ...
... Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forc ...
Forces and the Laws of Motion Section 3 What do you think?
... – Depends on location • ag varies slightly with location on Earth. • ag is different on other planets. ...
... – Depends on location • ag varies slightly with location on Earth. • ag is different on other planets. ...
Document
... Unbalanced forces: when 2 or more forces are action on an object that are unequal. The object will move in the direction that the stronger force is pushing it. ...
... Unbalanced forces: when 2 or more forces are action on an object that are unequal. The object will move in the direction that the stronger force is pushing it. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.