Section 8.7 Mutations
... 2. Mutagens – Environmental factors that cause changes in DNA Examples: - Radiation - Chemicals in environment ...
... 2. Mutagens – Environmental factors that cause changes in DNA Examples: - Radiation - Chemicals in environment ...
Mutation
... A mutated gene can be passed on to every cell that develops from the cell with the mutated gene. If one cell with an altered gene divides and forms two cells, then both cells will have the mutated gene. Changes in mRNA or tRNA affect the protein formed but are not passed on when cells divide. ...
... A mutated gene can be passed on to every cell that develops from the cell with the mutated gene. If one cell with an altered gene divides and forms two cells, then both cells will have the mutated gene. Changes in mRNA or tRNA affect the protein formed but are not passed on when cells divide. ...
What is a mutation?
... • Missense : ANY mutation that changes the codon and makes a different amino acid in the protein • Nonsense : ANY mutation that changes a codon into one of the STOP codons • Silent : ANY mutation that causes no change in the protein and cannot be detected without sequencing the gene ...
... • Missense : ANY mutation that changes the codon and makes a different amino acid in the protein • Nonsense : ANY mutation that changes a codon into one of the STOP codons • Silent : ANY mutation that causes no change in the protein and cannot be detected without sequencing the gene ...
Microbial Overview: Physiology and Evolution
... • A mutation is any change in the proper nucleic acid sequence of a specific gene in a cell’s genome. It may result from a single base pair mismatch during DNA replication. • Mutation can create genetic diversity within a population; either beneficial, neutral, bad, or lethal. • Mutation could resul ...
... • A mutation is any change in the proper nucleic acid sequence of a specific gene in a cell’s genome. It may result from a single base pair mismatch during DNA replication. • Mutation can create genetic diversity within a population; either beneficial, neutral, bad, or lethal. • Mutation could resul ...
Notes Unit 4 Part 8
... errors in DNA provide the ______________ that is fundamental to the evolution of a species most mutations result in ___________ or the lack of normal development in an organism if the mutation occurs in ____________, birth defects can occur if the mutation occurs in ____________, cancer may ...
... errors in DNA provide the ______________ that is fundamental to the evolution of a species most mutations result in ___________ or the lack of normal development in an organism if the mutation occurs in ____________, birth defects can occur if the mutation occurs in ____________, cancer may ...
Grade 9 Science Ch 4 - Answers to Comprehensive Questions
... 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called "the control center of the cell"? Because the nucleus is responsible for controlling the functions of the cell. The info contained in the nucleus instructs your cells to produce or import all the materials they need to survive. 5. Why is DNA required in every c ...
... 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called "the control center of the cell"? Because the nucleus is responsible for controlling the functions of the cell. The info contained in the nucleus instructs your cells to produce or import all the materials they need to survive. 5. Why is DNA required in every c ...
2. The histogram below shows the total estimated new breast cancer
... *A mastectomy is the surgical removal of one or both breasts, either partially of fully. An oophorectomy is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. Please be sure to answer the following questions: 1. Describe how mutations lead to genetic variations. Mutations happen when your genetic code get ...
... *A mastectomy is the surgical removal of one or both breasts, either partially of fully. An oophorectomy is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. Please be sure to answer the following questions: 1. Describe how mutations lead to genetic variations. Mutations happen when your genetic code get ...
Mutation - Liberty Union High School District
... (Well, except the X-Men part) So, are mutations good, bad, neutral, or all of these? ...
... (Well, except the X-Men part) So, are mutations good, bad, neutral, or all of these? ...
Document
... Nucleotides (Gout, Lesh-Nyhan) De Novo Pathway Activated ribose (PRPP) + amino acids + ATP + CO2 +………. Nucleotides ...
... Nucleotides (Gout, Lesh-Nyhan) De Novo Pathway Activated ribose (PRPP) + amino acids + ATP + CO2 +………. Nucleotides ...
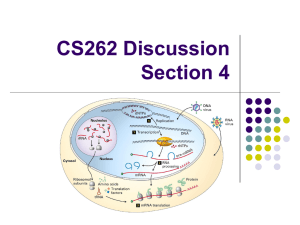
CS262 Discussion Section 4
... regions are classified according to their effect on the protein synthesized. ...
... regions are classified according to their effect on the protein synthesized. ...
flyer
... When time is of the utmost importance. GenomeScan knows that in genetic testing, sometimes every day counts. With Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) we find the mutations that cause the patients’ clinical features. From DNA to report letter in 12 to 14 days! ...
... When time is of the utmost importance. GenomeScan knows that in genetic testing, sometimes every day counts. With Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) we find the mutations that cause the patients’ clinical features. From DNA to report letter in 12 to 14 days! ...
Changes in DNA can produce variation
... • There is a large number of DNA bases in any organism that need to be copied • Errors can occur when DNA is copied or affected by environment – UV radiation – X-rays – Toxins ...
... • There is a large number of DNA bases in any organism that need to be copied • Errors can occur when DNA is copied or affected by environment – UV radiation – X-rays – Toxins ...
Mutations
... Each gene has a ~1/100,000 chance of mutating We all likely have several mutations in our DNA but most DNA is non-coding ...
... Each gene has a ~1/100,000 chance of mutating We all likely have several mutations in our DNA but most DNA is non-coding ...
Regulation of Gene Expression – Part III
... _____________________ in DNA The “change” can result in a) no effect on protein activity to b) complete inactivity A ____________________ is one that occurs in _______________ and can be passed to subsequent generations. A ____________________ is one that occurs in ___________—and therefore may only ...
... _____________________ in DNA The “change” can result in a) no effect on protein activity to b) complete inactivity A ____________________ is one that occurs in _______________ and can be passed to subsequent generations. A ____________________ is one that occurs in ___________—and therefore may only ...
MUTATIONS
... which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
... which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.