Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics
... • Mutation can take place spontaneously. DNA polymerase makes a mistake and inserts a wrong NB during DNA replication. • Mutation frequency is increased by certain agents – mutagens • Chemicals – nitrous acid changes shape Of adenine – cytosine • X-rays – pull e- out of molecules – breaks in the ch ...
... • Mutation can take place spontaneously. DNA polymerase makes a mistake and inserts a wrong NB during DNA replication. • Mutation frequency is increased by certain agents – mutagens • Chemicals – nitrous acid changes shape Of adenine – cytosine • X-rays – pull e- out of molecules – breaks in the ch ...
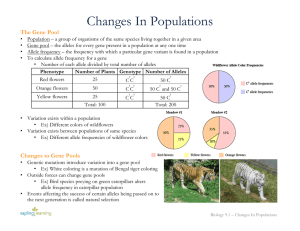
Changes In Populations
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
Exam 3
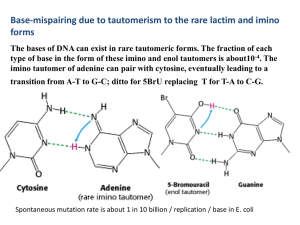
... another. This shift alters the hydrogen bonding between bases which results in improper basepairing, allowing the tautomerized base to pair with bases other than the one it is normally paired with during DNA replication. Base analogues are compounds sufficiently similar to basepair with the correct ...
... another. This shift alters the hydrogen bonding between bases which results in improper basepairing, allowing the tautomerized base to pair with bases other than the one it is normally paired with during DNA replication. Base analogues are compounds sufficiently similar to basepair with the correct ...
Mutations Associated with Second-line Tuberculosis Drug
... Supported in part by the NIH Fogarty International Center (D43TW007124) DTRA (Defense Threat Reduction Agency ) ...
... Supported in part by the NIH Fogarty International Center (D43TW007124) DTRA (Defense Threat Reduction Agency ) ...
DNA Replication Paper Clip Activity
... *This type of mutation can be caused by a variety of circumstances, including radiation, chemical exposure, or it can occur spontaneously without known cause. ...
... *This type of mutation can be caused by a variety of circumstances, including radiation, chemical exposure, or it can occur spontaneously without known cause. ...
BRCA1 and BRCA2 in Men
... Men can inherit a BRCA gene mutation from their mother or father and can pass on their BRCA gene mutation to their male and female children. Medical management for men with BRCA1/2 mutations changes at age 35–40. Starting at age 35, male BRCA mutation carriers should begin yearly clinical breast exa ...
... Men can inherit a BRCA gene mutation from their mother or father and can pass on their BRCA gene mutation to their male and female children. Medical management for men with BRCA1/2 mutations changes at age 35–40. Starting at age 35, male BRCA mutation carriers should begin yearly clinical breast exa ...
4.1 HUMAN GENETIC DISEASES - e
... completely different band sizes, and their son-in-law has different band sizes again. It is much more likely that some sizes of CA repeat are more frequent in the population than others, and will therefore be over represented in families. For diagnostic purposes, the closest, most ‘informative’ mark ...
... completely different band sizes, and their son-in-law has different band sizes again. It is much more likely that some sizes of CA repeat are more frequent in the population than others, and will therefore be over represented in families. For diagnostic purposes, the closest, most ‘informative’ mark ...
ANSWER KEY Nucleic Acid and DNA Replication Outline Notes
... Which statement below BEST summarizes the role of the DNA molecule in cells? A) guides cell division B) protects cells from infection C) provides the instructions for making proteins D) regulates the chemical processes that provide the cell with energy ...
... Which statement below BEST summarizes the role of the DNA molecule in cells? A) guides cell division B) protects cells from infection C) provides the instructions for making proteins D) regulates the chemical processes that provide the cell with energy ...
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... Deamination of bases: Chemical mutagenesis and possibly carcinogenesis Nitrous acid (HNO2) hydrolyzes amino groups on bases via diazotization. Adenine is deaminated to hypoxanthine, cytosine to uracil, and guanine to xanthine. Hypoxanthine pairs with cytosine, inducing a mutation of A-T to G-C. It ...
... Deamination of bases: Chemical mutagenesis and possibly carcinogenesis Nitrous acid (HNO2) hydrolyzes amino groups on bases via diazotization. Adenine is deaminated to hypoxanthine, cytosine to uracil, and guanine to xanthine. Hypoxanthine pairs with cytosine, inducing a mutation of A-T to G-C. It ...
Nitrogen Base Pairs
... Different gene combinations, dominant and recessive Same gene pairs 9.What is a mutation? Are they always harmful? Permanent change to an organism No create variety ...
... Different gene combinations, dominant and recessive Same gene pairs 9.What is a mutation? Are they always harmful? Permanent change to an organism No create variety ...
Final Study Guide
... white fur color. In a litter of eight offspring, there would probably be _____. 10. The numbers in the figure below represent the chromosome number found in each of the dog cells shown. The processes that are occurring at A and B are _____ & _____. ...
... white fur color. In a litter of eight offspring, there would probably be _____. 10. The numbers in the figure below represent the chromosome number found in each of the dog cells shown. The processes that are occurring at A and B are _____ & _____. ...
Gene Expression
... As each new tRNA enters the ribosome, one leaves. Before tRNA can leave the ribosome, the animo acids will bond together to make a polypeptide chain ...
... As each new tRNA enters the ribosome, one leaves. Before tRNA can leave the ribosome, the animo acids will bond together to make a polypeptide chain ...
Supplemental Note
... identify classes of genes that were differentially expressed as a result of mtDNA mutations. Hiona et al., MIAME p.3 ...
... identify classes of genes that were differentially expressed as a result of mtDNA mutations. Hiona et al., MIAME p.3 ...
MASTER SYLLABUS
... describe sex determination systems and the structure of sex chromosomes. describe the different types of chromosome mutations. recognize sequence variations that occur within eukaryotic chromosomes. recognize that linked genes do not display independent assortment. explain how crossing over produces ...
... describe sex determination systems and the structure of sex chromosomes. describe the different types of chromosome mutations. recognize sequence variations that occur within eukaryotic chromosomes. recognize that linked genes do not display independent assortment. explain how crossing over produces ...
Science 9 Unit A 3.0
... • These pairs of genes are always found at the same position on a chromosome • However, the code for each gene in the pair may be different ...
... • These pairs of genes are always found at the same position on a chromosome • However, the code for each gene in the pair may be different ...
Word
... *Note: to get in and out of the simulator you may need to use the ‘Win + D’ (PC) or ‘F11’ (Mac) keyboard shortcuts. ...
... *Note: to get in and out of the simulator you may need to use the ‘Win + D’ (PC) or ‘F11’ (Mac) keyboard shortcuts. ...
Chromosomes & Inheritance
... Piece of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosme ...
... Piece of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosme ...
Neo Darwinian Evolution - Fall River Public Schools
... • If there was no variation, then there could be no new traits • If there were no new traits, then changes in environment could quickly lead to extinction. ...
... • If there was no variation, then there could be no new traits • If there were no new traits, then changes in environment could quickly lead to extinction. ...
26.1 and 26.2 Notes - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... a. Genome: Full set of genetic information of a species or a virus b. Genetic Engineering: Alteration of genomes for medical or industrial purposes 2. Cloning: a. May be whole-organism cloning i. Complete organism reproduction through asexual means ii. E.g. Identical twins, “Dolly” the sheep b. Gene ...
... a. Genome: Full set of genetic information of a species or a virus b. Genetic Engineering: Alteration of genomes for medical or industrial purposes 2. Cloning: a. May be whole-organism cloning i. Complete organism reproduction through asexual means ii. E.g. Identical twins, “Dolly” the sheep b. Gene ...
Document
... Answer: These results can be explained by gene conversion. The gene conversion took place in a limited region of the chromosome (within the pdx-1 gene), but it did not affect the flanking genes (pyr-1 and col-4) located on either side of the pdx-1 gene. In the asci containing two pdx-1 alleles and s ...
... Answer: These results can be explained by gene conversion. The gene conversion took place in a limited region of the chromosome (within the pdx-1 gene), but it did not affect the flanking genes (pyr-1 and col-4) located on either side of the pdx-1 gene. In the asci containing two pdx-1 alleles and s ...
FINAL_FALL2005frmHw.doc
... 48. Which of the following is a mechanism or cause of evolution? a. mutation b. gene flow c. genetic drift d. natural selection e. all of the above 49. Selection against individuals at both ends of a phenotypic distribution for a character, favoring those in the middle or average of the distribution ...
... 48. Which of the following is a mechanism or cause of evolution? a. mutation b. gene flow c. genetic drift d. natural selection e. all of the above 49. Selection against individuals at both ends of a phenotypic distribution for a character, favoring those in the middle or average of the distribution ...
UNIT 7 TEST DNA TEST BLUEPRINT
... 1. When the __ for insulin is inserted into bacteria, they can be used to mass-produce insulin. a) chromosome b) gene c) fragment d) base 2. Who discovered the structure of DNA and made a model of it? a) Mendel b) Hershey and Chase c) Watson and Crick d) Wilkins and Franklin 3. Which of the followin ...
... 1. When the __ for insulin is inserted into bacteria, they can be used to mass-produce insulin. a) chromosome b) gene c) fragment d) base 2. Who discovered the structure of DNA and made a model of it? a) Mendel b) Hershey and Chase c) Watson and Crick d) Wilkins and Franklin 3. Which of the followin ...
CS691K Bioinformatics Kulp Lecture Notes #0 Molecular
... – How does DNA polymerase find the origins? Are there sequence patterns? ...
... – How does DNA polymerase find the origins? Are there sequence patterns? ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.