acromegaly - Hormone Health Network
... Acromegaly W h at i s a c r ome galy? Acromegaly is a rare but serious condition caused by too much growth hormone (GH) in the blood. GH is released into the bloodstream by the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain. The blood carries GH to other parts of the body where it has specific ef ...
... Acromegaly W h at i s a c r ome galy? Acromegaly is a rare but serious condition caused by too much growth hormone (GH) in the blood. GH is released into the bloodstream by the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain. The blood carries GH to other parts of the body where it has specific ef ...
TRT: A Recipe for Success
... Estrogen is absolutely necessary for our physical health. Of note, same also provides the emotional component of a mature gentleman’s sexual being. This is why estrogens must be evaluated and, when necessary, controlled. The “sweet spot” E concentration depends upon SHBG. Rule of thumb is mid-range ...
... Estrogen is absolutely necessary for our physical health. Of note, same also provides the emotional component of a mature gentleman’s sexual being. This is why estrogens must be evaluated and, when necessary, controlled. The “sweet spot” E concentration depends upon SHBG. Rule of thumb is mid-range ...
Guidelines on the management of sexual problems in men: the role
... • Measurements of serum levels of luteinising hormone will assist in differentiating between primary and secondary hypogonadism, and a determination of serum prolactin level is indicated when the serum testosterone is lower than 5.2 nmol/l (150 ng/dl) or when secondary hypogonadism is suspected. The ...
... • Measurements of serum levels of luteinising hormone will assist in differentiating between primary and secondary hypogonadism, and a determination of serum prolactin level is indicated when the serum testosterone is lower than 5.2 nmol/l (150 ng/dl) or when secondary hypogonadism is suspected. The ...
The Endocrine System
... development, reproduction, metabolism and body defense -endocrine organs are small and widely separated in the body, some are part of mixed glands (both exocrine and endocrine function) example: gonads and pancrease ...
... development, reproduction, metabolism and body defense -endocrine organs are small and widely separated in the body, some are part of mixed glands (both exocrine and endocrine function) example: gonads and pancrease ...
Chapter 45 Hormones And Endocrine System
... Growth factors: are peptides and proteins that stimulate cell proliferation. ...
... Growth factors: are peptides and proteins that stimulate cell proliferation. ...
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems
... the body. Hormones travel throughout the body in the bloodstream. • Hormones bind to target cells, which are cells that have specific receptors for a hormone either in the cell membrane or inside the cell. • A hormone will not affect a cell that does not have receptors for the hormone. ▶ Glands are ...
... the body. Hormones travel throughout the body in the bloodstream. • Hormones bind to target cells, which are cells that have specific receptors for a hormone either in the cell membrane or inside the cell. • A hormone will not affect a cell that does not have receptors for the hormone. ▶ Glands are ...
growth hormone (GH)
... melatonin a hormone produced by the pineal gland which helps regulate a persons daily cycle or circadian rhythms; levels are high at night promoting sleepiness and low during the day as we awake. methamphetamine a stimulant sometimes called speed which causes a sensation of a rush similar to cocaine ...
... melatonin a hormone produced by the pineal gland which helps regulate a persons daily cycle or circadian rhythms; levels are high at night promoting sleepiness and low during the day as we awake. methamphetamine a stimulant sometimes called speed which causes a sensation of a rush similar to cocaine ...
Chapter2 Endocrine System for handouts
... Too much growth hormone produced in adults; enlargement of bones and thickened skin Addison’s disease Adrenal gland fails to produce enough corticosteroids Cretinism Extreme form of hypothyroidism present prior to or soon after birth Cushing’s disease Hypercortisolism; over-production of cortisol ...
... Too much growth hormone produced in adults; enlargement of bones and thickened skin Addison’s disease Adrenal gland fails to produce enough corticosteroids Cretinism Extreme form of hypothyroidism present prior to or soon after birth Cushing’s disease Hypercortisolism; over-production of cortisol ...
The Endocrine System Notes
... Endocrine system: produces and releases chemical messages; slower speed Both systems are integrated and help maintain homeostasis Both systems are regulated by positive and negative feedback mechanisms Negative feedback A change in an internal condition is sensed by the brain The brain cau ...
... Endocrine system: produces and releases chemical messages; slower speed Both systems are integrated and help maintain homeostasis Both systems are regulated by positive and negative feedback mechanisms Negative feedback A change in an internal condition is sensed by the brain The brain cau ...
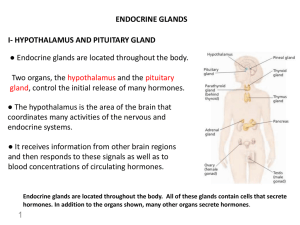
Chapter 15-B Endocrine Glands
... – CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone : Causes ant. pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone – GnRH. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone: Causes anterior pituitary to produce FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone) – PRH. Prolactin-releasing hormone : Causes the anterior ...
... – CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone : Causes ant. pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone – GnRH. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone: Causes anterior pituitary to produce FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone) – PRH. Prolactin-releasing hormone : Causes the anterior ...
Hormone
... Learning Outcomes In today’s topic you will learn: The endocrine system, it’s structure, function and common pathologies. ...
... Learning Outcomes In today’s topic you will learn: The endocrine system, it’s structure, function and common pathologies. ...
CRYDERS-Endocrine System
... – CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone : Causes ant. pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone – GnRH. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone: Causes anterior pituitary to produce FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone) – PRH. Prolactin-releasing hormone : Causes the anterior ...
... – CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone : Causes ant. pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone – GnRH. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone: Causes anterior pituitary to produce FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone) – PRH. Prolactin-releasing hormone : Causes the anterior ...
File
... Nodule size > 4 cm Nodule growth on serial imaging Multiple if not disease related CT imaging: solid, complex Bosniak 2F, 3, 4, capsular invasion and/or enlarged lymph nodes ...
... Nodule size > 4 cm Nodule growth on serial imaging Multiple if not disease related CT imaging: solid, complex Bosniak 2F, 3, 4, capsular invasion and/or enlarged lymph nodes ...
Unit 7_Endocrine System
... Small amounts are made throughout life Mostly androgens (male sex hormones/ testosterone) are made but some estrogens (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
... Small amounts are made throughout life Mostly androgens (male sex hormones/ testosterone) are made but some estrogens (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
File - Mrs. Riggs Online
... This results in the glucose level of the blood dropping, which then triggers the pancreas to switch off the release of insulin. The problem in people with diabetes is that either they don’t produce enough insulin, or the insulin they do produce doesn’t work properly, or their cells don’t respond pro ...
... This results in the glucose level of the blood dropping, which then triggers the pancreas to switch off the release of insulin. The problem in people with diabetes is that either they don’t produce enough insulin, or the insulin they do produce doesn’t work properly, or their cells don’t respond pro ...
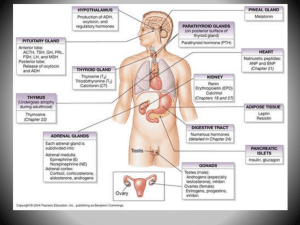
Glands of the Endocrine System
... Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Stimulation: Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from hypothalamus Target Cell: Adrenal cortex Action: Increase adrenal cortex secretions ...
... Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Stimulation: Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from hypothalamus Target Cell: Adrenal cortex Action: Increase adrenal cortex secretions ...
Physiology Lecture 2
... ● The adrenal cortex responds to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which is secreted by the anterior pituitary. ● Stress causes the hypothalamus to secrete ACTH-releasing hormone. ACTH then stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce the steroid hormone cortisol and aldosterone. ...
... ● The adrenal cortex responds to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which is secreted by the anterior pituitary. ● Stress causes the hypothalamus to secrete ACTH-releasing hormone. ACTH then stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce the steroid hormone cortisol and aldosterone. ...
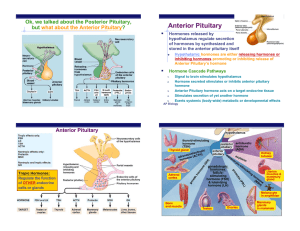
Anterior Pituitary
... Promote glucose synthesis from noncarbohydrate sources like proteins Cortisol causes skeletal muscle to breakdown muscle proteins Anti-inflammatory effect as they suppress parts of immune system ...
... Promote glucose synthesis from noncarbohydrate sources like proteins Cortisol causes skeletal muscle to breakdown muscle proteins Anti-inflammatory effect as they suppress parts of immune system ...
Endocrine System
... – two hormones acting together for greater effect ex. estrogen & LH are both needed for oocyte production ...
... – two hormones acting together for greater effect ex. estrogen & LH are both needed for oocyte production ...
The Endocrine System
... Testosterone – responsible for development of primary and secondary sex characteristics (primary – reproductive organs; ...
... Testosterone – responsible for development of primary and secondary sex characteristics (primary – reproductive organs; ...
Sheehan`s syndrome with recurrent hyponatremia and anemia: A
... clinical finding in the case was HN that is a common electrolytic abnormality, occurring in 33% to 69% of all cases with SS (8). The etiologic factors of HN in the present case were volume depletion, cortisol deficiency and hypothyroidism. In SS patients, HN responds to combined saline (NaCl), hydro ...
... clinical finding in the case was HN that is a common electrolytic abnormality, occurring in 33% to 69% of all cases with SS (8). The etiologic factors of HN in the present case were volume depletion, cortisol deficiency and hypothyroidism. In SS patients, HN responds to combined saline (NaCl), hydro ...
Natural Hormone Replacement Therapy
... among the first drugs to be patented. “HRT”= alien molecules with hormone effects ...
... among the first drugs to be patented. “HRT”= alien molecules with hormone effects ...