Gravity & Friction
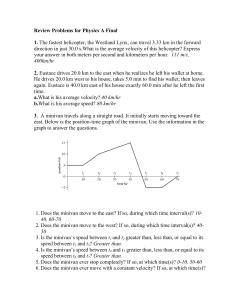
... The force that tries to slow objects down when they move through a liquid or a gas. It's also known as "drag", or "air resistance". All gases and liquids are fluids. An airplane and a swimmer both experience fluid friction. ...
... The force that tries to slow objects down when they move through a liquid or a gas. It's also known as "drag", or "air resistance". All gases and liquids are fluids. An airplane and a swimmer both experience fluid friction. ...
momentum - Pearland ISD
... • Stopping time and distances depend on the impulse-momentum theorem. • Highway safety engineers use the impulsemomentum theorem to determine stopping ...
... • Stopping time and distances depend on the impulse-momentum theorem. • Highway safety engineers use the impulsemomentum theorem to determine stopping ...
Kinematics
... and acceleration vs. time. What the above device shows is that, when looking at a graph of x vs. t, the velocity at some time is found by looking at the slope of the graph at that point. For instance, if I want to know the velocity of an object at t = 5 s, I would determine the slope of the displace ...
... and acceleration vs. time. What the above device shows is that, when looking at a graph of x vs. t, the velocity at some time is found by looking at the slope of the graph at that point. For instance, if I want to know the velocity of an object at t = 5 s, I would determine the slope of the displace ...
forces christina danielle ali
... the bottom arrow, it does not mean it is only moving up. It could also be slowing down in the negative direction. If the arrows are equal to each other, it does not only mean it is in motion, because if an object has a constant speed of 0 m/s, it has the same free-body diagram as an object that is t ...
... the bottom arrow, it does not mean it is only moving up. It could also be slowing down in the negative direction. If the arrows are equal to each other, it does not only mean it is in motion, because if an object has a constant speed of 0 m/s, it has the same free-body diagram as an object that is t ...
Physics
... Q.12 The viscous force ‘F’ acting on a body of ‘r’ moving with a velocity ' υ ' in a medium of coefficient of viscosity 'η ' is given by f = 6πη r υ . Check the correctness of the formula. Chapter 2. Motion in a straight line Q.1 Derive the three equations of motion by calculus method. Express condi ...
... Q.12 The viscous force ‘F’ acting on a body of ‘r’ moving with a velocity ' υ ' in a medium of coefficient of viscosity 'η ' is given by f = 6πη r υ . Check the correctness of the formula. Chapter 2. Motion in a straight line Q.1 Derive the three equations of motion by calculus method. Express condi ...
Dynamics Homework
... Online: Newton’s Laws Lesson 1a, 1b, 1c http://www.physicsclassroom.com/PhysicsTutorial/Newton-s-Laws * problems are for all students ** problems are for honors physics 1. * (a) If an object is at rest, can you conclude that no external forces are acting on it? (b) Is it possible for an object to be ...
... Online: Newton’s Laws Lesson 1a, 1b, 1c http://www.physicsclassroom.com/PhysicsTutorial/Newton-s-Laws * problems are for all students ** problems are for honors physics 1. * (a) If an object is at rest, can you conclude that no external forces are acting on it? (b) Is it possible for an object to be ...
Dynamics Homework
... Online: Newton’s Laws Lesson 1a, 1b, 1c http://www.physicsclassroom.com/PhysicsTutorial/Newton-s-Laws * problems are for all students ** problems are for honors physics 1. * (a) If an object is at rest, can you conclude that no external forces are acting on it? (b) Is it possible for an object to be ...
... Online: Newton’s Laws Lesson 1a, 1b, 1c http://www.physicsclassroom.com/PhysicsTutorial/Newton-s-Laws * problems are for all students ** problems are for honors physics 1. * (a) If an object is at rest, can you conclude that no external forces are acting on it? (b) Is it possible for an object to be ...
gravity quest key
... Solution: Technically speaking, in a region where gravity is extremely intense, Newton’s mechanics cannot be used. Rather, one needs to apply the “general theory of relativity” developed by Albert Einstein. Knowing this is the case, we still would like to see what Newtonian mechanics tells us. Setti ...
... Solution: Technically speaking, in a region where gravity is extremely intense, Newton’s mechanics cannot be used. Rather, one needs to apply the “general theory of relativity” developed by Albert Einstein. Knowing this is the case, we still would like to see what Newtonian mechanics tells us. Setti ...
First Diploma in Engineering Mathematics for Engineering
... a) The force required to move and accelerate a mass up an incline is given by the equation:F = mgsinθ + mgμcosθ + ma, where m is the mass, g is gravity, a is acceleration, μ is the coefficient of friction, and θ is the angle of the incline. If g = 9.8, m = 25kg, a = 3msˉ², μ = 0.4 and θ= 35°, calcul ...
... a) The force required to move and accelerate a mass up an incline is given by the equation:F = mgsinθ + mgμcosθ + ma, where m is the mass, g is gravity, a is acceleration, μ is the coefficient of friction, and θ is the angle of the incline. If g = 9.8, m = 25kg, a = 3msˉ², μ = 0.4 and θ= 35°, calcul ...
CP-S-HW-ch-5-detailed
... car first accelerates from rest (b) just as the car reaches its maximum speed (c) when the car reaches half its maximum speed (d) The question is misleading because the power required is constant. (e) More information is needed. If the car is to have uniform acceleration, a constant net force F must ...
... car first accelerates from rest (b) just as the car reaches its maximum speed (c) when the car reaches half its maximum speed (d) The question is misleading because the power required is constant. (e) More information is needed. If the car is to have uniform acceleration, a constant net force F must ...
Chapter 6 Rotational File
... • Torque is a vector quantity – The direction is perpendicular to the plane determined by the position vector and the force – If the turning tendency of the force is counterclockwise, the torque will be positive – If the turning tendency is clockwise, the torque will be negative ...
... • Torque is a vector quantity – The direction is perpendicular to the plane determined by the position vector and the force – If the turning tendency of the force is counterclockwise, the torque will be positive – If the turning tendency is clockwise, the torque will be negative ...
Newtons Three Laws - Haiku for Ignatius
... its engines down, how far will it drift? A thousand feet? A mile? ...
... its engines down, how far will it drift? A thousand feet? A mile? ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.