Mutation
... abnormally during embryonic development and the embryo begins to develop as conjoined twins, but later stops developing and leaves remaining developments of the disintegrated fetus attached to the body of the other. • The extra limbs and legs were the result of a genetic disease which would affect o ...
... abnormally during embryonic development and the embryo begins to develop as conjoined twins, but later stops developing and leaves remaining developments of the disintegrated fetus attached to the body of the other. • The extra limbs and legs were the result of a genetic disease which would affect o ...
13.3_201-204
... In a substitution, one base is changed to a different base, which may affect only a single amino acid and have no effect at all. In insertions and deletions, one base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. Insertions and deletions are called frameshift mutations because they shift the “re ...
... In a substitution, one base is changed to a different base, which may affect only a single amino acid and have no effect at all. In insertions and deletions, one base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. Insertions and deletions are called frameshift mutations because they shift the “re ...
13.3 Study Workbook
... In a substitution, one base is changed to a different base, which may affect only a single amino acid and have no effect at all. In insertions and deletions, one base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. Insertions and deletions are called frameshift mutations because they shift the “re ...
... In a substitution, one base is changed to a different base, which may affect only a single amino acid and have no effect at all. In insertions and deletions, one base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. Insertions and deletions are called frameshift mutations because they shift the “re ...
Mutations
... SC STANDARD B-4.9: The student will exemplify ways in which new characteristics are introduced into an organism or a population ...
... SC STANDARD B-4.9: The student will exemplify ways in which new characteristics are introduced into an organism or a population ...
Transcription andTranslation Flip Book
... might be altered. The incidence of gene mutations is relatively low due to the enzymes proofread action of _________ that _________ the replication DNA sequence after __________.There are two types of gene mutations: ...
... might be altered. The incidence of gene mutations is relatively low due to the enzymes proofread action of _________ that _________ the replication DNA sequence after __________.There are two types of gene mutations: ...
Introns and Exons - Mr. Dalton
... Types of Mutations • A frameshift mutation is a deletion or insertion of one or more nucleotides that changes the reading frame of the base sequence. • Deletions remove nucleotides. • Insertions add nucleotides. • A frameshift mutation can dramatically change how the codons in mRNA are read. • EX. ...
... Types of Mutations • A frameshift mutation is a deletion or insertion of one or more nucleotides that changes the reading frame of the base sequence. • Deletions remove nucleotides. • Insertions add nucleotides. • A frameshift mutation can dramatically change how the codons in mRNA are read. • EX. ...
Handout
... A mutation may be silent because…. – It occurs in a _________________________________________. – It may not affect protein ______________________ or the __________________________________________. ...
... A mutation may be silent because…. – It occurs in a _________________________________________. – It may not affect protein ______________________ or the __________________________________________. ...
Chapter 2
... A mutation in a gene affects only the protein coded by the mutant copy of the gene and does not affect the protein coded by any other allele. Failure of two mutations to complement (produce wild phenotype when they are present in trans configuration in a heterozygote means that they are part of the ...
... A mutation in a gene affects only the protein coded by the mutant copy of the gene and does not affect the protein coded by any other allele. Failure of two mutations to complement (produce wild phenotype when they are present in trans configuration in a heterozygote means that they are part of the ...
Mutations
... • Almost all mutations are neutral • Chemicals & UV radiation cause mutations • Many mutations are repaired by enzymes ...
... • Almost all mutations are neutral • Chemicals & UV radiation cause mutations • Many mutations are repaired by enzymes ...
DNA: The molecular basis of mutations
... proteins that are as useless as "hef atc ats at" is uninformative. There are other types of mutations as well, but this short list should give you an idea of the possibilities. ...
... proteins that are as useless as "hef atc ats at" is uninformative. There are other types of mutations as well, but this short list should give you an idea of the possibilities. ...
Chapter 34 Study Guide File
... 10. What is the difference between sickle-cell anemia and sickle-cell trait? ...
... 10. What is the difference between sickle-cell anemia and sickle-cell trait? ...
Mutations Website Assignment - Mercer Island School District
... 2. A DNA triplet is ACG which is transcribed into an mRNA codon UGC and causes the amino acid cysteine to be added to the protein in translation. Explain the effect of each of the following substitution mutations. Remember to determine what mRNA codon would be transcribed by each of the mutated DNA ...
... 2. A DNA triplet is ACG which is transcribed into an mRNA codon UGC and causes the amino acid cysteine to be added to the protein in translation. Explain the effect of each of the following substitution mutations. Remember to determine what mRNA codon would be transcribed by each of the mutated DNA ...
Chapter 12 Gene Mutation
... Early-Onset Alzheimer Disease 1. In one form of Alzheimer’s disease, a mutation in a receptor protein may lead to beta-amyloid buildup. 2. The gene for the protein, called presenilin 1, is found on chromosome 14. One Disorder or Several? 1. What is classified as a single disease phenotype may, in fa ...
... Early-Onset Alzheimer Disease 1. In one form of Alzheimer’s disease, a mutation in a receptor protein may lead to beta-amyloid buildup. 2. The gene for the protein, called presenilin 1, is found on chromosome 14. One Disorder or Several? 1. What is classified as a single disease phenotype may, in fa ...
7.1: Variations, Mutations, and Selective Advantage Learning Check:
... both biological parents. The number of possible combinations of genes that offspring inherit from their parents results in genetic variation among individuals within the population. ...
... both biological parents. The number of possible combinations of genes that offspring inherit from their parents results in genetic variation among individuals within the population. ...
17 - Genetic Mutation
... individual or the function of the cell. Mutations to somatic cells are not inherited by offspring. The reproductive process, either meiosis or mitosis, is not flawless. There are many opportunities for errors to occur in both processes. A list of genetic mutations is shown below. Chromosome Abnormal ...
... individual or the function of the cell. Mutations to somatic cells are not inherited by offspring. The reproductive process, either meiosis or mitosis, is not flawless. There are many opportunities for errors to occur in both processes. A list of genetic mutations is shown below. Chromosome Abnormal ...
Genetic Engineering
... individuals with similar characteristics • Keep desired characteristics of a line of organisms • The cross can bring together 2 recessive alleles for a genetic defect-BAD! ...
... individuals with similar characteristics • Keep desired characteristics of a line of organisms • The cross can bring together 2 recessive alleles for a genetic defect-BAD! ...
AP Biology
... 11. A protein-coding gene in a eukaryote has three introns. How many different proteins could theoretically be produced by alternative splicing of the pre-mRNA from this gene? ...
... 11. A protein-coding gene in a eukaryote has three introns. How many different proteins could theoretically be produced by alternative splicing of the pre-mRNA from this gene? ...
Review - Molecular and Cell Biology
... The origin of mutations most mutations are spontaneous and rare DNA repair mechanisms eliminate most mutations mutagens such as Xrays or chemicals like EMS can greatly increase the mutation rate, and are essential tools for experimental isolation of mutants Mutations can affect the DNA sequence of g ...
... The origin of mutations most mutations are spontaneous and rare DNA repair mechanisms eliminate most mutations mutagens such as Xrays or chemicals like EMS can greatly increase the mutation rate, and are essential tools for experimental isolation of mutants Mutations can affect the DNA sequence of g ...
Types of Genetic Mutations
... • Humans inherit 3 x 109 base pairs of DNA from each parent. Just considering single-base substitutions, this means that each cell has 6 billion (6 x 109) different base pairs that can be the target of a substitution. • Single-base substitutions are most apt to occur when DNA is being copied; for e ...
... • Humans inherit 3 x 109 base pairs of DNA from each parent. Just considering single-base substitutions, this means that each cell has 6 billion (6 x 109) different base pairs that can be the target of a substitution. • Single-base substitutions are most apt to occur when DNA is being copied; for e ...
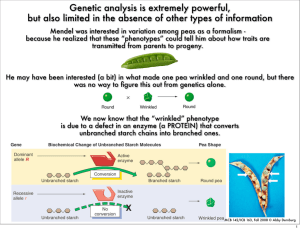
Genetic analysis is extremely powerful, but also limited in the
... and discovered the first mutagen: X-rays ...
... and discovered the first mutagen: X-rays ...
Carcinogenesis1
... molecules in every organism (amoebas to humans) • Genes (units of information) are the same in every cell of an organism, but expression of genes varies by cell/tissue • Conserved and variable regions of code ...
... molecules in every organism (amoebas to humans) • Genes (units of information) are the same in every cell of an organism, but expression of genes varies by cell/tissue • Conserved and variable regions of code ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.