Imaging properties of supercritical angle
... A fundamental goal of physical optics is the characterization of the imaging properties of a given optical system. When dealing with imaging of non-coherent fluorescent sources, this is equivalent to calculating the image of single dipole emitters as a function of their position in sample space. For ...
... A fundamental goal of physical optics is the characterization of the imaging properties of a given optical system. When dealing with imaging of non-coherent fluorescent sources, this is equivalent to calculating the image of single dipole emitters as a function of their position in sample space. For ...
Utilizing a 4-F Fourier Optical System to Learn More About Image
... attempted to test what would happen to images if we applied differently shaped filters to the Fourier plane. We decided to experiment with two more shapes: a triangle and a square. To do this for a high-pass filter, we drew a small triangle on a transparent film and a small square on another film. W ...
... attempted to test what would happen to images if we applied differently shaped filters to the Fourier plane. We decided to experiment with two more shapes: a triangle and a square. To do this for a high-pass filter, we drew a small triangle on a transparent film and a small square on another film. W ...
waves - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... that occur in a given time) Hertz (Hz) (# of vibrations per second) High frequency waves produce waves with short periods and short wavelengths Period (T) (the time it takes for one wave cycle to pass) Seconds (s) The lower the frequency, the longer the period ...
... that occur in a given time) Hertz (Hz) (# of vibrations per second) High frequency waves produce waves with short periods and short wavelengths Period (T) (the time it takes for one wave cycle to pass) Seconds (s) The lower the frequency, the longer the period ...
VII-I
... • If an ideal mirror is stroked by rays coming parallel with the principal axis the rays either focus in the focal point – in the case of concave mirrors or they seem to come from a virtual focal point behind the mirror, if the mirror is convex. • Optical properties of ideal mirror are described by ...
... • If an ideal mirror is stroked by rays coming parallel with the principal axis the rays either focus in the focal point – in the case of concave mirrors or they seem to come from a virtual focal point behind the mirror, if the mirror is convex. • Optical properties of ideal mirror are described by ...
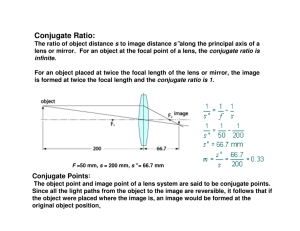
Conjugate Ratio:
... The first approximation we can make is to replace all sine functions with their arguments (i.e., replace sin θ 1 with θ 1 itself and so on). This is called first-order or paraxial theory because only the first terms of the sine expansions are used. Design of any optical system starts with this appro ...
... The first approximation we can make is to replace all sine functions with their arguments (i.e., replace sin θ 1 with θ 1 itself and so on). This is called first-order or paraxial theory because only the first terms of the sine expansions are used. Design of any optical system starts with this appro ...
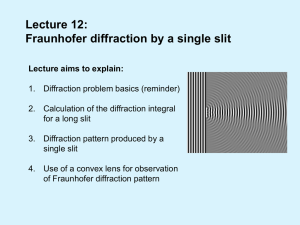
Chapter 5: Geometrical Optics
... Finding an image using ray diagrams: Three key rays in locating an image point: 1) Ray through the optical center: a straight line. 2) Ray parallel to the optical axis: emerging passing through the focal point. 3) Ray passing through the focal point: emerging parallel to the optical axis. ...
... Finding an image using ray diagrams: Three key rays in locating an image point: 1) Ray through the optical center: a straight line. 2) Ray parallel to the optical axis: emerging passing through the focal point. 3) Ray passing through the focal point: emerging parallel to the optical axis. ...
RF Component Definition - Center for Simulation of RF Wave
... functions, (2) a wave solver incorporating this non-Maxwellian conductivity, (3) the quasilinear operator that drives the non-thermal distribution, and (4) a Fokker-Planck solver to advance the distribution function. Solution of the Fokker-Planck equation is not considered part of the RF component, ...
... functions, (2) a wave solver incorporating this non-Maxwellian conductivity, (3) the quasilinear operator that drives the non-thermal distribution, and (4) a Fokker-Planck solver to advance the distribution function. Solution of the Fokker-Planck equation is not considered part of the RF component, ...
waves - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... that occur in a given time) Hertz (Hz) (# of vibrations per second) High frequency waves produce waves with short periods and short wavelengths Period (P) (the time it takes for one wave cycle to pass) Seconds (s) The lower the frequency, the longer the period ...
... that occur in a given time) Hertz (Hz) (# of vibrations per second) High frequency waves produce waves with short periods and short wavelengths Period (P) (the time it takes for one wave cycle to pass) Seconds (s) The lower the frequency, the longer the period ...
[pdf]
... surface. Using Eq. (5), it is now possible to transform Eq. (3) into an integral equation, the solution of which will provide one with a physical picture of the interaction of the diffuse photon density wave with the turbid media. The basic interaction of light with the molecules of the turbid media ...
... surface. Using Eq. (5), it is now possible to transform Eq. (3) into an integral equation, the solution of which will provide one with a physical picture of the interaction of the diffuse photon density wave with the turbid media. The basic interaction of light with the molecules of the turbid media ...
LAB 3 - SPATIAL COHERENCE AND OPTICAL IMAGING
... distance ~1m from the slits. You will need to expand the HeNe beam in some manner before impinging on the slits, similar to the previous labs. Be sure to record the distance ...
... distance ~1m from the slits. You will need to expand the HeNe beam in some manner before impinging on the slits, similar to the previous labs. Be sure to record the distance ...
6.1. Gabor`s (In-line) Holography. In 1948, Dennis Gabor introduced
... The advancement of holography, from Gabor’s initial work to the more practical implementation using the off-axis method is well captured by Adolf W. Lohmann [3]: “To a large extent the success of holography is associated with the invention of the off-axis reference hologram by Emmett Leith and Juris ...
... The advancement of holography, from Gabor’s initial work to the more practical implementation using the off-axis method is well captured by Adolf W. Lohmann [3]: “To a large extent the success of holography is associated with the invention of the off-axis reference hologram by Emmett Leith and Juris ...
IQSE Banner News Page
... scattered light integrated over the 2π steradians of backscatter solid angle for a small length along the incident propagation direction. The most common solution is to measure the volume scattering coefficient at a single angle and estimate bb assuming that the shape of the volume scattering functi ...
... scattered light integrated over the 2π steradians of backscatter solid angle for a small length along the incident propagation direction. The most common solution is to measure the volume scattering coefficient at a single angle and estimate bb assuming that the shape of the volume scattering functi ...

















![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852277_1-2045a3551aa6b77e10f6e1bfc991b19e-300x300.png)



