Genetic Engineering (and other cool molecular biology techniques)
... – Nucleotides (to synthesize new DNA) – Primers (specific to the gene of interest) ...
... – Nucleotides (to synthesize new DNA) – Primers (specific to the gene of interest) ...
molecular genetics unit review
... c) Explain translation: initiation, elongation and termination d) Understand the genetic code: i. codons (including start and stop) ii. anticodons iii. DNA mRNA polypeptide/protein (know how to transcribe DNA and translate mRNA if given a sequence) What are the four ways gene expression is contr ...
... c) Explain translation: initiation, elongation and termination d) Understand the genetic code: i. codons (including start and stop) ii. anticodons iii. DNA mRNA polypeptide/protein (know how to transcribe DNA and translate mRNA if given a sequence) What are the four ways gene expression is contr ...
BRAF: from gene to cancer therapy
... Red boxes indicate a base change in the DNA sequence compared to the reference human genome sequenced. A mutation will be displayed as a base change occurring multiple times in the same location on both blue and yellow reads. A single red box on its own can indicate that the sequencing machine has m ...
... Red boxes indicate a base change in the DNA sequence compared to the reference human genome sequenced. A mutation will be displayed as a base change occurring multiple times in the same location on both blue and yellow reads. A single red box on its own can indicate that the sequencing machine has m ...
Genes - Revision World
... 2) Population numbers in a species stay constant over time 3) Each species displays a wide variation in features 4) Some of these variations are passed on to offspring ...
... 2) Population numbers in a species stay constant over time 3) Each species displays a wide variation in features 4) Some of these variations are passed on to offspring ...
Gene Expression, Inheritance Patterns, and DNA Technology
... Somatic = Body cells; can affect organism; not passed to offspring Lethal = death, often before birth Beneficial? = better chance of reproducing and have ...
... Somatic = Body cells; can affect organism; not passed to offspring Lethal = death, often before birth Beneficial? = better chance of reproducing and have ...
Genes that only humans have - Smurfit Institute of Genetics
... about the function at all yet.” What is extraordinary about the genes is their evolutionary past. Most new genes arise when existing ones are duplicated and “The three new genes seem the copies slowly acquire different to have arisen as a result of mutations in non-coding functions. The three new ge ...
... about the function at all yet.” What is extraordinary about the genes is their evolutionary past. Most new genes arise when existing ones are duplicated and “The three new genes seem the copies slowly acquire different to have arisen as a result of mutations in non-coding functions. The three new ge ...
Human karyotype preparation
... By selecting characteristics of offspring, we are engaging in a form of evolutionary selection - which genes are passed on to offspring Genetic screening allows for selection against deleterious alleles Heterozygous carriers advised to opt for testing and screening to stop transmission to next gener ...
... By selecting characteristics of offspring, we are engaging in a form of evolutionary selection - which genes are passed on to offspring Genetic screening allows for selection against deleterious alleles Heterozygous carriers advised to opt for testing and screening to stop transmission to next gener ...
Chapter 5A
... Diploid organisms have two copies of each gene; haploid organisms (e.g., some unicellular organisms) contain only one. A recessive mutant allele must be present in two copies (be homozygous) to cause a phenotype in a diploid organism (Fig. 5.2). Only one copy of a recessive allele must be present fo ...
... Diploid organisms have two copies of each gene; haploid organisms (e.g., some unicellular organisms) contain only one. A recessive mutant allele must be present in two copies (be homozygous) to cause a phenotype in a diploid organism (Fig. 5.2). Only one copy of a recessive allele must be present fo ...
What is a gene?
... • Two mutations, lzs and lzg, were considered alleles of the same gene because lzs/lzg heterozygotes have lozenge, not wild-type, eyes. • But when lzs/lzg females are crossed to lzs or lzg males, about 0.2% of the progeny are wild-type! • These must result from recombination between lzs and lzg , be ...
... • Two mutations, lzs and lzg, were considered alleles of the same gene because lzs/lzg heterozygotes have lozenge, not wild-type, eyes. • But when lzs/lzg females are crossed to lzs or lzg males, about 0.2% of the progeny are wild-type! • These must result from recombination between lzs and lzg , be ...
Document
... 1. Proteins A and B have different functions and different amino acid chains. 2. Proteins A and B have different functions but the same amino acid chains. 3. Proteins A and B have the same function but a different sequence of bases (A,C,T, and G). 4. Proteins A and B have the same function and the s ...
... 1. Proteins A and B have different functions and different amino acid chains. 2. Proteins A and B have different functions but the same amino acid chains. 3. Proteins A and B have the same function but a different sequence of bases (A,C,T, and G). 4. Proteins A and B have the same function and the s ...
DNA and RNA Notes
... DNA and RNA Notes Discovery of DNA _____________ - pneumonia causing bacteria and mice. (Determined…) _____________ - process of one bacteria changing its DNA from the addition of another. Avery- DNA is the nucleic acid that ___________ and __________ genetic information from one generation to ...
... DNA and RNA Notes Discovery of DNA _____________ - pneumonia causing bacteria and mice. (Determined…) _____________ - process of one bacteria changing its DNA from the addition of another. Avery- DNA is the nucleic acid that ___________ and __________ genetic information from one generation to ...
The Genome of Theobroma Cacao
... The genome, consisting of long strings of chemicals called DNA sequence, includes all the genes of a given organism, but also DNA that is not part of a gene, or noncoding DNA sequence. Each gene contains instructions for assembly of proteins, which consist of strands of amino acids that fold into an ...
... The genome, consisting of long strings of chemicals called DNA sequence, includes all the genes of a given organism, but also DNA that is not part of a gene, or noncoding DNA sequence. Each gene contains instructions for assembly of proteins, which consist of strands of amino acids that fold into an ...
(1) End labelling
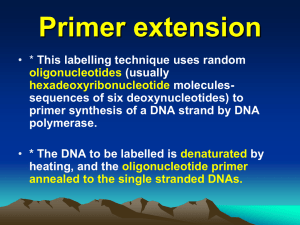
... Primer extension • * This labelling technique uses random oligonucleotides (usually hexadeoxyribonucleotide moleculessequences of six deoxynucleotides) to primer synthesis of a DNA strand by DNA polymerase. • * The DNA to be labelled is denaturated by heating, and the oligonucleotide primer annealed ...
... Primer extension • * This labelling technique uses random oligonucleotides (usually hexadeoxyribonucleotide moleculessequences of six deoxynucleotides) to primer synthesis of a DNA strand by DNA polymerase. • * The DNA to be labelled is denaturated by heating, and the oligonucleotide primer annealed ...
Proto-oncogenes normally regulate cell division, but can
... the DNA sequence will result in a less functional (or non-functional) protein. The result is detrimental to the cell and will likely prevent the cell from completing the cell cycle; however, the organism is not harmed because the mutation will not be carried forward. If a cell cannot reproduce, the ...
... the DNA sequence will result in a less functional (or non-functional) protein. The result is detrimental to the cell and will likely prevent the cell from completing the cell cycle; however, the organism is not harmed because the mutation will not be carried forward. If a cell cannot reproduce, the ...
Molecular Evolution - Faculty Web Sites at the University of Virginia
... -Point mutation; mutations of single genes; small alterations in sequence or number of nucleotides -Chromsomal mutations; alterations that are more extensive than point mutations; four types – deletions duplications, inversions, translocations -scope extends from point mutations in introns or exons, ...
... -Point mutation; mutations of single genes; small alterations in sequence or number of nucleotides -Chromsomal mutations; alterations that are more extensive than point mutations; four types – deletions duplications, inversions, translocations -scope extends from point mutations in introns or exons, ...
3.1 Teacher Notes
... b. Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. i. These are often proteins ...
... b. Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. i. These are often proteins ...
Evolution Tutorial
... 8. New individuals born in a ______________________ can potentially inherit any of the genes in the __________ __________ . 9. Gene frequency refers to how frequent a ___________ or ___________ is in a population. 10. Gene frequency can change because of __________. When the gene ____________ change ...
... 8. New individuals born in a ______________________ can potentially inherit any of the genes in the __________ __________ . 9. Gene frequency refers to how frequent a ___________ or ___________ is in a population. 10. Gene frequency can change because of __________. When the gene ____________ change ...
This exam is worth 50 points Evolutionary Biology You may take this
... This is a true statement. The Reformation starting in the early 1500’s initiated when Martin Luther broke from the Roman Catholic Church and continued into the present times by the formation of many Protestant religions, brought about the liberalization of thought no longer controlled by Rome. Thus, ...
... This is a true statement. The Reformation starting in the early 1500’s initiated when Martin Luther broke from the Roman Catholic Church and continued into the present times by the formation of many Protestant religions, brought about the liberalization of thought no longer controlled by Rome. Thus, ...
Title of Unit: DNA, Genetics and Biotechnology Course and Grade
... Skills in Science: Cellular genetics, Describe the method and steps in structure and function of Mendel's true breeding experiments DNA in cells, genetic State the two laws of heredity developed mechanisms and from Mendel's work inheritance, mutation and c. Describe how Mendel's work can now ...
... Skills in Science: Cellular genetics, Describe the method and steps in structure and function of Mendel's true breeding experiments DNA in cells, genetic State the two laws of heredity developed mechanisms and from Mendel's work inheritance, mutation and c. Describe how Mendel's work can now ...
Foundations in Microbiology
... • Conjugation – transfer of a plasmid or chromosomal fragment from a donor cell to a recipient cell via a direct connection – Gram-negative cell donor has a fertility plasmid (F plasmid, F′ factor) that allows the synthesis of a conjugation (sex) pilus – recipient cell is a related species or genus ...
... • Conjugation – transfer of a plasmid or chromosomal fragment from a donor cell to a recipient cell via a direct connection – Gram-negative cell donor has a fertility plasmid (F plasmid, F′ factor) that allows the synthesis of a conjugation (sex) pilus – recipient cell is a related species or genus ...
Photo Album
... Figure 21.1 Senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Under normal physiological conditions, the amyloid precursor protein (APP) is cleaved by α-secretase to form sAPPα. The remaining fragment of the APP protein may be further cleaved by γ-secreta ...
... Figure 21.1 Senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Under normal physiological conditions, the amyloid precursor protein (APP) is cleaved by α-secretase to form sAPPα. The remaining fragment of the APP protein may be further cleaved by γ-secreta ...
DNA
... • Transfer RNA- carries amino acids to the ribosome and adds them to the growing proteins. ...
... • Transfer RNA- carries amino acids to the ribosome and adds them to the growing proteins. ...
DNA Replication
... 2. The enzyme moves down the DNA, building a strand of RNA that is complementary to the DNA. ...
... 2. The enzyme moves down the DNA, building a strand of RNA that is complementary to the DNA. ...
Protein Synthesis - Building Directory
... single gene Can seriously affect phenotype genetic disorder Sickle cell anemia results from one nucleotide substitution. ...
... single gene Can seriously affect phenotype genetic disorder Sickle cell anemia results from one nucleotide substitution. ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.