Newton`s Laws Review Sheet
... valley between two hills. For kicks he likes to stop pedaling and coast down the first hill – a 40 m long stretch at a 20° incline - then see if he can coast all the way up the second hill – a 20 m long stretch at a 30° incline. He starts at the top of the first hill going 5 m/s. The coefficient of ...
... valley between two hills. For kicks he likes to stop pedaling and coast down the first hill – a 40 m long stretch at a 20° incline - then see if he can coast all the way up the second hill – a 20 m long stretch at a 30° incline. He starts at the top of the first hill going 5 m/s. The coefficient of ...
review game
... color button to move their car. 3.Seven correct answers will cross the finish line and win the race. ...
... color button to move their car. 3.Seven correct answers will cross the finish line and win the race. ...
Ch 8.3 - 8.5 chap 8.3
... Momentum If the resultant external force on a system is zero, then the vector sum of the momenta of the objects will remain ...
... Momentum If the resultant external force on a system is zero, then the vector sum of the momenta of the objects will remain ...
Lab 4: Work and Energy - Instructional Physics Lab
... 1. Potential energy is the stored energy of an interaction. The key identifying characteristic of potential energy is that it can be converted into kinetic energy by the force associated with the interaction. a. The most familiar example of potential energy is gravitational potential energy. An obje ...
... 1. Potential energy is the stored energy of an interaction. The key identifying characteristic of potential energy is that it can be converted into kinetic energy by the force associated with the interaction. a. The most familiar example of potential energy is gravitational potential energy. An obje ...
force of gravity
... • Circular and elliptical motion were clearly departures from the inertial paths (straight-line) of objects; and as such, these celestial motions required a cause in the form of an unbalanced force. As learned in Lesson 1, circular motion (as well as elliptical motion) requires a centripetal force. ...
... • Circular and elliptical motion were clearly departures from the inertial paths (straight-line) of objects; and as such, these celestial motions required a cause in the form of an unbalanced force. As learned in Lesson 1, circular motion (as well as elliptical motion) requires a centripetal force. ...
3D Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
... change dG = d(mv) in its momentum dv :: same dirn as F as per Newton’s second law F = Ġ : F = Ġ ≡ Fdt = dG ...
... change dG = d(mv) in its momentum dv :: same dirn as F as per Newton’s second law F = Ġ : F = Ġ ≡ Fdt = dG ...
Vectors
... notation. More often a vector is expressed as an angle. • For example, the velocity of a projectile might be given as 30 m/s at 25o above the plain. ...
... notation. More often a vector is expressed as an angle. • For example, the velocity of a projectile might be given as 30 m/s at 25o above the plain. ...
Chapter 1 Falling Chapter Check In You have two balls of the same
... very, very, very weak force. Imagine two 1 kg masses 1 m apart. Then the gravitational force between them is a mere 6.67 x 10-11 newtons. (One newton, a standard unit of force, is the amount of force need to accelerate a mass of 1 kg at a rate of 1 m per second per second.) That is 0.0000000000667 N ...
... very, very, very weak force. Imagine two 1 kg masses 1 m apart. Then the gravitational force between them is a mere 6.67 x 10-11 newtons. (One newton, a standard unit of force, is the amount of force need to accelerate a mass of 1 kg at a rate of 1 m per second per second.) That is 0.0000000000667 N ...
pompton lakes high school - Pompton Lakes School District
... the duck during that interval is zero. That does not mean that the duck did not move, distance and displacement are different. Yes, a car may be decelerating, which would indicate that the acceleration is opposing the direction in which the car is moving. The velocity decreases at a rate of 9.8 ...
... the duck during that interval is zero. That does not mean that the duck did not move, distance and displacement are different. Yes, a car may be decelerating, which would indicate that the acceleration is opposing the direction in which the car is moving. The velocity decreases at a rate of 9.8 ...
Work and power notes
... If the work done on an object in a given time doubles, then the power doubles. For a given time, work done is directly proportional to power. How is power related to the amount of time it takes to do the work? If it takes you half the time to move an object over the same distance, you are twice as p ...
... If the work done on an object in a given time doubles, then the power doubles. For a given time, work done is directly proportional to power. How is power related to the amount of time it takes to do the work? If it takes you half the time to move an object over the same distance, you are twice as p ...
2-d motion - U of M Physics
... The problems in this laboratory will help you investigate objects moving in uniform circular motion. This is the same motion that describes satellites in orbit around the earth, or objects whirled around on a rope. Circular motion can be explained with the same concepts as those used in explaining p ...
... The problems in this laboratory will help you investigate objects moving in uniform circular motion. This is the same motion that describes satellites in orbit around the earth, or objects whirled around on a rope. Circular motion can be explained with the same concepts as those used in explaining p ...
Lecture 03 - Eunil Won
... acted upon by an outside force If the net force is zero, there is a reference frame with zero acceleration ...
... acted upon by an outside force If the net force is zero, there is a reference frame with zero acceleration ...
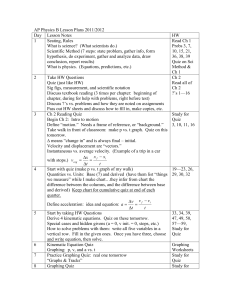
AP Physics B Lesson Plans
... “non-conservative” force. So really, it’s mechanical energy that is not being conserved. Conservative vs. non-conservative forces Springs: Hooke’s Law ...
... “non-conservative” force. So really, it’s mechanical energy that is not being conserved. Conservative vs. non-conservative forces Springs: Hooke’s Law ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.