J Comp Physiol A (1993) 173:143-149
... the tip of the individual photoreceptor cell is not equivalent with the image forming ray path. At the tip of photoreceptors the optical acceptance region is particularly large in the part of the retina under the middle of the lens (Fig. 4a). lt is relatively small in the retinal region below the ed ...
... the tip of the individual photoreceptor cell is not equivalent with the image forming ray path. At the tip of photoreceptors the optical acceptance region is particularly large in the part of the retina under the middle of the lens (Fig. 4a). lt is relatively small in the retinal region below the ed ...
Assessment of optical systems by means of point
... of the wavelength of the light. Interferometric methods are mostly used for this purpose. Although the achievable precision is very high, these methods need refined and delicate optical set-ups and, in practice, special laser sources to achieve sufficient signal-to-noise ratio. When a measurement at ...
... of the wavelength of the light. Interferometric methods are mostly used for this purpose. Although the achievable precision is very high, these methods need refined and delicate optical set-ups and, in practice, special laser sources to achieve sufficient signal-to-noise ratio. When a measurement at ...
Asphere Metrology
... The talysurf must measure through the axis of rotation; profiles are normally measured and provided at 0º and 90º on axis, but if more data is desired they can also be measured in other places, at 45º on axis for example. Optimax also has new software available to combine multiple measurements from ...
... The talysurf must measure through the axis of rotation; profiles are normally measured and provided at 0º and 90º on axis, but if more data is desired they can also be measured in other places, at 45º on axis for example. Optimax also has new software available to combine multiple measurements from ...
Fresnel Diffraction Geometrical optics… …light can`t turn a corner. I
... - wavelets propagate isotropically—in forward and reverse directions - to use the Huygens approach, modify amplitude of wavefront as a function of q: ...
... - wavelets propagate isotropically—in forward and reverse directions - to use the Huygens approach, modify amplitude of wavefront as a function of q: ...
Lecture Note No. 3 Reflection and Refraction (Sections 4.3 to 4.8)
... Ferma’s Principle … The beam path between two points takes one that needs the least travel time, or shortest optical path length (OPL ns ds n j s j ). The resulting travel time is b ...
... Ferma’s Principle … The beam path between two points takes one that needs the least travel time, or shortest optical path length (OPL ns ds n j s j ). The resulting travel time is b ...
1.5 MB
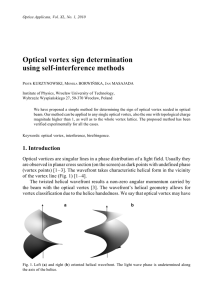
... line the positive and negative vortices can be observed while intersecting with the plane Σ. Here the single well defined singular line can be observed as carrying both the positive and negative topological charges. For the monochromatic waves propagating in a well defined direction the topological ...
... line the positive and negative vortices can be observed while intersecting with the plane Σ. Here the single well defined singular line can be observed as carrying both the positive and negative topological charges. For the monochromatic waves propagating in a well defined direction the topological ...
Digital Fourier Microscopy for Soft Matter Dynamics
... G ⇠ [nP a, kP a], which is way smaller than the ones characterising typical solids (G ⇠ 10 1000 GP a), accounting for the softness of these materials. The study of materials with length scales varying in such a wide range requires the combination of several experimental methods, including microscopy ...
... G ⇠ [nP a, kP a], which is way smaller than the ones characterising typical solids (G ⇠ 10 1000 GP a), accounting for the softness of these materials. The study of materials with length scales varying in such a wide range requires the combination of several experimental methods, including microscopy ...
Quantitative Phase Imaging
... be predicted with certainty. In other words, unlike in the case of plane waves, we cannot find a function f(r, t) that prescribes the field at each point in space and each moment in time. Instead, we describe the source as emitting a random signal, s(r, t) (Figure 2). Knowledge about the random so ...
... be predicted with certainty. In other words, unlike in the case of plane waves, we cannot find a function f(r, t) that prescribes the field at each point in space and each moment in time. Instead, we describe the source as emitting a random signal, s(r, t) (Figure 2). Knowledge about the random so ...
IMPORTANT FEATURES FOR A RIGHT - pi
... the intensity distribution of a laser beam is solved by so called beam shaping optics1. Today there are available many optical systems realizing various beam shaping techniques: truncation of a beam by an aperture or attenuation by an apodizing filters, integration systems based on arrays of microle ...
... the intensity distribution of a laser beam is solved by so called beam shaping optics1. Today there are available many optical systems realizing various beam shaping techniques: truncation of a beam by an aperture or attenuation by an apodizing filters, integration systems based on arrays of microle ...
Fabry-Perot Interferometer
... • Three pairs of mirrors are provided, two spherical sets with radii of curvature r of 75 mm and 100 mm, respectively; and one set of plane mirrors. The reflectivity of the mirrors is 96% for each set. Please, do not touch the mirror surfaces! The coatings are extremely damageable and expensive. Han ...
... • Three pairs of mirrors are provided, two spherical sets with radii of curvature r of 75 mm and 100 mm, respectively; and one set of plane mirrors. The reflectivity of the mirrors is 96% for each set. Please, do not touch the mirror surfaces! The coatings are extremely damageable and expensive. Han ...
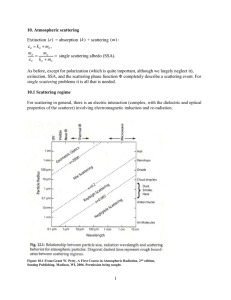
9 Exact Scattering and Absorption by Spheres: Lorenz
... mie(m, x) computes Qext, Qsca, Qabs, Qb, g=, for non-magnetic spheres
mie2(eps1, mu1, x) computes Qext, Qsca, Qabs, Qb, , for magnetic spheres
miecoated(m1,m2,x,y,opt) computes Qext, Qsca, Qabs, Qb, , for non-magnetic, coated spheres for size
parameters x and y, of core an ...
... mie(m, x) computes Qext, Qsca, Qabs, Qb, g=
11: Waves and Imaging
... zero when the string frequencies are equal. Acoustic beats may be thought of as interference of the summed oscillations in time. We also could consider this relationship in a broader sense. If the sinusoids are considered to be functions of the independent variable (coordinate) t, the phase angles o ...
... zero when the string frequencies are equal. Acoustic beats may be thought of as interference of the summed oscillations in time. We also could consider this relationship in a broader sense. If the sinusoids are considered to be functions of the independent variable (coordinate) t, the phase angles o ...
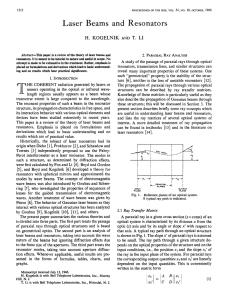
Kogelnik and Li
... Schwering [7]. The present discussion followsan analysis given in [ 111. 3.1 Approximate Solution of the Wave Equation Laser beams are similar in many respects to plane waves; however, their intensity distributions are not uniform, but are concentrated near the axis of propagation and their phase fr ...
... Schwering [7]. The present discussion followsan analysis given in [ 111. 3.1 Approximate Solution of the Wave Equation Laser beams are similar in many respects to plane waves; however, their intensity distributions are not uniform, but are concentrated near the axis of propagation and their phase fr ...
Canonical and singular propagation of ultrashort pulses in a
... and z0 is the shortest distance (usually zNL or zdiff over which E0 changes. The nondimensional coefficients B and A describe how the real and imaginary parts of the linear susceptibility deviate from constant values. The operator δ 2 is the Laplacian ∂2 /∂x2 + ∂2 /∂y 2 = ∂2 /∂r 2 + (1/r)(∂/∂r) if the ...
... and z0 is the shortest distance (usually zNL or zdiff over which E0 changes. The nondimensional coefficients B and A describe how the real and imaginary parts of the linear susceptibility deviate from constant values. The operator δ 2 is the Laplacian ∂2 /∂x2 + ∂2 /∂y 2 = ∂2 /∂r 2 + (1/r)(∂/∂r) if the ...
Excitation of a one-dimensional evanescent wave by conical edge
... To measure the interaction of a surface plasmon and a 90◦ metal corner, We have developed a far-field excitation/detection schemes for exciting and characterizing surface plasmon running in metal surfaces. By use of high-numerical aperture (N.A.) objectives (N.A=1.49), photons incident from the glas ...
... To measure the interaction of a surface plasmon and a 90◦ metal corner, We have developed a far-field excitation/detection schemes for exciting and characterizing surface plasmon running in metal surfaces. By use of high-numerical aperture (N.A.) objectives (N.A=1.49), photons incident from the glas ...