Connected Particles
... relative to each other (for example a block sliding along a table) to eventually slow them down. Many of the examples involving moving objects have involved a resistive force. This is often due to friction. Friction depends on the roughness of the bodies touching and on the normal contact force. The ...
... relative to each other (for example a block sliding along a table) to eventually slow them down. Many of the examples involving moving objects have involved a resistive force. This is often due to friction. Friction depends on the roughness of the bodies touching and on the normal contact force. The ...
Semester Exam Review
... Which distance-time graph(s) above show(s) an object with a non-zero constant velocity? Which distance-time graph(s) above show(s) an object undergoing uniform positive acceleration? Which distance-time graph(s) above show(s) an object that is not moving? Which distance-time graph(s) above show(s) a ...
... Which distance-time graph(s) above show(s) an object with a non-zero constant velocity? Which distance-time graph(s) above show(s) an object undergoing uniform positive acceleration? Which distance-time graph(s) above show(s) an object that is not moving? Which distance-time graph(s) above show(s) a ...
Motion & Forces
... • Displacement is the distance and direction of an object's change in position from a reference point. • Suppose a runner jogs to the 50-m mark and then turns around and runs back to the 20-m mark. • The runner travels 50 m in the original direction (north) plus 30 m in the opposite direction (south ...
... • Displacement is the distance and direction of an object's change in position from a reference point. • Suppose a runner jogs to the 50-m mark and then turns around and runs back to the 20-m mark. • The runner travels 50 m in the original direction (north) plus 30 m in the opposite direction (south ...
Adiabatic Charged Particle Motion in Rapidly Rotating
... drifts. If one has presentin addition the other five drifts, the proofcannotbe carriedthrough.The samedifficultyappearsin The theory of adiabatic particle motion in electromagnetic differentguiseif onetriesto carry out thoseproofsthat employ fieldsis well developedthrough first order in gyroradius[e ...
... drifts. If one has presentin addition the other five drifts, the proofcannotbe carriedthrough.The samedifficultyappearsin The theory of adiabatic particle motion in electromagnetic differentguiseif onetriesto carry out thoseproofsthat employ fieldsis well developedthrough first order in gyroradius[e ...
Reading Graphs and Interpreting slope: A math/Science
... a team of teachers, each a content specialist in their own discipline, to allow the concepts from both disciplines to be almost equally taught (Vasques-Mireles & West, 2007). A strength is the team-teaching approach; conversations occur around the language and the parallel relationships that are bei ...
... a team of teachers, each a content specialist in their own discipline, to allow the concepts from both disciplines to be almost equally taught (Vasques-Mireles & West, 2007). A strength is the team-teaching approach; conversations occur around the language and the parallel relationships that are bei ...
Variable forces
... acceleration formulas could be used. However, if the forces are dependent upon time, t, velocity, v, or displacement, x, then the constant acceleration formulas cannot be used. In situations where the forces are not constant, a differential equation must be set up and solved. Note: The notation used ...
... acceleration formulas could be used. However, if the forces are dependent upon time, t, velocity, v, or displacement, x, then the constant acceleration formulas cannot be used. In situations where the forces are not constant, a differential equation must be set up and solved. Note: The notation used ...
Conceptual Physics Ch 7 Newton`s Laws Project
... mass. How can you either increase the force acting on your vehicle or decrease its mass? Draw a diagram of your vehicle. Use labeled arrows to show each place that a force is acting on it. Be sure to include friction forces in your diagram. Brainstorm ways to reduce forces that slow down your vehicl ...
... mass. How can you either increase the force acting on your vehicle or decrease its mass? Draw a diagram of your vehicle. Use labeled arrows to show each place that a force is acting on it. Be sure to include friction forces in your diagram. Brainstorm ways to reduce forces that slow down your vehicl ...
I L - IBPhysicsLund
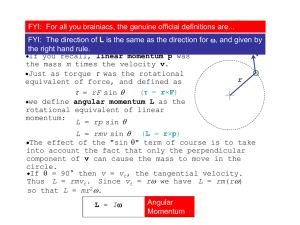
... FYI: You may recall Topic doing the same when we looked at linear 2.2thing Extended ...
... FYI: You may recall Topic doing the same when we looked at linear 2.2thing Extended ...
ExamView - Untitled.tst
... 1. What is necessary for an object to accelerate? 2. If two equal forces act on an object in opposite directions, what is the net force? What is the acceleration? 3. Can an object be in motion if the net force acting on it is zero? Explain. 4. A bowling ball loses momentum of 0.5 kg × m/s when it hi ...
... 1. What is necessary for an object to accelerate? 2. If two equal forces act on an object in opposite directions, what is the net force? What is the acceleration? 3. Can an object be in motion if the net force acting on it is zero? Explain. 4. A bowling ball loses momentum of 0.5 kg × m/s when it hi ...
Chapter 8
... • Remember back to Newton’s 1st Law of Motion, Objects tend to stay in motion, or at rest, unless acted upon by a net force. • Notice it says Motion, but does not specify whether the motion is linear or rotational. • We also said that Newton’s 1st Law describes the term inertia, or the the resistanc ...
... • Remember back to Newton’s 1st Law of Motion, Objects tend to stay in motion, or at rest, unless acted upon by a net force. • Notice it says Motion, but does not specify whether the motion is linear or rotational. • We also said that Newton’s 1st Law describes the term inertia, or the the resistanc ...
Document
... intersection, as shown in the figure. A 1300 kg minivan traveling northward is heading for the same intersection. The car and minivan collide and stick together. If the direction of the wreckage after the collision is 37.0° above the x axis, what is the initial speed of the minivan and the final spe ...
... intersection, as shown in the figure. A 1300 kg minivan traveling northward is heading for the same intersection. The car and minivan collide and stick together. If the direction of the wreckage after the collision is 37.0° above the x axis, what is the initial speed of the minivan and the final spe ...
simple harmonic motion and oscilation
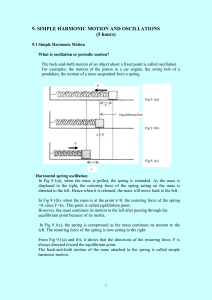
... extended by 2.00 cm. If the mass is oscillating in vertical plane, a) Prove that the mass is in simple harmonic motion, and b) Find i) the period of the motion. ii) the frequency of its oscillation. iii) the maximum velocity of the particle iv) the maximum kinetic energy of the particle. ...
... extended by 2.00 cm. If the mass is oscillating in vertical plane, a) Prove that the mass is in simple harmonic motion, and b) Find i) the period of the motion. ii) the frequency of its oscillation. iii) the maximum velocity of the particle iv) the maximum kinetic energy of the particle. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.