AS 90715 version 2 Describe the role of DNA in relation to gene
... Concepts and processes relating to gene expression include: the role of DNA in gene expression: selected from o nucleic acid structure and function o protein structure and function o the genetic code o DNA replication o protein synthesis (transcription, translation) allele interactions: selected ...
... Concepts and processes relating to gene expression include: the role of DNA in gene expression: selected from o nucleic acid structure and function o protein structure and function o the genetic code o DNA replication o protein synthesis (transcription, translation) allele interactions: selected ...
Prioritizing Regions of Candidate genes for efficient
... Consideration of parameters resulted in significantly higher discoveries per unit of effort Algorithm can be easily modified and expanded Most useful for large number of candidate genes in large number of patients Select best two or four regions in each candidate gene Screen all as initial screeni ...
... Consideration of parameters resulted in significantly higher discoveries per unit of effort Algorithm can be easily modified and expanded Most useful for large number of candidate genes in large number of patients Select best two or four regions in each candidate gene Screen all as initial screeni ...
Biology Final Exam
... 4. During DNA replication, complementary strands of DNA are made from the original DNA strands. Using this template (original strand of DNA) and the base-pairing rules, give the complementary strand: TACCCCGAGAGG 5. What would be the complementary sequence of nucleotides for an mRNA molecule on the ...
... 4. During DNA replication, complementary strands of DNA are made from the original DNA strands. Using this template (original strand of DNA) and the base-pairing rules, give the complementary strand: TACCCCGAGAGG 5. What would be the complementary sequence of nucleotides for an mRNA molecule on the ...
Mutations and Cancer Review Sheet Key
... HEB IGC ATA TET HER AT This results in a frame shift. Why would a deletion of 3 letters be less harmful? The rest of the sentence would still make sense. ...
... HEB IGC ATA TET HER AT This results in a frame shift. Why would a deletion of 3 letters be less harmful? The rest of the sentence would still make sense. ...
Document
... A gene is a heritable factor that consists of a length of DNA and influences a specific characteristic A gene occupies a specific position on a chromosome The various specific forms of a gene are alleles Alleles differ from each other by one or only a few bases New alleles are formed by mutation The ...
... A gene is a heritable factor that consists of a length of DNA and influences a specific characteristic A gene occupies a specific position on a chromosome The various specific forms of a gene are alleles Alleles differ from each other by one or only a few bases New alleles are formed by mutation The ...
Nucleic Acids DNA & RNA
... •Happens during the S phase of Interphase. •Ensures each daughter cells is an exact copy of the parent cell. •Assisted by enzymes called DNA polmerase. ...
... •Happens during the S phase of Interphase. •Ensures each daughter cells is an exact copy of the parent cell. •Assisted by enzymes called DNA polmerase. ...
Genetic Markers
... • Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes or in non-coding DNA may or may not affect phenotype • SNPs can cause Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) if in a restriction enzyme site • Tandem repeat sequences (or microsatellies), such as dinucleotides (CA)n, tri- and tetra-nucleot ...
... • Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes or in non-coding DNA may or may not affect phenotype • SNPs can cause Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) if in a restriction enzyme site • Tandem repeat sequences (or microsatellies), such as dinucleotides (CA)n, tri- and tetra-nucleot ...
13.3 Mutations
... few nucleotides are known as point mutations because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence. They generally occur during replication. – If a gene in one cell is altered, the alteration can be passed on to every cell that develops from the original one. – Point mutations include substitutio ...
... few nucleotides are known as point mutations because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence. They generally occur during replication. – If a gene in one cell is altered, the alteration can be passed on to every cell that develops from the original one. – Point mutations include substitutio ...
Genetics
... Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that organism. As a basis for understanding this concept: ...
... Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that organism. As a basis for understanding this concept: ...
13.3 Mutations
... few nucleotides are known as point mutations because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence. They generally occur during replication. – If a gene in one cell is altered, the alteration can be passed on to every cell that develops from the original one. – Point mutations include substitutio ...
... few nucleotides are known as point mutations because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence. They generally occur during replication. – If a gene in one cell is altered, the alteration can be passed on to every cell that develops from the original one. – Point mutations include substitutio ...
The making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation
... Dramatic changes in traits can occur through mutations in a small number of genes, or even a single gene. Different environments can provide different selective pressures on an organism’s morphology. In the stickleback, pelvic spines provide a selective advantage in environments with large predatory ...
... Dramatic changes in traits can occur through mutations in a small number of genes, or even a single gene. Different environments can provide different selective pressures on an organism’s morphology. In the stickleback, pelvic spines provide a selective advantage in environments with large predatory ...
point mutations - Plant Developmental Biology
... ... alloploidy (origin of wheat) ... meiotic nondysjunction and consequences ... Turner, Klinefelter, Down Syndromes ... deletion, inversion, translocation ...
... ... alloploidy (origin of wheat) ... meiotic nondysjunction and consequences ... Turner, Klinefelter, Down Syndromes ... deletion, inversion, translocation ...
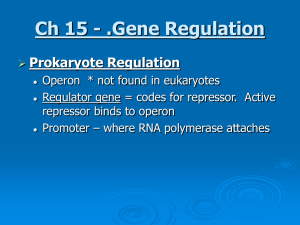
Regulatory genes
... • Binary fission – asexual (production of offspring from one parent) process for prokaryotic cell division • Each fission results in two daughter cells each with 1 copy of the original chromosome ...
... • Binary fission – asexual (production of offspring from one parent) process for prokaryotic cell division • Each fission results in two daughter cells each with 1 copy of the original chromosome ...
This is to serve as a general overview of important topics. I highly
... Euchromatin is in an “open” configuration is able to be transcribed Euchromatin has high rates of methylation Heterochromatin is able to be transcribed Heterochromatin is heavily methylated The majority of our genome is the heterochromatin state ...
... Euchromatin is in an “open” configuration is able to be transcribed Euchromatin has high rates of methylation Heterochromatin is able to be transcribed Heterochromatin is heavily methylated The majority of our genome is the heterochromatin state ...
LECTURE 8: Genetic dissection of biochemical pathways
... They proposed that ARG-E encodes the enzyme responsible for the first step, ARG-F encodes an enzyme for the second step, ARG-G for the third, and ARG-H for the fourth. Beadle and Tatum proposed “one gene, one enzyme”. For their work, they won the Nobel Prize. Their hypothesis was later revised to “o ...
... They proposed that ARG-E encodes the enzyme responsible for the first step, ARG-F encodes an enzyme for the second step, ARG-G for the third, and ARG-H for the fourth. Beadle and Tatum proposed “one gene, one enzyme”. For their work, they won the Nobel Prize. Their hypothesis was later revised to “o ...
Biological information
... Transcriptional control can be modified by the insertion of transposable elements (e.g. Alu sequences) or mutation. ...
... Transcriptional control can be modified by the insertion of transposable elements (e.g. Alu sequences) or mutation. ...
Press release - Humangenetik
... Markus Storbeck, postdoctor in Wirth’s lab, has analyzed sequence data of more than 20,000 genes of muscular atrophy patients and has identified so-called homozygous frameshift mutations in the PIEZO2 gene. This means that a short piece of sequence is either missing or inserted so that the language ...
... Markus Storbeck, postdoctor in Wirth’s lab, has analyzed sequence data of more than 20,000 genes of muscular atrophy patients and has identified so-called homozygous frameshift mutations in the PIEZO2 gene. This means that a short piece of sequence is either missing or inserted so that the language ...
NOTES: Darwin vs. Lamarck
... The giraffes with longer necks survive and pass their genes (for longer necks) on to their offspring…the process continues, and whole population ...
... The giraffes with longer necks survive and pass their genes (for longer necks) on to their offspring…the process continues, and whole population ...
name
... 8. HMS Beagle & The Galapagos Islands 9. Four main points of Darwin’s theory of Natural selection are? 10. Gradualism 11. Tracking changes (evidence of evolution) 12. homologous structures (p 468) 13. vestigial structures (466-467)14. analogous structures – Which evolutionary term is shown in the pi ...
... 8. HMS Beagle & The Galapagos Islands 9. Four main points of Darwin’s theory of Natural selection are? 10. Gradualism 11. Tracking changes (evidence of evolution) 12. homologous structures (p 468) 13. vestigial structures (466-467)14. analogous structures – Which evolutionary term is shown in the pi ...
Mutations - Warren County Schools
... changed from an 'a' to a 't'. This changes the codon from 'gag' to 'gtg' resulting in the 6th amino acid of the chain being changed from glutamic acid to valine. This apparently trivial alteration to the beta globin gene alters the quaternary structure of hemoglobin, which has a profound influence o ...
... changed from an 'a' to a 't'. This changes the codon from 'gag' to 'gtg' resulting in the 6th amino acid of the chain being changed from glutamic acid to valine. This apparently trivial alteration to the beta globin gene alters the quaternary structure of hemoglobin, which has a profound influence o ...
(HOM) genes. Antennapedia and Bithorax Complexes (WR
... that lies outside the BX-C locus, can apparently activate all of the BX-C genes in all segments T2-A8, generating a mutant fly in which all segments resemble A8. This model, based purely on genetics, was a remarkable achievement and contains the essence of the truth. However, when the BX-C was clone ...
... that lies outside the BX-C locus, can apparently activate all of the BX-C genes in all segments T2-A8, generating a mutant fly in which all segments resemble A8. This model, based purely on genetics, was a remarkable achievement and contains the essence of the truth. However, when the BX-C was clone ...
Name of structure?
... The code is the same in different species After genes have been transferred, (one species to another) They can be transcribed and translated ...
... The code is the same in different species After genes have been transferred, (one species to another) They can be transcribed and translated ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.