Chapter
... Measuring Reaction Rate • To measure the reaction rate you need to be able to measure the concentration of at least one component in the mixture at many points in time • There are two ways of approaching this problem 1. for reactions that are complete in less than 1 hour, it is best to use continuo ...
... Measuring Reaction Rate • To measure the reaction rate you need to be able to measure the concentration of at least one component in the mixture at many points in time • There are two ways of approaching this problem 1. for reactions that are complete in less than 1 hour, it is best to use continuo ...
Week 1 - School of Chemical Sciences
... Starting with a well-characterized transition metal complex from the inorganic literature, propose its development into a viable catalytic system for application towards a synthetically useful process. NIH postdoctoral fellowship style recommended. Length may not exceed 4 pages (including all figure ...
... Starting with a well-characterized transition metal complex from the inorganic literature, propose its development into a viable catalytic system for application towards a synthetically useful process. NIH postdoctoral fellowship style recommended. Length may not exceed 4 pages (including all figure ...
3.2 MB - KFUPM Resources v3
... NOT the masses of the molecules BUT the numbers of the molecules (or moles). • However, in laboratory, the amounts of substances needed can not determined by counting the molecules. ...
... NOT the masses of the molecules BUT the numbers of the molecules (or moles). • However, in laboratory, the amounts of substances needed can not determined by counting the molecules. ...
electrical energy and capacitance
... Example 1. A compound is discovered with a 58.12 g/mol molar mass. Its empirical formula is C2H5. What is the molecular formula of this compound? 1A. (1) C = 12.01 amu (2) H = 1.01 amu (3) C2 + H5 (4) C2H5 = 2(12.01 amu) + 5(1.01 amu) (5) EF = C2H5 = 29.07 g/mol (6) MF = 58.12 g/mol (7) MF = n(EF) ( ...
... Example 1. A compound is discovered with a 58.12 g/mol molar mass. Its empirical formula is C2H5. What is the molecular formula of this compound? 1A. (1) C = 12.01 amu (2) H = 1.01 amu (3) C2 + H5 (4) C2H5 = 2(12.01 amu) + 5(1.01 amu) (5) EF = C2H5 = 29.07 g/mol (6) MF = 58.12 g/mol (7) MF = n(EF) ( ...
Final Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... In CO2 there are 2 CO σ-bonds, 2 CO π-bonds and 4 lone pairs, 2 on each oxygen. At each oxygen the σ-pair structure is formed by a triangle made up from the CO σ-bond and the 2 lone pairs. For these 3 electron pairs on each oxygen three hybrid orbitals are needed and thus an sp2 hybrid on each oxyge ...
... In CO2 there are 2 CO σ-bonds, 2 CO π-bonds and 4 lone pairs, 2 on each oxygen. At each oxygen the σ-pair structure is formed by a triangle made up from the CO σ-bond and the 2 lone pairs. For these 3 electron pairs on each oxygen three hybrid orbitals are needed and thus an sp2 hybrid on each oxyge ...
CHAPTER I
... Electron spin. Three quantum numbers (n, ℓ , and mℓ ) allow us to define the orbital for an electron. To describe completely an electron in an atom with many electrons, however, we still need one more quantum number, the electron spin quantum number, ms. In approximately 1920, theoretical chemists r ...
... Electron spin. Three quantum numbers (n, ℓ , and mℓ ) allow us to define the orbital for an electron. To describe completely an electron in an atom with many electrons, however, we still need one more quantum number, the electron spin quantum number, ms. In approximately 1920, theoretical chemists r ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Analyze We are told that isopropyl alcohol contains C, H, and O atoms and given the quantities of CO 2 and H2O produced when a given quantity of the alcohol is combusted. We must use this information to determine the empirical formula for isopropyl alcohol, a task that requires us to calculate the n ...
... Analyze We are told that isopropyl alcohol contains C, H, and O atoms and given the quantities of CO 2 and H2O produced when a given quantity of the alcohol is combusted. We must use this information to determine the empirical formula for isopropyl alcohol, a task that requires us to calculate the n ...
17 ADSORPTION AND CATALYSIS S MODULE - 5
... (i) Nature and Surface Area of the Adsorbent Different solids would adsorb different amounts of the same gas even under similar conditions. Substances like charcoal and silica gel are excellent adsorbents. The substances that are porous in nature and have rough surfaces are better adsorbents. The ex ...
... (i) Nature and Surface Area of the Adsorbent Different solids would adsorb different amounts of the same gas even under similar conditions. Substances like charcoal and silica gel are excellent adsorbents. The substances that are porous in nature and have rough surfaces are better adsorbents. The ex ...
Chapter 4: Experimental Techniques
... using a wavelength corresponding to one specific transition is selected for the analysis (e.g. 217.0 or 283.3 nm for Pb). The metal being analysed is not usually in its elemental form, and so the first step is digestion (decomposition) of the sample and of a series of standards. The standards contai ...
... using a wavelength corresponding to one specific transition is selected for the analysis (e.g. 217.0 or 283.3 nm for Pb). The metal being analysed is not usually in its elemental form, and so the first step is digestion (decomposition) of the sample and of a series of standards. The standards contai ...
Learning Algorithms for Separable Approximations of
... be the case with two-stage stochastic programs. Furthermore, the observed speed of convergence is much faster than techniques such as Benders decomposition, especially for higher dimensional problems. The paper is divided into two parts. Sections 2-6 deal exclusively with problems where the original ...
... be the case with two-stage stochastic programs. Furthermore, the observed speed of convergence is much faster than techniques such as Benders decomposition, especially for higher dimensional problems. The paper is divided into two parts. Sections 2-6 deal exclusively with problems where the original ...
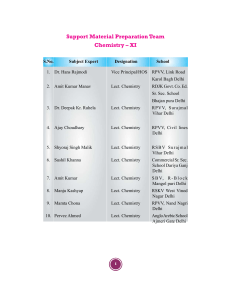
Support Material
... Discovery of Electron, Proton and Neutron, atomic number, isotopes and isobars. Thomson’s model and its limitations. Rutherford’s model and its limitations, Bohr’s model and its limitations, concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light, cle Broglie’s relationship, Heisenberg unce ...
... Discovery of Electron, Proton and Neutron, atomic number, isotopes and isobars. Thomson’s model and its limitations. Rutherford’s model and its limitations, Bohr’s model and its limitations, concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light, cle Broglie’s relationship, Heisenberg unce ...
Calculations and Chemical Equations Atomic mass: Mass of an
... Chemical Reaction: Interaction between substances that results in one or more new substances being produced ...
... Chemical Reaction: Interaction between substances that results in one or more new substances being produced ...
CHM2045 Exam 2 Review Questions Fall 2015
... 13) Select the false statements below. A) In any given atom, a l = 2 subshell can accommodate up to 5 electrons that have ms = –1/2 B) The n = 1 shell of any given atom can accommodate up to 2 electrons C) The following set of quantum numbers is allowed: n = 4, l = 2, ml = −2, ms = +1/2 D) The n = 4 ...
... 13) Select the false statements below. A) In any given atom, a l = 2 subshell can accommodate up to 5 electrons that have ms = –1/2 B) The n = 1 shell of any given atom can accommodate up to 2 electrons C) The following set of quantum numbers is allowed: n = 4, l = 2, ml = −2, ms = +1/2 D) The n = 4 ...
1.9 M - Thierry Karsenti
... PEDAGOGICAL COMMENTS FOR LEARNERS IMPORTANT TIPS: • You will be able to appreciate why various substances behave the way they do by understanding the theory and structure of atoms. This is quite fundamental in conceptualizing the very existence of inter- and intra bonding between the components that ...
... PEDAGOGICAL COMMENTS FOR LEARNERS IMPORTANT TIPS: • You will be able to appreciate why various substances behave the way they do by understanding the theory and structure of atoms. This is quite fundamental in conceptualizing the very existence of inter- and intra bonding between the components that ...
Chemical Quantities: Stoichiometry and the Mole
... you follow the steps you can get to the answer. Think about the “steps” I mentioned when we talked about problem solving. When we learned how to write the names of compounds for their formulas, and the formulas for the names. When we do conversions and stoichiometry. I am half cliche when I describe ...
... you follow the steps you can get to the answer. Think about the “steps” I mentioned when we talked about problem solving. When we learned how to write the names of compounds for their formulas, and the formulas for the names. When we do conversions and stoichiometry. I am half cliche when I describe ...
Stoichiometry - Bruder Chemistry
... (vitamin C) composed of only C, H, and O is burned completely with excess O2 . 0.2998 g of CO2 and 0.0819 g of H2O are produced. What is the empirical formula? ...
... (vitamin C) composed of only C, H, and O is burned completely with excess O2 . 0.2998 g of CO2 and 0.0819 g of H2O are produced. What is the empirical formula? ...
Basic Agricultural Chemistry - Macmillan Education South Africa
... and shape of its container. A gas can be compressed to occupy a smaller volume, or it can expand to occupy a larger one. The particles in a gas state of matter have very high kinetic energy and will move about very rapidly. They collide against one another so strongly that they move quite far apart ...
... and shape of its container. A gas can be compressed to occupy a smaller volume, or it can expand to occupy a larger one. The particles in a gas state of matter have very high kinetic energy and will move about very rapidly. They collide against one another so strongly that they move quite far apart ...
Atkins/ de Paula
... becomes a gas. Hence, all liquids can be expected to have similar standard entropies of vaporization. Liquids that show significant deviations from Trouton’s rule do so on account of strong molecular interactions that restrict molecular motion. As a result, there is a greater dispersal of energy and ...
... becomes a gas. Hence, all liquids can be expected to have similar standard entropies of vaporization. Liquids that show significant deviations from Trouton’s rule do so on account of strong molecular interactions that restrict molecular motion. As a result, there is a greater dispersal of energy and ...
the chemistry of life: organic and biological chemistry
... Hydrocarbons can be divided into four general types, depending on the kinds of carbon-carbon bonds in their molecules. Figure 25.3 ..,. shows an example of each of the four types: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons. In these hydrocarbons, as well as in other organic compounds, each ...
... Hydrocarbons can be divided into four general types, depending on the kinds of carbon-carbon bonds in their molecules. Figure 25.3 ..,. shows an example of each of the four types: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons. In these hydrocarbons, as well as in other organic compounds, each ...
CHE 110 Dr. Nicholas Bizier Office DS 337b email
... Lysine is an amino acid which has the following elemental composition: C, H, O, N. In one experiment, 2.175 g of lysine was combusted to produce 3.94 g of CO2 and 1.89 g H2O. In a separate experiment, 1.873 g of lysine was burned to produce 0.436 g of NH2. The molar mass of lysine is 150 g/mol. Dete ...
... Lysine is an amino acid which has the following elemental composition: C, H, O, N. In one experiment, 2.175 g of lysine was combusted to produce 3.94 g of CO2 and 1.89 g H2O. In a separate experiment, 1.873 g of lysine was burned to produce 0.436 g of NH2. The molar mass of lysine is 150 g/mol. Dete ...
A solution method for general contact±impact problems - Z
... where u and f are the incremental displacements and unbalanced force vectors, respectively. The right superscript show the corresponding element and the o-diagonal terms are zero which implies that the two elements are independent. However, after contact and imposing Eq. (11) nonzero o-diagonals w ...
... where u and f are the incremental displacements and unbalanced force vectors, respectively. The right superscript show the corresponding element and the o-diagonal terms are zero which implies that the two elements are independent. However, after contact and imposing Eq. (11) nonzero o-diagonals w ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • In a lab, we cannot work with individual molecules. They are too small. • 6.02 × 1023 atoms or molecules is an amount that brings us to lab size. It is ONE MOLE. • One mole of 12C has a mass of 12.000 g. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • In a lab, we cannot work with individual molecules. They are too small. • 6.02 × 1023 atoms or molecules is an amount that brings us to lab size. It is ONE MOLE. • One mole of 12C has a mass of 12.000 g. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
ME 2105 – Fall 2010 Suggested Homework Problems – The Key
... concentrations at room temperature. Compute the unit cell edge length for a 75 wt% Ag–25 wt% Pd alloy. The room-temperature density of Pd is 12.02 g/cm3, and its atomic weight and atomic radius are 106.4 g/mol and 0.138 nm, respectively. Solution First of all, the atomic radii for Ag (using the tabl ...
... concentrations at room temperature. Compute the unit cell edge length for a 75 wt% Ag–25 wt% Pd alloy. The room-temperature density of Pd is 12.02 g/cm3, and its atomic weight and atomic radius are 106.4 g/mol and 0.138 nm, respectively. Solution First of all, the atomic radii for Ag (using the tabl ...