DNA Webquest - Fredericksburg City Schools
... On the menu at the right click on Molecules of Genetics tab and then number 27, “Mutations are changes in genetic information”. Read the text and answer the following questions. 1. DNA differences results from a mutation of what 3 possibilities? 2. In humans, where do the majority of mutations occur ...
... On the menu at the right click on Molecules of Genetics tab and then number 27, “Mutations are changes in genetic information”. Read the text and answer the following questions. 1. DNA differences results from a mutation of what 3 possibilities? 2. In humans, where do the majority of mutations occur ...
revolution in evolution
... • Molecular mechanisms worked out for DNA replication and protein synthesis • Multiple methods invented to study genetic variation and evolution ...
... • Molecular mechanisms worked out for DNA replication and protein synthesis • Multiple methods invented to study genetic variation and evolution ...
I. GENETIC APPARATUS OF HUMAN CELL – SUPPORT OF
... Genome - the total complement of cellular DNA. In the cell could be identified nuclear genome (46 molecules of linear DNA) and mitochondrial genome (several identical molecules of circular DNA) Genotype - the total complement of genes contained in a cell or virus; commonly used in eukaryotes to refe ...
... Genome - the total complement of cellular DNA. In the cell could be identified nuclear genome (46 molecules of linear DNA) and mitochondrial genome (several identical molecules of circular DNA) Genotype - the total complement of genes contained in a cell or virus; commonly used in eukaryotes to refe ...
Mutations and Genetic Disease There are more than 4,000 genetic
... This image and caption from The Book of Man by Walter Bodmer and Robin McKie. The type of mutation exemplified in sickle cell anemia is called a substitution, because one nucleotide base is substituted for another. Other types of mutations include insertions and deletions, both of which can have dis ...
... This image and caption from The Book of Man by Walter Bodmer and Robin McKie. The type of mutation exemplified in sickle cell anemia is called a substitution, because one nucleotide base is substituted for another. Other types of mutations include insertions and deletions, both of which can have dis ...
Additional Glossary and Concepts List for Vertebrate Genetics
... An animal bearing cells or tissues derived from transplantation from another animal. Typically the host animal is genotypically distinct from the donor. Dosage compensation The mechanism whereby loci on the shared sex chromosome are expressed at equivalent levels between the sexes. In mice and human ...
... An animal bearing cells or tissues derived from transplantation from another animal. Typically the host animal is genotypically distinct from the donor. Dosage compensation The mechanism whereby loci on the shared sex chromosome are expressed at equivalent levels between the sexes. In mice and human ...
Gene Section WNK2 (WNK lysine deficient protein kinase 2)
... Human WNK2 modulates the activation level of ERK1 and ERK2. Experimental depletion of WNK2 or overexpression of a kinase-dead WNK2K207M mutant led to increased phospho-ERK1/2 levels when a basal ERK stimulation was present but not, for example, in serum-free culture conditions (Moniz et al., 2007). ...
... Human WNK2 modulates the activation level of ERK1 and ERK2. Experimental depletion of WNK2 or overexpression of a kinase-dead WNK2K207M mutant led to increased phospho-ERK1/2 levels when a basal ERK stimulation was present but not, for example, in serum-free culture conditions (Moniz et al., 2007). ...
3.1 Genetics
... DNA that is not used for protein synthesis or the mutated protein is not required for survival. These are known as NEUTRAL MUTATIONS and have they have NO EFFECT on the organism. • e.g. mutation in the gene that codes for fur colour (Spirit Bear). Although white, the survival rate of the organism is ...
... DNA that is not used for protein synthesis or the mutated protein is not required for survival. These are known as NEUTRAL MUTATIONS and have they have NO EFFECT on the organism. • e.g. mutation in the gene that codes for fur colour (Spirit Bear). Although white, the survival rate of the organism is ...
chapter 27 - applied genetics
... CYSTIC FIBROSIS SICKLE-CELL DISEASE PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) HUNTINGTON DISEASE DOWN’S SYNDROME ...
... CYSTIC FIBROSIS SICKLE-CELL DISEASE PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) HUNTINGTON DISEASE DOWN’S SYNDROME ...
BIOL 1101 Introduction to Human Genetics
... a. Sex determination in human beings b. X-linked inheritance and X-linked disorders c. Inactivation of X-linked genes in female mammals Multifactorial traits a. Quantitative traits and continuous variation b. The concept of heritability c. Methods to study multifactorial traits: Twin studies The Str ...
... a. Sex determination in human beings b. X-linked inheritance and X-linked disorders c. Inactivation of X-linked genes in female mammals Multifactorial traits a. Quantitative traits and continuous variation b. The concept of heritability c. Methods to study multifactorial traits: Twin studies The Str ...
Genetic Disorders and Gene Therapy
... Hybridization: Crossing individuals that are not closely related to introduce new, beneficial alleles to the population. New individuals are generally hardier than either parent. This is called ________________________. Mutations In biology, mutations are changes to the nucleotide sequence of th ...
... Hybridization: Crossing individuals that are not closely related to introduce new, beneficial alleles to the population. New individuals are generally hardier than either parent. This is called ________________________. Mutations In biology, mutations are changes to the nucleotide sequence of th ...
2/8
... other to a suboptimal concentration in the cell (usually one allelespecific) •Combined haplo-insufficiency (allele non-specific) ...
... other to a suboptimal concentration in the cell (usually one allelespecific) •Combined haplo-insufficiency (allele non-specific) ...
Designer Genes - Heredity
... chromosomes (esp. X) Y-chromosome shorter – some genes from X missing X-linked traits more common in men Men get X-chromosome from mom Red-green colorblindness, hemophilia ...
... chromosomes (esp. X) Y-chromosome shorter – some genes from X missing X-linked traits more common in men Men get X-chromosome from mom Red-green colorblindness, hemophilia ...
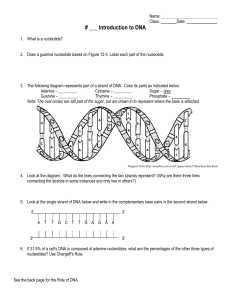
Cytosine – ______ Sugar
... 4. Look at the diagram. What do the lines connecting the two strands represent? (Why are there three lines connecting the strands in some instances and only two in others?) ...
... 4. Look at the diagram. What do the lines connecting the two strands represent? (Why are there three lines connecting the strands in some instances and only two in others?) ...
Chapter 4 Genetics: The Science of Heredity C4S1 `Mendel`s Work
... cytoplasm ii. RNA only has one ‘handrail’ iii. There is a different nitrogen base in RNA (Thymine is replaced by uracil) b. Types of the RNA i. M RNA is used to copy DNA and carry the ‘instructions’ from the nucleus to the ...
... cytoplasm ii. RNA only has one ‘handrail’ iii. There is a different nitrogen base in RNA (Thymine is replaced by uracil) b. Types of the RNA i. M RNA is used to copy DNA and carry the ‘instructions’ from the nucleus to the ...
Review Materials for Gene to Protein and DNA
... How is the template strand for a particular gene determined? 1. It is the DNA strand that runs from the 5' → 3' direction. 2. It is the DNA strand that runs from the 3' → 5' direction. 3. It depends on the orientation of RNA polymerase, whose position is determined by particular sequences of nucleot ...
... How is the template strand for a particular gene determined? 1. It is the DNA strand that runs from the 5' → 3' direction. 2. It is the DNA strand that runs from the 3' → 5' direction. 3. It depends on the orientation of RNA polymerase, whose position is determined by particular sequences of nucleot ...
DNA and RNA
... • Two types: 1. Gene mutations 2. Chromosomal mutations • Many mutations are harmless • Pros: increase adaptation or survival • Cons: some can be lethal or debilitating ...
... • Two types: 1. Gene mutations 2. Chromosomal mutations • Many mutations are harmless • Pros: increase adaptation or survival • Cons: some can be lethal or debilitating ...
Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... a. without an X chromosome. b. with one X chromosome. c. with four X chromosomes. d. with three X chromosomes. ...
... a. without an X chromosome. b. with one X chromosome. c. with four X chromosomes. d. with three X chromosomes. ...
1. The following processes are required to produce
... gene that encodes a tRNAs that suppress the effects of non-sense mutations. For an organism to be able to survive the mutation that creates a non-sense suppressor tRNA, which must be true? ❏ A. the gene with the original non-sense mutation must be relatively unimportant ❏ B. there must be multiple g ...
... gene that encodes a tRNAs that suppress the effects of non-sense mutations. For an organism to be able to survive the mutation that creates a non-sense suppressor tRNA, which must be true? ❏ A. the gene with the original non-sense mutation must be relatively unimportant ❏ B. there must be multiple g ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... Since DNA can’t leave the nucleus, its information for protein synthesis has to be carried to the ribosomes (site of protein synthesis) in the cytoplasm by RNA (same basic structure as DNA but with a 5 carbon ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose). To do this, DNA unzips and nucleotides form the RNA c ...
... Since DNA can’t leave the nucleus, its information for protein synthesis has to be carried to the ribosomes (site of protein synthesis) in the cytoplasm by RNA (same basic structure as DNA but with a 5 carbon ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose). To do this, DNA unzips and nucleotides form the RNA c ...
slides available - The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering
... Any manipulation will alter genes in 50% or 75% ...
... Any manipulation will alter genes in 50% or 75% ...
Human Genetics Powerpoint
... Mutations that involve changes in one or a few nucleotides are known as point mutations because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence. They generally occur during replication. If a gene in one cell is altered, the alteration can be passed on to every cell that develops from the original ...
... Mutations that involve changes in one or a few nucleotides are known as point mutations because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence. They generally occur during replication. If a gene in one cell is altered, the alteration can be passed on to every cell that develops from the original ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Act as microscopic tools to build or operate a component of a living cell Genes code for proteins that in turn determine genetic traits ...
... Act as microscopic tools to build or operate a component of a living cell Genes code for proteins that in turn determine genetic traits ...
Chapter 12 Notes - White Plains Public Schools
... DNA= “Master plan” -Stays in the nucleus RNA= “Blueprint” – Leaves the nucleus to go to protein building sites (Ribosomes) in cytoplasm Chapter 12 Lesson 4 Mutations: Changes in DNA sequence that affect genetic information 2 Types 1. Gene mutations- changes in single genes 2. Chromosomal mutatio ...
... DNA= “Master plan” -Stays in the nucleus RNA= “Blueprint” – Leaves the nucleus to go to protein building sites (Ribosomes) in cytoplasm Chapter 12 Lesson 4 Mutations: Changes in DNA sequence that affect genetic information 2 Types 1. Gene mutations- changes in single genes 2. Chromosomal mutatio ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.