Ovarian Androgen Production in Postmenopausal Women
... peripheral circulation (Table 2) and decreases in T of 42% from the preoperative to postoperative time period (Table 3). A nonsignificant 17% decrease in postoperative A levels was observed. This relative lack of change is possibly attributable to postoperative compensatory production by the adrenal ...
... peripheral circulation (Table 2) and decreases in T of 42% from the preoperative to postoperative time period (Table 3). A nonsignificant 17% decrease in postoperative A levels was observed. This relative lack of change is possibly attributable to postoperative compensatory production by the adrenal ...
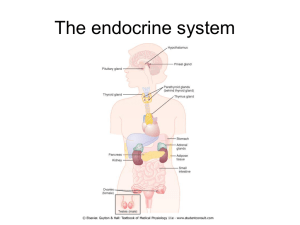
The Endocrine System
... • Depress immune response (decreases tissue rejection in transplant cases) • Secretion controlled by hypothalamus (corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)) based on cortisol level in blood • Increased release in response to stress, increasing availability of ATP and heightened response to vasoconstric ...
... • Depress immune response (decreases tissue rejection in transplant cases) • Secretion controlled by hypothalamus (corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)) based on cortisol level in blood • Increased release in response to stress, increasing availability of ATP and heightened response to vasoconstric ...
The Endocrine System Overview of Endocrine System • Endocrine
... • Depress immune response (decreases tissue rejection in transplant cases) • Secretion controlled by hypothalamus (corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)) based on cortisol level in blood • Increased release in response to stress, increasing availability of ATP and heightened response to vasoconstric ...
... • Depress immune response (decreases tissue rejection in transplant cases) • Secretion controlled by hypothalamus (corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)) based on cortisol level in blood • Increased release in response to stress, increasing availability of ATP and heightened response to vasoconstric ...
Pathomechanisms of the development of obesity in some
... women with PCOS and healthy women, so it seems unlikely that leptin plays a significant role in its pathogenesis [16]. It is still unclear whether obesity is a cause or a consequence of PCOS [45]. Insulin resistance and accompanying hyperinsulinaemia that characterise PCOS are important risk factors ...
... women with PCOS and healthy women, so it seems unlikely that leptin plays a significant role in its pathogenesis [16]. It is still unclear whether obesity is a cause or a consequence of PCOS [45]. Insulin resistance and accompanying hyperinsulinaemia that characterise PCOS are important risk factors ...
diagnosis and management of surgical adrenal diseases - e
... and neck.26 The annual incidence is 2 to 8 cases per million people.27,28 They occur with equal frequency between men and women and at any age, but primarily from age 30 to 50.17 On autopsy series, pheochromocytomas have been found in 0.05% to 0.13% of patients.29,30 Often called the “10% tumor,” ap ...
... and neck.26 The annual incidence is 2 to 8 cases per million people.27,28 They occur with equal frequency between men and women and at any age, but primarily from age 30 to 50.17 On autopsy series, pheochromocytomas have been found in 0.05% to 0.13% of patients.29,30 Often called the “10% tumor,” ap ...
endocrine system
... Adrenal Glands – Diseases and Abnormal Conditions • Addison’s Disease – Caused by a decreased secretion of aldosterone on the part of the adrenal cortex – This interferes with the reabsorption of sodium and water and causes an increased level of potassium in the blood – Signs and Symptoms: • Dehydr ...
... Adrenal Glands – Diseases and Abnormal Conditions • Addison’s Disease – Caused by a decreased secretion of aldosterone on the part of the adrenal cortex – This interferes with the reabsorption of sodium and water and causes an increased level of potassium in the blood – Signs and Symptoms: • Dehydr ...
Elevated prolactin levels
... through special receptors enhancing water reabsorption from tubules to the blood (without salts). it will dilute the blood and therefore corrects osmolality, but concentrated urine is produced. The reverse is true: when the subject drinks a lot of water/fluid, this will decrease blood osmolality and ...
... through special receptors enhancing water reabsorption from tubules to the blood (without salts). it will dilute the blood and therefore corrects osmolality, but concentrated urine is produced. The reverse is true: when the subject drinks a lot of water/fluid, this will decrease blood osmolality and ...
Hormone
... Langerhans by the body’s own immune system Symptoms – Constant thirst – Undiminished hunger – Excessive urination – Insulin injections are used to control glucose levels – Diet itself cannot control this condition Treatment – Injection of insulin into blood stream daily – Regular measurement of bloo ...
... Langerhans by the body’s own immune system Symptoms – Constant thirst – Undiminished hunger – Excessive urination – Insulin injections are used to control glucose levels – Diet itself cannot control this condition Treatment – Injection of insulin into blood stream daily – Regular measurement of bloo ...
Endocrine System Notes
... • Different hormone receptor interactions produce different regulatory changes within the target cell through chemical reactions • Most hormones have primary effects that directly regulate target cells and many secondary effects that influence or modulate other regulatory mechanisms in target cells ...
... • Different hormone receptor interactions produce different regulatory changes within the target cell through chemical reactions • Most hormones have primary effects that directly regulate target cells and many secondary effects that influence or modulate other regulatory mechanisms in target cells ...
Anatomy and Physiology - Manatee School for the Arts
... Forty-three percent of all adults suffer adverse health effects from stress. Seventy-five percent to 90% of all doctor's office visits are for stress-related ailments and complaints. Stress can play a part in problems such as headaches, high blood pressure, heart problems, diabetes, skin conditions, ...
... Forty-three percent of all adults suffer adverse health effects from stress. Seventy-five percent to 90% of all doctor's office visits are for stress-related ailments and complaints. Stress can play a part in problems such as headaches, high blood pressure, heart problems, diabetes, skin conditions, ...
Symptoms Diagnosis Heredity Other Enzyme Deficiencies Newborn
... degree but differs from 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Excess androgens produced during childhood cause rapid growth and skeletal advancement. This growth initially causes the child to be taller than most children their age; however, the end result of this growth and bone age advancement if untreated is ...
... degree but differs from 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Excess androgens produced during childhood cause rapid growth and skeletal advancement. This growth initially causes the child to be taller than most children their age; however, the end result of this growth and bone age advancement if untreated is ...
Endocrine, powerpoint notes
... cases.[2] With achondroplasia, one's limbs are proportionately shorter than one's trunk (abdominal area), with a larger head than average and characteristic facial features. Conditions in humans characterized by disproportional body parts are typically caused by one or more genetic disorders in bone ...
... cases.[2] With achondroplasia, one's limbs are proportionately shorter than one's trunk (abdominal area), with a larger head than average and characteristic facial features. Conditions in humans characterized by disproportional body parts are typically caused by one or more genetic disorders in bone ...
Document
... • Die more often from all 15 leading causes of death (except Alzheimer’s) • Greater risk of serious chronic diseases, and suffer from them at an earlier age • Are twice as likely to die from heart disease (3 of 4 heart attack deaths under 65 are men) ...
... • Die more often from all 15 leading causes of death (except Alzheimer’s) • Greater risk of serious chronic diseases, and suffer from them at an earlier age • Are twice as likely to die from heart disease (3 of 4 heart attack deaths under 65 are men) ...
Endocrinology - Zoology, UBC
... PRL has a role in regulation of the female reproductive cycle. However, its precise role has not be delineated yet. Excess PRL secretion is know to block synthesis and release of gonadotropins, disrupting menstruation and causing infertility. ...
... PRL has a role in regulation of the female reproductive cycle. However, its precise role has not be delineated yet. Excess PRL secretion is know to block synthesis and release of gonadotropins, disrupting menstruation and causing infertility. ...
Endocrine System Jeopardy
... of cell signaling in which the target cell is near the signalreleasing cell. What is paracrine (signaling)? ...
... of cell signaling in which the target cell is near the signalreleasing cell. What is paracrine (signaling)? ...
Endocrine System Jeopardy - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... of cell signaling in which the target cell is near the signalreleasing cell. What is paracrine (signaling)? ...
... of cell signaling in which the target cell is near the signalreleasing cell. What is paracrine (signaling)? ...
Final Exam - TeacherWeb
... 64. Which system coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environment? 65. Neurons are classified by the 66. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? 67. What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment? ...
... 64. Which system coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environment? 65. Neurons are classified by the 66. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? 67. What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment? ...
Chapter 45. - RMC Science Home
... receives information from nerves around body about internal conditions releasing hormones: regulates release of hormones from pituitary ...
... receives information from nerves around body about internal conditions releasing hormones: regulates release of hormones from pituitary ...
Hormone Replacement Therapy in the Geriatric Patient: Current
... and subclinical hypothyroidism are becoming misnomers, because they present clinically significant signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism that do benefit from correct treatment.67 The symptoms studied and directly connected to hypothyroidism include neuromuscular dysfunction,68 depression,69,70 memory ...
... and subclinical hypothyroidism are becoming misnomers, because they present clinically significant signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism that do benefit from correct treatment.67 The symptoms studied and directly connected to hypothyroidism include neuromuscular dysfunction,68 depression,69,70 memory ...
The Endocrine System Recall What are hormones? The endocrine s
... Both lobes release hormones after receiving signals from the hypothalamus. posterior lobe stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus ADH and oxytocin only ...
... Both lobes release hormones after receiving signals from the hypothalamus. posterior lobe stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus ADH and oxytocin only ...
Biochemistry and Disorders of Hormones of the Kidney, Heart and
... Excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone is seen in two forms: Primary hyperparathyroidism is the result of parathyroid gland disease. Secondary hyperparathyroidism is the situation where disease outside of the parathyroid gland leads to excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone. A common cau ...
... Excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone is seen in two forms: Primary hyperparathyroidism is the result of parathyroid gland disease. Secondary hyperparathyroidism is the situation where disease outside of the parathyroid gland leads to excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone. A common cau ...
session 16.rtf - Joyful Living Services
... formation of carbohydrates from protein and fat through secretion of enzymes from the liver. These glucocorticoids also decrease inflammation, help repair damaged tissue and act as the body’s buffer for stress. Another cortical steroid hormone is aldosterone, which regulates mineral balance within t ...
... formation of carbohydrates from protein and fat through secretion of enzymes from the liver. These glucocorticoids also decrease inflammation, help repair damaged tissue and act as the body’s buffer for stress. Another cortical steroid hormone is aldosterone, which regulates mineral balance within t ...
9 Endocrine physiology
... (ANP, produced by heart cells) is released when you have high blood pressure. It causes the kidney to secrete more water, so blood pressure can decrease. That is the opposite of ADH, which makes you urinate less. • Some hormones are permissive; you need one in order for a second to do its job well. ...
... (ANP, produced by heart cells) is released when you have high blood pressure. It causes the kidney to secrete more water, so blood pressure can decrease. That is the opposite of ADH, which makes you urinate less. • Some hormones are permissive; you need one in order for a second to do its job well. ...
TOPIC: Regulation AIM: What are the parts of the Endocrine System
... much growth hormone during adulthood. When this happens, your bones increase in size, including those of your hands, feet and face. Acromegaly usually affects middle-aged adults. It is characterized by an enlarged face and hands. As the face changes shape, the jaw may protrude, the nose may enlarge, ...
... much growth hormone during adulthood. When this happens, your bones increase in size, including those of your hands, feet and face. Acromegaly usually affects middle-aged adults. It is characterized by an enlarged face and hands. As the face changes shape, the jaw may protrude, the nose may enlarge, ...
the endocrine system - The Described and Captioned Media Program
... b. How do boys and girls develop sexually into men and women? c. How does the body react to stress? d. What causes diabetes? 2. Discuss the differences between endocrine and exocrine glands. 3. Research to find the heights of the shortest and tallest humans on record. a. Write this information in bo ...
... b. How do boys and girls develop sexually into men and women? c. How does the body react to stress? d. What causes diabetes? 2. Discuss the differences between endocrine and exocrine glands. 3. Research to find the heights of the shortest and tallest humans on record. a. Write this information in bo ...