F. Mutation and Repair 1. Background on DNA Mutations
... essential component of evolutionary change • Mutations that become part of the multicellular genome must occur in the cells of the germ line • Somatic mutations may or may not affect the individual but cannot affect the population • Low rates of mutation can result in high rates of evolution in sing ...
... essential component of evolutionary change • Mutations that become part of the multicellular genome must occur in the cells of the germ line • Somatic mutations may or may not affect the individual but cannot affect the population • Low rates of mutation can result in high rates of evolution in sing ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... 30. A person born with an inherited predisposition to cancer usually does not develop cancer until after A. B. C. D. ...
... 30. A person born with an inherited predisposition to cancer usually does not develop cancer until after A. B. C. D. ...
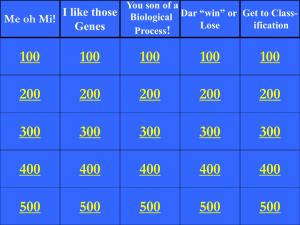
Me oh Mi!
... Name 3 things that can be used as DNA evidence that were used in the movie GATTACA ...
... Name 3 things that can be used as DNA evidence that were used in the movie GATTACA ...
Genetics
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
4.2 Mutation - WordPress.com
... kind – one from their mother and one from their father. If a person has one normal gene and one sickle gene, they are called a carrier and rarely feel the severe effects of sickle cell anemia. If a person has two sickle genes (one sickle gene from each carrier parent) then a person has only sickle c ...
... kind – one from their mother and one from their father. If a person has one normal gene and one sickle gene, they are called a carrier and rarely feel the severe effects of sickle cell anemia. If a person has two sickle genes (one sickle gene from each carrier parent) then a person has only sickle c ...
Mutations
... Think – pair - share • Which type(s) of mutation would have the most affect on an organism? • Insertion and deletion mutations have the most effect on an organism because they affect many amino acids and consequently the whole protein. ...
... Think – pair - share • Which type(s) of mutation would have the most affect on an organism? • Insertion and deletion mutations have the most effect on an organism because they affect many amino acids and consequently the whole protein. ...
Evolutionary Processes ()
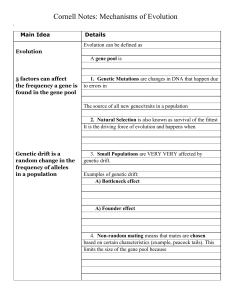
... • Can result from gene flow, non-random mating, genetic drift, mutation and natural selection. ...
... • Can result from gene flow, non-random mating, genetic drift, mutation and natural selection. ...
Bio 1 Unit Objectives Protein Synthesis Readings
... Exploring Life: Chapter 11 Online Activities ...
... Exploring Life: Chapter 11 Online Activities ...
Natural Selection and Specation
... gene that exist in frequencies different from other populations • Do not possess allele IB therefore cannot be B or AB blood groups • Isolation for over 50,000 years means limited gene flow • Increased genetic flow has lead this to change ...
... gene that exist in frequencies different from other populations • Do not possess allele IB therefore cannot be B or AB blood groups • Isolation for over 50,000 years means limited gene flow • Increased genetic flow has lead this to change ...
Slides-Brian_Charlesworth-Sex_and_molecular_evolution
... • Natural selection– differences in fitness (survival and reproductive success) between individuals with different genetic make-ups • Recombination– reshuffling of genetic material between the chromosomes derived from different parents • Genetic drift– random fluctuations in the frequencies of genet ...
... • Natural selection– differences in fitness (survival and reproductive success) between individuals with different genetic make-ups • Recombination– reshuffling of genetic material between the chromosomes derived from different parents • Genetic drift– random fluctuations in the frequencies of genet ...
View PDF
... or the color of their eyes, hair, or skin. Genes produce variation because the type or amount of the proteins they code for can vary from person to person. For example, skin color comes from a protein called melanin. The amount of melanin an individual produces affects the color of their skin. Given ...
... or the color of their eyes, hair, or skin. Genes produce variation because the type or amount of the proteins they code for can vary from person to person. For example, skin color comes from a protein called melanin. The amount of melanin an individual produces affects the color of their skin. Given ...
Keystone Review: Quiz 4
... cytoplasm. For this reason, most of its proteins are able to function in acidic conditions. This property distinguishes Acetoacter aceti proteins from those of most other organisms. Which characteristic does Acetobacter aceti most likely share with other organisms? a. The method that the organism us ...
... cytoplasm. For this reason, most of its proteins are able to function in acidic conditions. This property distinguishes Acetoacter aceti proteins from those of most other organisms. Which characteristic does Acetobacter aceti most likely share with other organisms? a. The method that the organism us ...
4 chapter_test_b 4 chapter_test_b
... Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used. ...
... Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used. ...
Phenotypic effects and variations in the genetic material (part 2)
... II. Mutation (or point mutation) They include variations at the DNA level. It is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence within a single gene of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA (DNA of plastids and mitochondria) or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage ...
... II. Mutation (or point mutation) They include variations at the DNA level. It is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence within a single gene of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA (DNA of plastids and mitochondria) or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage ...
Human Genetics
... Differentiation causes cells to differ in appearance and function - Controlled by variation in gene expression Stem cells are less specialized and can become many different cell types ...
... Differentiation causes cells to differ in appearance and function - Controlled by variation in gene expression Stem cells are less specialized and can become many different cell types ...
Summer 2007
... DNA/RNA, Protein Synthesis and Mutations - REVIEW I. Understand all vocabulary. II. Understand Cell Reproduction III. Understand the scientific process involved in establishing DNA as the heredity ...
... DNA/RNA, Protein Synthesis and Mutations - REVIEW I. Understand all vocabulary. II. Understand Cell Reproduction III. Understand the scientific process involved in establishing DNA as the heredity ...
Human Genome Project - College Heights Secondary School
... • Consider ethical, legal, and social issues associated with this research ...
... • Consider ethical, legal, and social issues associated with this research ...
Biotechnology Glow Genes
... Provides permanent markers that follow the cancerous cells as they grow or spread throughout the body. ...
... Provides permanent markers that follow the cancerous cells as they grow or spread throughout the body. ...
Could there be a Protective Gene?
... Hereditary dementia in Australian families: could there be a protective gene? William Brooks, Olivier Piguet, Hayley Bennett, G Anthony Broe Prince of Wales Medical Research Institute ...
... Hereditary dementia in Australian families: could there be a protective gene? William Brooks, Olivier Piguet, Hayley Bennett, G Anthony Broe Prince of Wales Medical Research Institute ...
G protein Mutations Causing Disease
... Somatic mutation of Gs alpha early in development Effects of activating MSH and gonadotrophin receptors evident ...
... Somatic mutation of Gs alpha early in development Effects of activating MSH and gonadotrophin receptors evident ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.