Bio07_TR__U04_CH13.QXD
... 11. Is the following sentence true or false? The genetic variation that exists in nature is enough to satisfy the needs of breeders. ____________________ 12. Breeders can increase the genetic variation by inducing ____________________ , which are the ultimate source of genetic variability. 13. Circl ...
... 11. Is the following sentence true or false? The genetic variation that exists in nature is enough to satisfy the needs of breeders. ____________________ 12. Breeders can increase the genetic variation by inducing ____________________ , which are the ultimate source of genetic variability. 13. Circl ...
The Egyptian American International School
... such that new types of organisms develop from preexisting types. ● Scientific understanding of evolution began to develop in the 17th and 18th centuries as geologists and naturalists compared geologic processes and living and fossil organisms around the world. ● After making many observations and co ...
... such that new types of organisms develop from preexisting types. ● Scientific understanding of evolution began to develop in the 17th and 18th centuries as geologists and naturalists compared geologic processes and living and fossil organisms around the world. ● After making many observations and co ...
Genetic determination of diseases
... – polymorphism = existence of several (at least 2) alleles for given gene with MAF ≥ 1% sometimes are mutations vs. polymorphisms classified according to the functional impact (mutations = significantly pathogenis, polymorphisms = mild or neutral) ...
... – polymorphism = existence of several (at least 2) alleles for given gene with MAF ≥ 1% sometimes are mutations vs. polymorphisms classified according to the functional impact (mutations = significantly pathogenis, polymorphisms = mild or neutral) ...
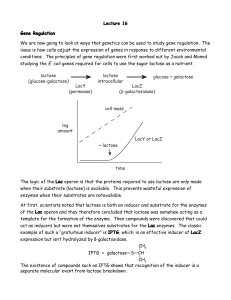
Lecture 16 Gene Regulation
... LacI– mutations that are dominant. Such mutations are known as LacI-d. They are dominant because the repressor protein is a tetramer and LacI-d mutant subunits can combine with normal subunits and interfere with their function. –IPTG ...
... LacI– mutations that are dominant. Such mutations are known as LacI-d. They are dominant because the repressor protein is a tetramer and LacI-d mutant subunits can combine with normal subunits and interfere with their function. –IPTG ...
Carcinomas with DNA Mismatch Repair Deficiency
... mutations are heterozygous, and involve only one allele. Small frameshift mutations are the most common and result in premature protein truncation, followed by nonsense mutations and larger genomic deletions. Some patients with HNPCC harbor point mutations that result in amino acid substitutions at ...
... mutations are heterozygous, and involve only one allele. Small frameshift mutations are the most common and result in premature protein truncation, followed by nonsense mutations and larger genomic deletions. Some patients with HNPCC harbor point mutations that result in amino acid substitutions at ...
The Human Genome Project
... region of the genome, produce a virtually unlimited number of copies of it, and determine its nucleotide sequence overnight. • At the height of the Human Genome Project, sequencing factories were generating DNA sequences at a rate of 1000 nucleotides per second 24/7. • Technical breakthroughs that a ...
... region of the genome, produce a virtually unlimited number of copies of it, and determine its nucleotide sequence overnight. • At the height of the Human Genome Project, sequencing factories were generating DNA sequences at a rate of 1000 nucleotides per second 24/7. • Technical breakthroughs that a ...
Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... Parameters that influence the proportion of targeted events? 1. length of flanking homologies (Bailis and Maines, 1996) 2. systematic investigation of ends-out recombination (Štafa et al., manuscript in preparation): ...
... Parameters that influence the proportion of targeted events? 1. length of flanking homologies (Bailis and Maines, 1996) 2. systematic investigation of ends-out recombination (Štafa et al., manuscript in preparation): ...
Day 3 - Scott County Schools
... patient with a defective gene. This is called gene therapy. Ideally, it can cure a genetic disorder. ● produce human proteins. Insulin is one example. This protein is needed to treat diabetes. The human insulin gene is inserted into bacteria. The bacteria reproduce rapidly so there are soon enough o ...
... patient with a defective gene. This is called gene therapy. Ideally, it can cure a genetic disorder. ● produce human proteins. Insulin is one example. This protein is needed to treat diabetes. The human insulin gene is inserted into bacteria. The bacteria reproduce rapidly so there are soon enough o ...
GENETICS
... and their expression can be modified by their interaction with the environment. DNA Structure Deoxyribonucleic acid replicates itself and is passed from generation to generation. Controls cellular activity by influencing the production of enzymes. Found in the nucleus of cells. ...
... and their expression can be modified by their interaction with the environment. DNA Structure Deoxyribonucleic acid replicates itself and is passed from generation to generation. Controls cellular activity by influencing the production of enzymes. Found in the nucleus of cells. ...
View PDF - Genetics
... Previous studies have shown that Neanderthals were inbred compared to humans, and also that Neanderthals interbred with the ancestors of people living outside Africa today, contributing 1 to 4% of their modern gene pool. We use simulations to show that Neanderthal inbreeding likely caused accumulati ...
... Previous studies have shown that Neanderthals were inbred compared to humans, and also that Neanderthals interbred with the ancestors of people living outside Africa today, contributing 1 to 4% of their modern gene pool. We use simulations to show that Neanderthal inbreeding likely caused accumulati ...
BRCA1 - BioSyL
... > 90% of mutations introduce a premature termination codon in the coding sequence (PTC) = truncating mutations - small insertions/deletions that create a frameshift - nonsense mutations - splice sites mutations - deletion/duplication of one or several exons Very few missense mutations ...
... > 90% of mutations introduce a premature termination codon in the coding sequence (PTC) = truncating mutations - small insertions/deletions that create a frameshift - nonsense mutations - splice sites mutations - deletion/duplication of one or several exons Very few missense mutations ...
Albena Jordanova - the Department of Molecular Genetics
... axonal degeneration of the peripheral nerves only. We were the first to establish that the DICMTC phenotype is not due to haploinsufficiency of enzymatic activity, but to a gain-offunction alteration of the mutant YARS or interference with an unknown function of the wild type protein. To unravel the ...
... axonal degeneration of the peripheral nerves only. We were the first to establish that the DICMTC phenotype is not due to haploinsufficiency of enzymatic activity, but to a gain-offunction alteration of the mutant YARS or interference with an unknown function of the wild type protein. To unravel the ...
CSHL-CBW Lab Module 15 Answers
... Contraction annotations reflect a shared set of genes. These genes represent voltagegated ion channels, which are a group of transmembrane ion channels that activated by changes in electrical potential difference. Even though ion channels are especially critical in neurons and muscle tissue, they ar ...
... Contraction annotations reflect a shared set of genes. These genes represent voltagegated ion channels, which are a group of transmembrane ion channels that activated by changes in electrical potential difference. Even though ion channels are especially critical in neurons and muscle tissue, they ar ...
AP Bio Molecular Genetics Review Sheet
... Mosaic Virus, then spray it on tobacco plants, what do you expect to happen next? What is the most common source for diversity in a bacterial colony? The fundamental form of chromatin is what? Antibody diversity is due to what? What are the characteristics of the p53 gene? Tobacco Mosaic Virus has R ...
... Mosaic Virus, then spray it on tobacco plants, what do you expect to happen next? What is the most common source for diversity in a bacterial colony? The fundamental form of chromatin is what? Antibody diversity is due to what? What are the characteristics of the p53 gene? Tobacco Mosaic Virus has R ...
N.S. 100 Lecture 15 - PPT Evolution Spring 2009 Assignment Page
... Best adapted moth reproduces more offspring ...
... Best adapted moth reproduces more offspring ...
retinitis pigmentosa - Foundation Fighting Blindness
... visual field of less than 20 degrees in diameter. It is a genetic disorder and, therefore, is almost always inherited. How is RP inherited? An estimated 100,000 people in the U.S. have RP, mainly caused by gene mutations (variations) inherited from one or both parents. Mutated genes give the wrong i ...
... visual field of less than 20 degrees in diameter. It is a genetic disorder and, therefore, is almost always inherited. How is RP inherited? An estimated 100,000 people in the U.S. have RP, mainly caused by gene mutations (variations) inherited from one or both parents. Mutated genes give the wrong i ...
EPIGENETICS Textbook
... – Define cell identity and function – maintain differentiated state, – Complexes highly conserved in plants and animals; 1st described in Drosophila • Trithorax Group (trxG) maintains active transcription • Polycomb Group (PcG) maintains transcription repression ...
... – Define cell identity and function – maintain differentiated state, – Complexes highly conserved in plants and animals; 1st described in Drosophila • Trithorax Group (trxG) maintains active transcription • Polycomb Group (PcG) maintains transcription repression ...
DNA structure and replication Three key features needed for any
... the pairs of bases holding the chains together. The vertical line marks the fibre axis. …………….It ...
... the pairs of bases holding the chains together. The vertical line marks the fibre axis. …………….It ...
Mcbio 316: Exam 1A Answers (10)1. A wild
... 8. The Bacillus subtilis yqfI gene encodes a protein which catalyzes recombination between circular DNA molecules. Epistasis analysis was done between yqfI and other mutations known to affect recombination. The results are shown below. In the last column of the table, indicate the interpretation of ...
... 8. The Bacillus subtilis yqfI gene encodes a protein which catalyzes recombination between circular DNA molecules. Epistasis analysis was done between yqfI and other mutations known to affect recombination. The results are shown below. In the last column of the table, indicate the interpretation of ...
Slide 1
... Control the production of proteins in the organism’s cells. Proteins help to determine the ...
... Control the production of proteins in the organism’s cells. Proteins help to determine the ...
Document
... 13. If the body cells of an organism have 10 chromosomes, then the sex cells produced during meiosis would have__________________chromosomes. 14. What is the haploid number of chromosomes for a human sperm or egg cell? 15. What is the number of chromosomes in a body cell known as? 16. Who is respons ...
... 13. If the body cells of an organism have 10 chromosomes, then the sex cells produced during meiosis would have__________________chromosomes. 14. What is the haploid number of chromosomes for a human sperm or egg cell? 15. What is the number of chromosomes in a body cell known as? 16. Who is respons ...
Name Class Date Study guide for biology final Review evolution
... 2. is when nature determines the variety of traits, but humans pick which traits are desirable. 3. An inheritable characteristic that increases an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce is called a(n) ...
... 2. is when nature determines the variety of traits, but humans pick which traits are desirable. 3. An inheritable characteristic that increases an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce is called a(n) ...
pres2_odell - Harlem Children Society
... it to see what sort of differences there were • When using CLUSTW the tool lines up both genetic sequences one over the other and show’s similarities and differences allowing for there to be a thorough examination ...
... it to see what sort of differences there were • When using CLUSTW the tool lines up both genetic sequences one over the other and show’s similarities and differences allowing for there to be a thorough examination ...
Genetic Technology
... DNA code of living organisms uses DNA technology to cure diseases, treat genetic disorders, improve food crops, etc. ...
... DNA code of living organisms uses DNA technology to cure diseases, treat genetic disorders, improve food crops, etc. ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.