What causes gene mutations?
... Most mutations happen when the cell makes errors as it copies its genes during interphase. Each time one of your cells divides, it must copy around 6,000 million letters of DNA code. Very rarely, mistakes are made, causing mutations. ...
... Most mutations happen when the cell makes errors as it copies its genes during interphase. Each time one of your cells divides, it must copy around 6,000 million letters of DNA code. Very rarely, mistakes are made, causing mutations. ...
Mutation Notes - West Branch Schools
... Types of Mutations and Resulting Phenotypic Changes Deletions - A large section of a chromosome can be deleted resulting in the loss of a number of genes. •Ex:Cystic fibrosis-characterized by abnormally thick mucus in the lungs, intestines, and pancreas ...
... Types of Mutations and Resulting Phenotypic Changes Deletions - A large section of a chromosome can be deleted resulting in the loss of a number of genes. •Ex:Cystic fibrosis-characterized by abnormally thick mucus in the lungs, intestines, and pancreas ...
Genetic Variation Mutations
... There are some sorts of changes that a single mutation, or even a lot of mutations, could not cause. Neither mutations nor wishful thinking will make pigs have wings; only pop culture could have created Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles — mutations could not have done it. ...
... There are some sorts of changes that a single mutation, or even a lot of mutations, could not cause. Neither mutations nor wishful thinking will make pigs have wings; only pop culture could have created Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles — mutations could not have done it. ...
VII. DNA/ GENES/ AND GENETICS • Describe the relationship
... Give examples of emerging biotechnologies. What modern technologies are currently being implemented to determine evolutionary relationships among species? How are viruses used to treat disease? How can over exposure to sunlight cause skin cancer? Describe the structure and function of the DNA molecu ...
... Give examples of emerging biotechnologies. What modern technologies are currently being implemented to determine evolutionary relationships among species? How are viruses used to treat disease? How can over exposure to sunlight cause skin cancer? Describe the structure and function of the DNA molecu ...
Mutations & Genetic Engineering
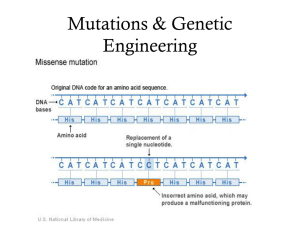
... – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense ...
... – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense ...
Unit 4 Resources - Schoolwires.net
... Complete the chart on the three chemical differences between DNA and RNA. Structure ...
... Complete the chart on the three chemical differences between DNA and RNA. Structure ...
Changes in Genetic Material your chromosomes are made up of
... mutations can often result in problems for the organism involved because it results in a change in DNA structure ...
... mutations can often result in problems for the organism involved because it results in a change in DNA structure ...
Genetics Guided Notes Use Chapter 12
... “Significance of Mutations” Explain one beneficial, one harmful, and one neutral significance of mutations Benefit- ...
... “Significance of Mutations” Explain one beneficial, one harmful, and one neutral significance of mutations Benefit- ...
Assume that a particular genetic condition in a mammalian species
... variety of levels of understanding of the effects of mutation were accepted as students could address the mutation as affecting DNA, transcription, translation, protein structure, or protein function. Students were also expected to demonstrate their understanding of modern techniques that could dete ...
... variety of levels of understanding of the effects of mutation were accepted as students could address the mutation as affecting DNA, transcription, translation, protein structure, or protein function. Students were also expected to demonstrate their understanding of modern techniques that could dete ...
Ch. 8 Mutations
... contains 3.2 billion base pairs. During DNA Replication, DNA makes an error every 100,000 base pairs and repairs it to an average of one error every 10 billion base pairs. That’s an average of 0.31 base pairs each time DNA is replicated. ...
... contains 3.2 billion base pairs. During DNA Replication, DNA makes an error every 100,000 base pairs and repairs it to an average of one error every 10 billion base pairs. That’s an average of 0.31 base pairs each time DNA is replicated. ...
Genetic Mutations and Biotechnology
... no effect at all. Some mutations in DNA can be repaired by enzymes that your cells contain before it becomes a problem. • Mutations in DNA could also result in death or for an individual having a genetic disorder. ...
... no effect at all. Some mutations in DNA can be repaired by enzymes that your cells contain before it becomes a problem. • Mutations in DNA could also result in death or for an individual having a genetic disorder. ...
People Pieces
... sequences. The genome is the entire DNA of an organism. In 2003, the Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed. This provided the actual sequence, or spelling, of the human DNA. Research is continuing to understand the actual details of the genes, as well as the function of each gene. Researchers are ...
... sequences. The genome is the entire DNA of an organism. In 2003, the Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed. This provided the actual sequence, or spelling, of the human DNA. Research is continuing to understand the actual details of the genes, as well as the function of each gene. Researchers are ...
Mutations - The Super Heroes of Biology
... • One nucleotide is replaced by another but it still codes for the same amino acid ...
... • One nucleotide is replaced by another but it still codes for the same amino acid ...
MUTATIONS
... • May lead to amino acid change – See animation • May not lead to any change (Silent Mutation) – Ex: DNA “CCC” is mutated into “CCG” » Same amino acid is created (glycine) ...
... • May lead to amino acid change – See animation • May not lead to any change (Silent Mutation) – Ex: DNA “CCC” is mutated into “CCG” » Same amino acid is created (glycine) ...
DNA Repair - College of Arts and Sciences at Lamar University
... -Mutations are inherited changes in the DNA sequence. They can result (i) from replication errors,(ii) from damage to the DNA, or (iii) from errors during repair of damage. Point mutations are the changes of a single base pair. Transitions are mutations in which one purine is substituted for another ...
... -Mutations are inherited changes in the DNA sequence. They can result (i) from replication errors,(ii) from damage to the DNA, or (iii) from errors during repair of damage. Point mutations are the changes of a single base pair. Transitions are mutations in which one purine is substituted for another ...
Transposons_&_DNA_Mutations
... Genetic characteristics of a population can change over time – “Evolution” ...
... Genetic characteristics of a population can change over time – “Evolution” ...
BSC 219
... May be determined under normal conditions May be determined under altered conditions May be determined in the presence of harmful chemicals Spontaneous Replication Errors Caused by mispairing through wobble Spontaneous Replication Errors Strand slippage Unequal crossing over Depurination: loss of pu ...
... May be determined under normal conditions May be determined under altered conditions May be determined in the presence of harmful chemicals Spontaneous Replication Errors Caused by mispairing through wobble Spontaneous Replication Errors Strand slippage Unequal crossing over Depurination: loss of pu ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.