HWU4-21 QUESTION: The principal quantum number, n, describes
... The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of a particular orbital as a function of the distance from the center of the nucleus. Additional quantum numbers exist to quantify the other characteristics of the electron. The angular momentum quantum number (ℓ), the magnetic quantum numb ...
... The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of a particular orbital as a function of the distance from the center of the nucleus. Additional quantum numbers exist to quantify the other characteristics of the electron. The angular momentum quantum number (ℓ), the magnetic quantum numb ...
Asymptotic Freedom: From Paradox to Paradigm
... Quarks behave independently when they’re close, but they can’t be pulled apart. An unprecedented hypothesis: CONFINEMENT! Hard-hit quarks accelerate rapidly, without radiating away energy. The strongest force of nature “turns off”: FREEDOM! ...
... Quarks behave independently when they’re close, but they can’t be pulled apart. An unprecedented hypothesis: CONFINEMENT! Hard-hit quarks accelerate rapidly, without radiating away energy. The strongest force of nature “turns off”: FREEDOM! ...
BasicQuantumMechanics18And20January2017
... • It is impossible to simultaneously describe with absolute accuracy the energy of a particle and the instant of time the particle has this energy ...
... • It is impossible to simultaneously describe with absolute accuracy the energy of a particle and the instant of time the particle has this energy ...
Dual Nature of Light. Light Quanta
... 1. Electrons only exist in certain allowed orbits 2. Within an orbit, the electron does not radiate 3. Radiation is emitted or absorbed when changing orbits (quantum leaps) ...
... 1. Electrons only exist in certain allowed orbits 2. Within an orbit, the electron does not radiate 3. Radiation is emitted or absorbed when changing orbits (quantum leaps) ...
Theory of quantum light and matter Research supervisor Prof. Paul Eastham
... the creation of new technologies such as quantum computers. ...
... the creation of new technologies such as quantum computers. ...
Introduction: what is quantum field theory
... of the same type are the same. This is much more serious than it initially sounds. For example, two electrons are identical in every way, regardless of where they came from and what they’ve been through. The same is true of every other fundamental particle. Suppose we capture a proton from a cosmic ...
... of the same type are the same. This is much more serious than it initially sounds. For example, two electrons are identical in every way, regardless of where they came from and what they’ve been through. The same is true of every other fundamental particle. Suppose we capture a proton from a cosmic ...
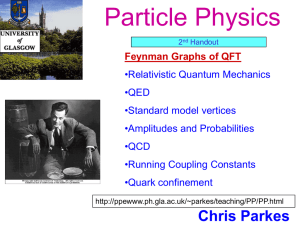
Particle Physics
... The lesson is more general: • Protons/nuclei can look point-like under many experimental conditions • Atoms/molecules can look point-like to a typical human QFT can be used to describe any such system… … it has nothing to do with the system being “fundamental” But QFT becomes essential when the ene ...
... The lesson is more general: • Protons/nuclei can look point-like under many experimental conditions • Atoms/molecules can look point-like to a typical human QFT can be used to describe any such system… … it has nothing to do with the system being “fundamental” But QFT becomes essential when the ene ...
Room: PHYS 238 Time: 9:00 10:15 Monday and Wednesday
... A complete description of electrons, positrons and photons using relativistic quantum mechanics. In quantum mechanics, observable quantities are calculated using the wavefunction for a particle. The definition of the wavefunction is not unique... it could be arbitrarily re-defined at each point in ...
... A complete description of electrons, positrons and photons using relativistic quantum mechanics. In quantum mechanics, observable quantities are calculated using the wavefunction for a particle. The definition of the wavefunction is not unique... it could be arbitrarily re-defined at each point in ...
Planck`s Law and Light Quantum Hypothesis.
... that is, the relation between the radiation density and the mean energy of an oscillator, and they make assumptions about the number of degrees of freedom of the ether, which appear in the above formula (the first factor on the right– hand side). This factor, however, can be derived only from classi ...
... that is, the relation between the radiation density and the mean energy of an oscillator, and they make assumptions about the number of degrees of freedom of the ether, which appear in the above formula (the first factor on the right– hand side). This factor, however, can be derived only from classi ...
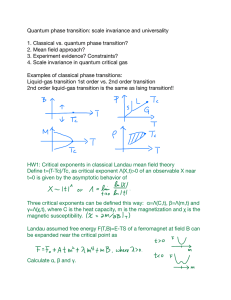
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.