DNA mutations 11.3 notes
... –EX. When you change one letter in a sentence: THE DOG BIT THE CAT. THE DOG BIT THE CAR. ...
... –EX. When you change one letter in a sentence: THE DOG BIT THE CAT. THE DOG BIT THE CAR. ...
Salmonella typhimurium
... • Some alleles directly cause specific traits, such as (in humans) rare genetic diseases e.g. Cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell anaemia; (in bacteria) ability to grow on certain sugars • Many alleles contribute to many traits of an organism such as size, shape, intelligence, behaviour, and risk of gettin ...
... • Some alleles directly cause specific traits, such as (in humans) rare genetic diseases e.g. Cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell anaemia; (in bacteria) ability to grow on certain sugars • Many alleles contribute to many traits of an organism such as size, shape, intelligence, behaviour, and risk of gettin ...
5 Agents of Evolutionary Change
... = any movement of genes from one population to another • If new genes are brought in, it can create new genetic variation • Can make populations more similar to each other • Example: If all red haired people left Scotland, the next generation would likely have very few people with this trait. The Sc ...
... = any movement of genes from one population to another • If new genes are brought in, it can create new genetic variation • Can make populations more similar to each other • Example: If all red haired people left Scotland, the next generation would likely have very few people with this trait. The Sc ...
Unit 8 Molecular Genetics: Chp 12 Mutations Notes PPT
... • Some proteins carry out functions within the cells of an organism. • Other proteins are exported out of the cell for other purposes. ...
... • Some proteins carry out functions within the cells of an organism. • Other proteins are exported out of the cell for other purposes. ...
Null hypotheses in evolutionary biology
... The neutral theory of molecular evolution Motoo Kimura (1968) High levels of polymorphism (variation) in protein and DNA sequences among individuals and species are difficult to reconcile with mutation-selection equilibrium (Ch 5.4) Most mutations affecting fitness are deleterious, hence quickly eli ...
... The neutral theory of molecular evolution Motoo Kimura (1968) High levels of polymorphism (variation) in protein and DNA sequences among individuals and species are difficult to reconcile with mutation-selection equilibrium (Ch 5.4) Most mutations affecting fitness are deleterious, hence quickly eli ...
Mutations - SchneiderSBI4U
... Nucleotide mutations occur when 1-4 nucleotides are altered, added or removed as a result of damage or errors in replication Transpositions occur when entire sections of DNA “jump” to a different location in the DNA, ...
... Nucleotide mutations occur when 1-4 nucleotides are altered, added or removed as a result of damage or errors in replication Transpositions occur when entire sections of DNA “jump” to a different location in the DNA, ...
Mutations - nimitz163
... • What happens if powerful radiation, such as gamma radiation, hits the DNA of a nonreproductive cell, a cell of the body such as in skin, muscle, or bone? • If the cell’s DNA is changed, this mutation would not be passed on to offspring. • However, the mutation may cause problems for the individual ...
... • What happens if powerful radiation, such as gamma radiation, hits the DNA of a nonreproductive cell, a cell of the body such as in skin, muscle, or bone? • If the cell’s DNA is changed, this mutation would not be passed on to offspring. • However, the mutation may cause problems for the individual ...
What are mutations and how do they affect the production
... The enzymes responsible for matching up the nucleotide bases can match the ______________ bases together, ___________ a base out, or __________ an extra base. This occurs during DNA ______________ ...
... The enzymes responsible for matching up the nucleotide bases can match the ______________ bases together, ___________ a base out, or __________ an extra base. This occurs during DNA ______________ ...
lecture 2: biological diversity in organisms
... it from the external environment; nuclear membrane protects the DNA…. • Adaptability: is essential to survival and creating the diversity of life that exists occur via mutations: • A mutation is a change, mostly permanent, to the DNA and can be classified into 2 types chromosomal mutation and point ...
... it from the external environment; nuclear membrane protects the DNA…. • Adaptability: is essential to survival and creating the diversity of life that exists occur via mutations: • A mutation is a change, mostly permanent, to the DNA and can be classified into 2 types chromosomal mutation and point ...
The origin of genetic variation
... II. What is a mutation??? -new variant of DNA that is different from both parents -deleterious alleles in population are often referred to as mutations Variation at third position is much greater than at other two Transitions are more common than transversions because DNA DNA repair enzymes can reco ...
... II. What is a mutation??? -new variant of DNA that is different from both parents -deleterious alleles in population are often referred to as mutations Variation at third position is much greater than at other two Transitions are more common than transversions because DNA DNA repair enzymes can reco ...
Mitochondrial DNA mutations affect male and
... within the mitochondria to affect longevity. "We identified genetic affects that could be pinned down to another core mitochondrial gene. With this gene, flies that produce lots of this protein suffer from shorter longevity – but only if they are male," Dr Morrow said. Dr Damian Dowling suggested th ...
... within the mitochondria to affect longevity. "We identified genetic affects that could be pinned down to another core mitochondrial gene. With this gene, flies that produce lots of this protein suffer from shorter longevity – but only if they are male," Dr Morrow said. Dr Damian Dowling suggested th ...
Ch 13 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Small mutations in DNA can cause huge changes in the proteins that are synthesized. Similarly, small changes in a word can dramatically alter its ...
... Small mutations in DNA can cause huge changes in the proteins that are synthesized. Similarly, small changes in a word can dramatically alter its ...
13.3_Mutations
... Small mutations in DNA can cause huge changes in the proteins that are synthesized. Similarly, small changes in a word can dramatically alter its ...
... Small mutations in DNA can cause huge changes in the proteins that are synthesized. Similarly, small changes in a word can dramatically alter its ...
Genetic Mutations
... It is caused by a number of different point mutations in the CFTR gene, which codes for a transmembrane protein that acts as an ion pump. ...
... It is caused by a number of different point mutations in the CFTR gene, which codes for a transmembrane protein that acts as an ion pump. ...
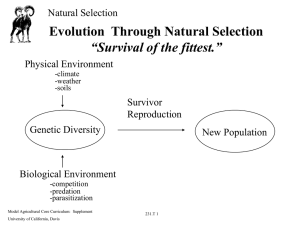
Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.”
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
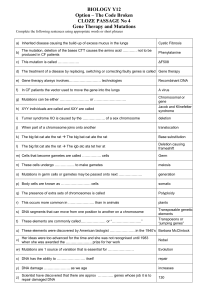
Cloze passage 4
... Gene Therapy and Mutations Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) Inherited disease causing the build-up of excess mucus in the lungs ...
... Gene Therapy and Mutations Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) Inherited disease causing the build-up of excess mucus in the lungs ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.