Chapter 18- The Endocrine System
... B) communicates via chemical signals C) regulates activities of muscles and glands D) A and B are correct. E) A, B and C are correct. 2) Which of the following statements about the endocrine system is NOT correct? A) It uses hormones, which are transported by the blood, to communicate with distant t ...
... B) communicates via chemical signals C) regulates activities of muscles and glands D) A and B are correct. E) A, B and C are correct. 2) Which of the following statements about the endocrine system is NOT correct? A) It uses hormones, which are transported by the blood, to communicate with distant t ...
9 Endocrine Physiology
... cell. So, T3 gets used first by the body cells. T4 takes longer to be ready; one iodine has to drop off. As T3 is used up, T4 is being converted to more T3. • To make thyroid hormone, you need iodine in your body. Iodized salt has enough to meet this need. Iodine is brought into the follicular cells ...
... cell. So, T3 gets used first by the body cells. T4 takes longer to be ready; one iodine has to drop off. As T3 is used up, T4 is being converted to more T3. • To make thyroid hormone, you need iodine in your body. Iodized salt has enough to meet this need. Iodine is brought into the follicular cells ...
Interpretive Guide for Adrenal Stress
... *This table is provided as a guide to potential ways that have been found to be beneficial when abnormal hormone patterns are found. Plus marks indicate when intervention is indicated for the various patterns and greater number of marks indicate higher level of support may be needed. Nutritional sup ...
... *This table is provided as a guide to potential ways that have been found to be beneficial when abnormal hormone patterns are found. Plus marks indicate when intervention is indicated for the various patterns and greater number of marks indicate higher level of support may be needed. Nutritional sup ...
Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology
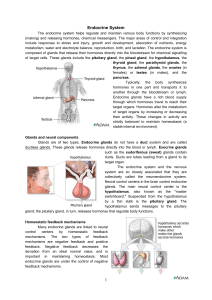
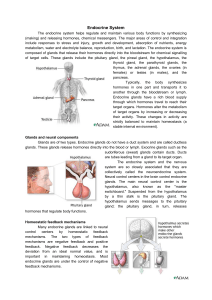
... There are five major endocrine organs in the body: the hypothalamus, the pituitary, the adrenal glands, the thyroid gland, and the pancreas. Other organs have endocrine functions as well, but will not be covered in this article. Endocrine organs secrete hormones that act on specific “target tissue ...
... There are five major endocrine organs in the body: the hypothalamus, the pituitary, the adrenal glands, the thyroid gland, and the pancreas. Other organs have endocrine functions as well, but will not be covered in this article. Endocrine organs secrete hormones that act on specific “target tissue ...
Part A
... Chemical Structure of Hormones Molecular size of hormones that regulate reproduction Hormone FSH ...
... Chemical Structure of Hormones Molecular size of hormones that regulate reproduction Hormone FSH ...
Endocrine Glands 11
... • Addison’s disease is the major hyposecretory disorder of the adrenal cortex, usually involving of both glucocorticoids and mineralcorticoids. Victims lose weight, demonstrate hypoglycemia and reduced levels of sodium, and show an increase in skin JFK had Addison’s, which he pigmentation (bronzing) ...
... • Addison’s disease is the major hyposecretory disorder of the adrenal cortex, usually involving of both glucocorticoids and mineralcorticoids. Victims lose weight, demonstrate hypoglycemia and reduced levels of sodium, and show an increase in skin JFK had Addison’s, which he pigmentation (bronzing) ...
Endocrine ppt 2014
... • C. Hormones activate target cells by 1 of 2 methods, depending upon the chemical nature of the hormone: • 1) peptide hormones {water soluble} that bind to a receptor protein on the plasma membrane of the cell. The receptor protein, then stimulates the production of a second messenger ...
... • C. Hormones activate target cells by 1 of 2 methods, depending upon the chemical nature of the hormone: • 1) peptide hormones {water soluble} that bind to a receptor protein on the plasma membrane of the cell. The receptor protein, then stimulates the production of a second messenger ...
Hormone review
... Type II diabetes is caused by a deficiency in insulin production or by changes in insulin receptors on the target cells. In either case, blood glucose level may be high because cells do not receive the message to metabolize glucose. This form of diabetes usually becomes noticeable in middle age. It ...
... Type II diabetes is caused by a deficiency in insulin production or by changes in insulin receptors on the target cells. In either case, blood glucose level may be high because cells do not receive the message to metabolize glucose. This form of diabetes usually becomes noticeable in middle age. It ...
The system that consists of group of ductless glands
... 1. Decreased secretion from adrenal glands that cause dehydration, low blood pressure, weight loss, muscle weakness, & bronzing of skin: ...
... 1. Decreased secretion from adrenal glands that cause dehydration, low blood pressure, weight loss, muscle weakness, & bronzing of skin: ...
test review key - Hartland High School
... - be able to label all endocrine glands on a human diagram - study & review your notes, homework, and the case study - understand and be able to explain the information covered in the following questions. 1. Describe the function of the Endocrine System. Along with the nervous system, it coordinates ...
... - be able to label all endocrine glands on a human diagram - study & review your notes, homework, and the case study - understand and be able to explain the information covered in the following questions. 1. Describe the function of the Endocrine System. Along with the nervous system, it coordinates ...
Objectives Goals of the male repro tract Chromosomal sex Gonadal
... 5. Describe the embryonic development of the prostate ...
... 5. Describe the embryonic development of the prostate ...
lec18
... Exert from Clinical Focus on Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Diabetes Mellitus have difficulty in controlling their blood sugar level. The causes are attributed to: – Inability to make insulin by pancreatic islet cells. Target cells lack membrane receptor for insulin on the cells of target tissues. ...
... Exert from Clinical Focus on Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Diabetes Mellitus have difficulty in controlling their blood sugar level. The causes are attributed to: – Inability to make insulin by pancreatic islet cells. Target cells lack membrane receptor for insulin on the cells of target tissues. ...
Endocrine System
... hormone, which regulates the blood calcium amount. If calcium decreases, the parathyroid glands sense the decrease and secrete more parathyroid hormone. The parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from the bones and increases the calcium uptake into the bloodstream from the collecting tubules ...
... hormone, which regulates the blood calcium amount. If calcium decreases, the parathyroid glands sense the decrease and secrete more parathyroid hormone. The parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from the bones and increases the calcium uptake into the bloodstream from the collecting tubules ...
Endocrine System
... • Causes ruptured follicle to become the corpus luteum • Stimulates testosterone production in males • Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
... • Causes ruptured follicle to become the corpus luteum • Stimulates testosterone production in males • Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
Principles of endocrinology
... otherwise rapid degradation of unbound hormones,and restrict hormone acces to certain sites – The binding proteins abnormalities (liver disease, certain medications) can cause short-term change in circulating free hormone levels, which in turn induce compensatory adaptation through feedback loops. E ...
... otherwise rapid degradation of unbound hormones,and restrict hormone acces to certain sites – The binding proteins abnormalities (liver disease, certain medications) can cause short-term change in circulating free hormone levels, which in turn induce compensatory adaptation through feedback loops. E ...
The Endocrine System: An Overview Endocrine - dr
... Steroids- lipid based derived from cholesterol ...
... Steroids- lipid based derived from cholesterol ...
Endocrine System
... do not require continuous adjustment. In positive feedback mechanisms, the original stimulus is promoted rather than negated. Positive feedback increases the deviation from an ideal normal value. Unlike negative feedback that maintains hormone levels within narrow ranges, positive feedback is rarely ...
... do not require continuous adjustment. In positive feedback mechanisms, the original stimulus is promoted rather than negated. Positive feedback increases the deviation from an ideal normal value. Unlike negative feedback that maintains hormone levels within narrow ranges, positive feedback is rarely ...
FREE TESTOSTERONE
... levels for their age and there has been significant improvement in walking distance ,ABI improvement by 0.4,pain scale pain improvement on VAS from 8 to 3 after 9 doses of testosterone administration. ...
... levels for their age and there has been significant improvement in walking distance ,ABI improvement by 0.4,pain scale pain improvement on VAS from 8 to 3 after 9 doses of testosterone administration. ...
File
... • The pancreas produces two antagonistic hormones that play important roles in managing the body’s energy supplies: 1. insulin, which reduces blood sugar levels and 2. glucagon, which increases blood sugar levels. ...
... • The pancreas produces two antagonistic hormones that play important roles in managing the body’s energy supplies: 1. insulin, which reduces blood sugar levels and 2. glucagon, which increases blood sugar levels. ...
Hypothalamic and pituitary disorders Diseases of the adrenal cortex
... Urine: random or collected Saliva: free fraction, easy implementation How? ...
... Urine: random or collected Saliva: free fraction, easy implementation How? ...
comp3_unit7_self
... 2. Which of the following endocrine glands has both an exocrine and an endocrine function? a) Adrenal b) Pancreas c) Pineal d) Thymus Answer: b) Pancreas Objective/Reference: Lecture 7a, Objective: Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to the endocrine system, Slide 11 ...
... 2. Which of the following endocrine glands has both an exocrine and an endocrine function? a) Adrenal b) Pancreas c) Pineal d) Thymus Answer: b) Pancreas Objective/Reference: Lecture 7a, Objective: Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to the endocrine system, Slide 11 ...
here
... If the ACTH is normal or high, you need to distinguish between pituitary and ectopic ACTH. The first line test is a high-dose dexamethasone suppression test; High-dose dexamethasone suppression test (2mg, 6 hourly for 48 hours) – if the patient has Cushing’s disease, this will cause at least partia ...
... If the ACTH is normal or high, you need to distinguish between pituitary and ectopic ACTH. The first line test is a high-dose dexamethasone suppression test; High-dose dexamethasone suppression test (2mg, 6 hourly for 48 hours) – if the patient has Cushing’s disease, this will cause at least partia ...