
12. confocal microscopy.
... In both cases, the out of focus light is rejected by the pinhole in front of the detector, which is placed at a plane conjugate to the illumination plane. The image reconstruction is performed either by scanning the sample or the specimen. Of course, scanning the beam can be made much faster by usin ...
... In both cases, the out of focus light is rejected by the pinhole in front of the detector, which is placed at a plane conjugate to the illumination plane. The image reconstruction is performed either by scanning the sample or the specimen. Of course, scanning the beam can be made much faster by usin ...
Resolving the wave vector in negative refractive index media
... negative refractive media and amplification for positive refractive media. Again we choose the positive square root, and we have only evanescently decaying waves in the semi-infinite medium. Region 4: 3 / 4 ⬍ Arg共kz兲 ⬍ corresponding to 3 / 2 ⬍ Arg共kz2兲 ⬍ 2. Now we move into the second Riemann s ...
... negative refractive media and amplification for positive refractive media. Again we choose the positive square root, and we have only evanescently decaying waves in the semi-infinite medium. Region 4: 3 / 4 ⬍ Arg共kz兲 ⬍ corresponding to 3 / 2 ⬍ Arg共kz2兲 ⬍ 2. Now we move into the second Riemann s ...
Isotropic Diffraction-Limited Focusing Using a Single Objective Lens
... imaging, lithography, data storage, or particle manipulation, the problem of focusing light beams into subwavelength volumes has become a major challenge. Numerous studies have been devoted to the development of novel lenses [1,2] in conjunction (or not) with beam shaping [3–6] that permit one to re ...
... imaging, lithography, data storage, or particle manipulation, the problem of focusing light beams into subwavelength volumes has become a major challenge. Numerous studies have been devoted to the development of novel lenses [1,2] in conjunction (or not) with beam shaping [3–6] that permit one to re ...
Leaving Cert Physics Notes by Mary Singleton
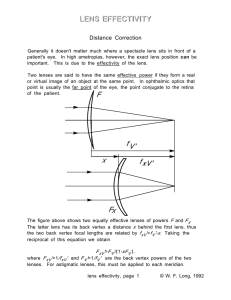
... Note: the object is always outside the focus of the eye. Hence the imageformed on the retina is always real and inverted. The brain translates this information into an image that is the right way up. The eye needs to be able to focus on both distant objects and on nearby objects. It does this by cha ...
... Note: the object is always outside the focus of the eye. Hence the imageformed on the retina is always real and inverted. The brain translates this information into an image that is the right way up. The eye needs to be able to focus on both distant objects and on nearby objects. It does this by cha ...
Intuitive explanation of the phase anomaly of focused light beams
... two wave fronts AB and BE are symmetrically located with respect to the beam waist at z = 0. According to geometrical optics the optical path length between wave front AB and wave front BE is given by the distance along the straight line BE. In a sense, diffraction causes the light to propagate alon ...
... two wave fronts AB and BE are symmetrically located with respect to the beam waist at z = 0. According to geometrical optics the optical path length between wave front AB and wave front BE is given by the distance along the straight line BE. In a sense, diffraction causes the light to propagate alon ...
OPTION.physics new
... output of battery is led to the inverted circuit Through switching S-S1 .The output of the inverter, is connected to the electric supply line. In the events of mains power failure, the inverter circuit may be automatically switched on by automatic change over circuit a and 220V,50HZ and 220V,50Hz su ...
... output of battery is led to the inverted circuit Through switching S-S1 .The output of the inverter, is connected to the electric supply line. In the events of mains power failure, the inverter circuit may be automatically switched on by automatic change over circuit a and 220V,50HZ and 220V,50Hz su ...
Abstract, Introduction, Conclusions and References
... analysis of the even-phase optimum quadruplicator, by using the electromagnetic theory of gratings, is presented in Sect. 3. Such a treatment of the problem allows us, for example, to understand the operational limits of the quadruplicator, to study its angular response, or to find solutions that are ...
... analysis of the even-phase optimum quadruplicator, by using the electromagnetic theory of gratings, is presented in Sect. 3. Such a treatment of the problem allows us, for example, to understand the operational limits of the quadruplicator, to study its angular response, or to find solutions that are ...
P2SF: Physically-based Point Spread Function for
... the PSF. The number of sample for the pupil function (NPUPIL) is, at least, 2 times NPSF to satisfy the Nyquist limit. In addition, the NPSF has to be a multiple of 2 in order to exploit the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). 3. Result and discussion P2SF has been implemented in MATLAB code and tested on ...
... the PSF. The number of sample for the pupil function (NPUPIL) is, at least, 2 times NPSF to satisfy the Nyquist limit. In addition, the NPSF has to be a multiple of 2 in order to exploit the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). 3. Result and discussion P2SF has been implemented in MATLAB code and tested on ...
Lecture 35: Holography.
... View what we would have seen if present at the original scene through the window defined by the hologram Provides depth perception and parallax ...
... View what we would have seen if present at the original scene through the window defined by the hologram Provides depth perception and parallax ...
Reflection and critical angle
... Now, if we take the plane wave solution to the wave equation, we can determine what happens when a wave strikes a dielectric interface. We know from our discussion on ray optics that when a ray hits a mirror, the angle of reflection (with respect to the normal) equals the angle of incidence. Also, we ...
... Now, if we take the plane wave solution to the wave equation, we can determine what happens when a wave strikes a dielectric interface. We know from our discussion on ray optics that when a ray hits a mirror, the angle of reflection (with respect to the normal) equals the angle of incidence. Also, we ...
Physics
... Internal Assessment: 10 Time: 3 Hours Note: 1. The syllabus is divided into 4 units. 9 questions will be set. 2. Question no 1 will be compulsory, it contains 6 parts (form all the four units) and answer should be brief but not in yes / no. 3. Four more questions are to be attempted, selecting one q ...
... Internal Assessment: 10 Time: 3 Hours Note: 1. The syllabus is divided into 4 units. 9 questions will be set. 2. Question no 1 will be compulsory, it contains 6 parts (form all the four units) and answer should be brief but not in yes / no. 3. Four more questions are to be attempted, selecting one q ...
Lecture 11
... what this is saying is that, in some sense, wave phenomena are absent in the paraxial approximation. As we will see, this transformation rule applies in more general situations as long as the paraxial approximation holds. But let痴 focus on the Gaussian beam for concreteness. The Gaussian beam stays ...
... what this is saying is that, in some sense, wave phenomena are absent in the paraxial approximation. As we will see, this transformation rule applies in more general situations as long as the paraxial approximation holds. But let痴 focus on the Gaussian beam for concreteness. The Gaussian beam stays ...






















![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852282_1-34a75f388cb1d60fa5a2254e9305255e-300x300.png)