Sample Scheme of Work
... describe the motion, plus an arrow with the direction and size of the resultant force. Higher tier: ask a student to try to start moving while wearing roller skates. Discuss why it is difficult. Consolidate the ideas of resultant forces, friction and reaction by discussing the forces that occur duri ...
... describe the motion, plus an arrow with the direction and size of the resultant force. Higher tier: ask a student to try to start moving while wearing roller skates. Discuss why it is difficult. Consolidate the ideas of resultant forces, friction and reaction by discussing the forces that occur duri ...
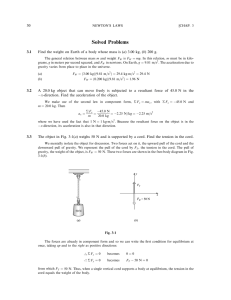
Torque Analyses of a Sliding Ladder
... Lagrange’s method is perhaps the simplest. If a torque analysis is desired, it is simplest to use the center of mass as the reference point so that no “coordinate” forces appear in the calculation. The use of reference points not on the ladder, such as points A and E is complicated by the fact that ...
... Lagrange’s method is perhaps the simplest. If a torque analysis is desired, it is simplest to use the center of mass as the reference point so that no “coordinate” forces appear in the calculation. The use of reference points not on the ladder, such as points A and E is complicated by the fact that ...
I = m • Δ v - CUSDPhysics
... Momentum is a conserved quantity in physics. This means that if you have several objects in a system, perhaps interacting with each other, but not being influenced by forces from outside of the system, then the total momentum of the system does not change over time. However, the separate momenta of ...
... Momentum is a conserved quantity in physics. This means that if you have several objects in a system, perhaps interacting with each other, but not being influenced by forces from outside of the system, then the total momentum of the system does not change over time. However, the separate momenta of ...
Chapter 5 Work, Energy, Power, and Simple Machines 5.1 Work-Constant Force
... 02. What is the average force exerted on a car from friction and air resistance if the car generates 12.5 hp when traveling at a constant 85.0 km/h? 03. Power companies send itemized bills each month to your home expressing the amount of electrical energy consumed by the household during the previou ...
... 02. What is the average force exerted on a car from friction and air resistance if the car generates 12.5 hp when traveling at a constant 85.0 km/h? 03. Power companies send itemized bills each month to your home expressing the amount of electrical energy consumed by the household during the previou ...
Analyzing a Dual Fan Carts Motion (Low Tech).
... In order to accurately measure the force produced by the fans each lab group will need an electronic lab scale or lab balance, such as a triple beam balance. Typically, each fan with fresh alkaline batteries will have a difference in mass of about 10g = 0.01kg, which is a difference in weight of 0.1 ...
... In order to accurately measure the force produced by the fans each lab group will need an electronic lab scale or lab balance, such as a triple beam balance. Typically, each fan with fresh alkaline batteries will have a difference in mass of about 10g = 0.01kg, which is a difference in weight of 0.1 ...
Gravity - Tripod
... gravity and electromagnetic forces arises from the fact that each of them involves an ...
... gravity and electromagnetic forces arises from the fact that each of them involves an ...
part2
... aB = 45 m/s2 as shown. For this instant determine the magnitude of the acceleration aC of the point C and sketch the vector in your solution. (Answer: aC = 149.6 m/s2). (Problem 5/16, M&K) ...
... aB = 45 m/s2 as shown. For this instant determine the magnitude of the acceleration aC of the point C and sketch the vector in your solution. (Answer: aC = 149.6 m/s2). (Problem 5/16, M&K) ...
Agendas - Ms. Gamm
... A 4.50 kg block rests on a smooth ramp as shown. It is attached to a 4.20 kg block by a very low mass string that is run over a low friction pulley. When the system is released, what direction will the blocks travel and what will their acceleration be? ...
... A 4.50 kg block rests on a smooth ramp as shown. It is attached to a 4.20 kg block by a very low mass string that is run over a low friction pulley. When the system is released, what direction will the blocks travel and what will their acceleration be? ...
Science
... 17. Akhtar, Kiran and Rahul were riding in a motorocar that was moving with a high velocity on an expressway when an insect hit the windshield and got stuck on the windscreen. Akhtar and Kiran started pondering over the situation. Kiran suggested that the insect suffered a greater change in momentum ...
... 17. Akhtar, Kiran and Rahul were riding in a motorocar that was moving with a high velocity on an expressway when an insect hit the windshield and got stuck on the windscreen. Akhtar and Kiran started pondering over the situation. Kiran suggested that the insect suffered a greater change in momentum ...
Momentum, Impulse and Law of Conservation of Momentum
... zero before and after the firing? • The momentum in the system must be conserved; so if the system starts with zero momentum, it must end with zero momentum. ...
... zero before and after the firing? • The momentum in the system must be conserved; so if the system starts with zero momentum, it must end with zero momentum. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.