Learning objectives for Human Papillomavirus Paper:
... *Explain why the investigators chose to target two different classes of molecules (Her2, which is a cell-signaling/receptor molecule, and Microtubules, which are structural molecules) to treat metastatic breast cancer. *Describe conceptually how a combination of mutations in tumor suppressor genes, ...
... *Explain why the investigators chose to target two different classes of molecules (Her2, which is a cell-signaling/receptor molecule, and Microtubules, which are structural molecules) to treat metastatic breast cancer. *Describe conceptually how a combination of mutations in tumor suppressor genes, ...
Acc_Bio_Biotechnology_12
... perfect coat color, but at the same time they were also selecting the gene for congenital deafness! 8% of all Dalmatians in the US are bilaterally deaf and 22% are unilaterally deaf ...
... perfect coat color, but at the same time they were also selecting the gene for congenital deafness! 8% of all Dalmatians in the US are bilaterally deaf and 22% are unilaterally deaf ...
answers
... Which kind of RNA has an ANTICODON? __t-RNA____ What kind of molecules make up ribosomes? ___PROTEINS______ & ___r-RNA__________ Which cell part makes r-RNA? ___NUCLEOLUS__ Which cell part makes proteins? _RIBOSOMES______________ The ribosome makes sure the amino acid is put in the right spot by mat ...
... Which kind of RNA has an ANTICODON? __t-RNA____ What kind of molecules make up ribosomes? ___PROTEINS______ & ___r-RNA__________ Which cell part makes r-RNA? ___NUCLEOLUS__ Which cell part makes proteins? _RIBOSOMES______________ The ribosome makes sure the amino acid is put in the right spot by mat ...
RC 2 Student Notes
... Complementary bases: C pairs with G A pairs with U Use mRNA on the codon chart to determine amino acid sequence of protein chain ...
... Complementary bases: C pairs with G A pairs with U Use mRNA on the codon chart to determine amino acid sequence of protein chain ...
test 1 2003
... A) large populations should have greater genetic diversity B) most phenotypic traits will have no effect on fitness C) regular rates of genetic divergence should occur after population division D) most codon changes will be at the third position 25) Genetic load is: A) a measure of genome size B) a ...
... A) large populations should have greater genetic diversity B) most phenotypic traits will have no effect on fitness C) regular rates of genetic divergence should occur after population division D) most codon changes will be at the third position 25) Genetic load is: A) a measure of genome size B) a ...
Genetic Defects in Beef Cattle
... Think of the toaster like an animal-it produces proteins that serve a function-one from each of it’s chromosomes ...
... Think of the toaster like an animal-it produces proteins that serve a function-one from each of it’s chromosomes ...
Genetic Engineering
... 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____small rings of DNA_____) 3. If host and foreign DNA have been cleaved by the same restriction enzyme, the ends can ___jo ...
... 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____small rings of DNA_____) 3. If host and foreign DNA have been cleaved by the same restriction enzyme, the ends can ___jo ...
Passing it on Notes
... Also, using Punnett square(s), show how two hearing dogs could produce deaf offspring. ...
... Also, using Punnett square(s), show how two hearing dogs could produce deaf offspring. ...
Document
... production. Cells will pass the G1 S checkpoint even when chromosomal damage exists. ...
... production. Cells will pass the G1 S checkpoint even when chromosomal damage exists. ...
Snímek 1
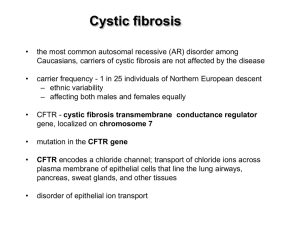
... • There is one the most commonly inherited allele which is known to cause up to 70% of all cystic fibrosis cases. This mutation is called the delta – F508 mutation • Δ F508 allele has 3 nucleotides deletion, which code for the amino acid phenylalanine (F) in the 508 position of the amino acid sequen ...
... • There is one the most commonly inherited allele which is known to cause up to 70% of all cystic fibrosis cases. This mutation is called the delta – F508 mutation • Δ F508 allele has 3 nucleotides deletion, which code for the amino acid phenylalanine (F) in the 508 position of the amino acid sequen ...
Chapter 2- Genetics
... Mutation = ______________ in the sequence of bases in the DNA. Most occur naturally or due to radiation exposure. Each change is carried to next generation and _________________________. Mutations increase variability and lead to _________________ (beneficial and harmful). a) Mechanism of M ...
... Mutation = ______________ in the sequence of bases in the DNA. Most occur naturally or due to radiation exposure. Each change is carried to next generation and _________________________. Mutations increase variability and lead to _________________ (beneficial and harmful). a) Mechanism of M ...
Natural Selection
... Adaptations can only happen if there is variety within the offspring of a species. ...
... Adaptations can only happen if there is variety within the offspring of a species. ...
Genetic Engineering PowerPoint
... ORGANISM, more specifically, it is the technology of preparing recombinant DNA in vitro (artificial environment outside of the organism) by cutting up DNA molecules and splicing together fragments from more than one organism. • Biotechnology is the APPLICATION OF THE PRINCIPLES OF ENGINEERING AND TE ...
... ORGANISM, more specifically, it is the technology of preparing recombinant DNA in vitro (artificial environment outside of the organism) by cutting up DNA molecules and splicing together fragments from more than one organism. • Biotechnology is the APPLICATION OF THE PRINCIPLES OF ENGINEERING AND TE ...
10.1 Methods of Recording Variation
... 10.5.1 Environmental effects Phenotype is the result of its _____________ and effect of ____________________. Because environmental influences are themselves very various and often form gradations, e.g. temperature, light intensity, etc., they are largely responsible for continuous variation within ...
... 10.5.1 Environmental effects Phenotype is the result of its _____________ and effect of ____________________. Because environmental influences are themselves very various and often form gradations, e.g. temperature, light intensity, etc., they are largely responsible for continuous variation within ...
Evolutionary Computation
... The genotype is the specific genetic makeup (the specific genome) of an individual, in the form of DNA. The phenotype of an individual organism is either its total physical appearance and constitution or a specific manifestation of a trait. For our purpose, we will assume a one-to-one correspond ...
... The genotype is the specific genetic makeup (the specific genome) of an individual, in the form of DNA. The phenotype of an individual organism is either its total physical appearance and constitution or a specific manifestation of a trait. For our purpose, we will assume a one-to-one correspond ...
Lecture #3 MICROBIAL GROWTH Restricted (due to exhaustion of
... caused by genetic segregation or recombination). (de Vries, 1901). The term sometimes also includes the process by which the change occurs. Mutant: An individual resulting from mutation. “Wild-type”: a strain, organism or gene of the type predominating in the wild population. Mutation provides the v ...
... caused by genetic segregation or recombination). (de Vries, 1901). The term sometimes also includes the process by which the change occurs. Mutant: An individual resulting from mutation. “Wild-type”: a strain, organism or gene of the type predominating in the wild population. Mutation provides the v ...
CHAPTER 27
... were protected from decay by the rapid burial, anaerobic conditions or acid or mineral rich waters. Thus fossils found in the lower strata are also the oldest. However, uplifting of the earth’s surface and subsequent erosion in earth’s natural rock cycle, could place the old sediments and their foss ...
... were protected from decay by the rapid burial, anaerobic conditions or acid or mineral rich waters. Thus fossils found in the lower strata are also the oldest. However, uplifting of the earth’s surface and subsequent erosion in earth’s natural rock cycle, could place the old sediments and their foss ...
The Twelfth Annual Janet L. Norwood Award Dr. Kathryn Roeder
... genes expressed at the same developmental period and brain region, and with highly correlated coexpression, are functionally interrelated and more likely to affect risk. To find these genes we model two kinds of data: gene co-expression in specific brain regions and periods of development; and the T ...
... genes expressed at the same developmental period and brain region, and with highly correlated coexpression, are functionally interrelated and more likely to affect risk. To find these genes we model two kinds of data: gene co-expression in specific brain regions and periods of development; and the T ...
Exam 2 Student Key
... Types of mutations: a. (2pts) Match the repressor structure with the most likely 1. frame shift early in coding LacI gene mutation. Each type of mutation will be used once. sequence 2 Repressor protein A: has normal protein sequence 2. silent mutation in 4th codon 3 Repressor protein B: cannot bind ...
... Types of mutations: a. (2pts) Match the repressor structure with the most likely 1. frame shift early in coding LacI gene mutation. Each type of mutation will be used once. sequence 2 Repressor protein A: has normal protein sequence 2. silent mutation in 4th codon 3 Repressor protein B: cannot bind ...
Oncogenes
... – Human tumor DNA to transform normal mouse cells – Human DNA isolated from transformants ...
... – Human tumor DNA to transform normal mouse cells – Human DNA isolated from transformants ...
S1.A codon for leucine is UUA. A mutation causing a single
... Answer: Homologous genes are derived from the same ancestral gene. Therefore, as a starting point, they had identical sequences. Over time, however, each gene accumulates random mutations that the other homologous genes did not acquire. These random mutations change the gene from its original sequen ...
... Answer: Homologous genes are derived from the same ancestral gene. Therefore, as a starting point, they had identical sequences. Over time, however, each gene accumulates random mutations that the other homologous genes did not acquire. These random mutations change the gene from its original sequen ...
protein synthesis lab
... To understand the three types of point mutations; silent, missense, and nonsense. To understand how an addition or deletion of a nucleotide causes a frameshift mutation. To understand the four types of chromosomal mutations; deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation. ...
... To understand the three types of point mutations; silent, missense, and nonsense. To understand how an addition or deletion of a nucleotide causes a frameshift mutation. To understand the four types of chromosomal mutations; deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation. ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.