Tutorial 1 - NUS Physics Department
... 7. In reactions of the type A B A C1 C2 (in which particle A scatters off particle B, producing C1 , C2 ,) , there is another inertial frame [besides the lab (B at rest) and the CM (PTOT = 0 )] which is sometimes useful. It is called the Breit, or “brick wall,” frame, and it is the syst ...
... 7. In reactions of the type A B A C1 C2 (in which particle A scatters off particle B, producing C1 , C2 ,) , there is another inertial frame [besides the lab (B at rest) and the CM (PTOT = 0 )] which is sometimes useful. It is called the Breit, or “brick wall,” frame, and it is the syst ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 16. (a) Explain the structure of space-time (Minkowski) diagram and bring out its salient features. (b) The coordinates of event A are ( x A, 0, 0, t A) and the coordinates of event B are ( x B, 0, 0, t B). Assuming the interval between them is space- like, find the velocity of the system in which t ...
... 16. (a) Explain the structure of space-time (Minkowski) diagram and bring out its salient features. (b) The coordinates of event A are ( x A, 0, 0, t A) and the coordinates of event B are ( x B, 0, 0, t B). Assuming the interval between them is space- like, find the velocity of the system in which t ...
The 1/N expansion method in quantum field theory
... In perturbation theory, when calculating radiative corrections, one usually finds powers of the quantity λ2 ln(p2/M 2), where p is a representative of the momenta of the external particles. Even if λ is chosen small, at high energies, i.e., at large values of p, the logarithm may become large enough ...
... In perturbation theory, when calculating radiative corrections, one usually finds powers of the quantity λ2 ln(p2/M 2), where p is a representative of the momenta of the external particles. Even if λ is chosen small, at high energies, i.e., at large values of p, the logarithm may become large enough ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 17. Prove the commutation relation [p2x, x] = -2iћp. 18. Illustrate the Pauli Exclusion Principle for the ground state of He atom. 19. At what distance from the nucleus is the probability of finding the electron a maximum for a 1S electron in hydrogen? 20. While the order is the same for both C3v a ...
... 17. Prove the commutation relation [p2x, x] = -2iћp. 18. Illustrate the Pauli Exclusion Principle for the ground state of He atom. 19. At what distance from the nucleus is the probability of finding the electron a maximum for a 1S electron in hydrogen? 20. While the order is the same for both C3v a ...
Midterm Review Sheet
... 5. Dalton - Law of multiple proportions also developed atomic theory, much of which is still in use today. 6. Crookes - using Crookes' tube discovered "cathode rays" as negative particles/radiation. This was the first evidence of electrons. 7. Thomson – determined: 1) that cathode rays were actually ...
... 5. Dalton - Law of multiple proportions also developed atomic theory, much of which is still in use today. 6. Crookes - using Crookes' tube discovered "cathode rays" as negative particles/radiation. This was the first evidence of electrons. 7. Thomson – determined: 1) that cathode rays were actually ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 5. What is a Green’s function? 6. What is screened Coulomb potential? 7. Distinguish between first and second order transitions of the time dependent perturbation theory with the help of schematic diagrams. 8. What is dipole approximation in emission/absorption process of an atom? 9. What is the lim ...
... 5. What is a Green’s function? 6. What is screened Coulomb potential? 7. Distinguish between first and second order transitions of the time dependent perturbation theory with the help of schematic diagrams. 8. What is dipole approximation in emission/absorption process of an atom? 9. What is the lim ...
3.4oquantum.4u
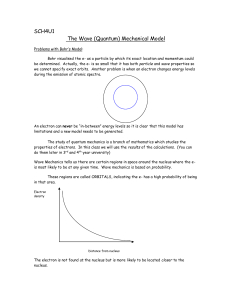
... The study of quantum mechanics is a branch of mathematics which studies the properties of electrons. In this class we will use the results of the calculations. (You can do them later in 3rd and 4th year university) Wave Mechanics tells us there are certain regions in space around the nucleus where t ...
... The study of quantum mechanics is a branch of mathematics which studies the properties of electrons. In this class we will use the results of the calculations. (You can do them later in 3rd and 4th year university) Wave Mechanics tells us there are certain regions in space around the nucleus where t ...
Natural Sciences
... electron microscope (electrons) particle accelerators (synchrotron radiation) ...
... electron microscope (electrons) particle accelerators (synchrotron radiation) ...
WAVE MECHANICS AND QUANTUM NUMBERS
... 2. supported by the facts that electrons undergo diffraction and interference 3. Werner Heisenberg 1927- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: it is impossible to simultaneously identify the position and velocity of an electron, or any particle. 4. wave mechanics looks to suggest the locations of electr ...
... 2. supported by the facts that electrons undergo diffraction and interference 3. Werner Heisenberg 1927- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: it is impossible to simultaneously identify the position and velocity of an electron, or any particle. 4. wave mechanics looks to suggest the locations of electr ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.