kuliah farmakologi antidepresan
... the spinal cord and motor neurons and to a lesser extent through interaction with α3-containing receptors ...
... the spinal cord and motor neurons and to a lesser extent through interaction with α3-containing receptors ...
Brief Receptor Theory
... sometimes another reference compound if the endogenous ligand is not known); a partial agonist causes less than a maximal response. – Intrinsic efficacy (outmoded): the property of how a ligand causes biological responses via a single receptor (hence a property of a drug). ...
... sometimes another reference compound if the endogenous ligand is not known); a partial agonist causes less than a maximal response. – Intrinsic efficacy (outmoded): the property of how a ligand causes biological responses via a single receptor (hence a property of a drug). ...
PSY650-Antipsychotics-Sedative-Hypnotics
... • Over 2,500 barb’s synthesized and 50 marketed • Now about 10 are “going strong” – Benzo’s knocked them out of the market • Better marketed • Lower abuse potential • Higher TI ...
... • Over 2,500 barb’s synthesized and 50 marketed • Now about 10 are “going strong” – Benzo’s knocked them out of the market • Better marketed • Lower abuse potential • Higher TI ...
Dr. Brown (Outlined) - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Nicotine, alcohol, marijuana, heroin, aphetamine and caffeine (?) trigger DA release Nucleus accumbens: DA “pleasure center”, lesions in this region reduce response to DA DA and cocaine addiction ...
... Nicotine, alcohol, marijuana, heroin, aphetamine and caffeine (?) trigger DA release Nucleus accumbens: DA “pleasure center”, lesions in this region reduce response to DA DA and cocaine addiction ...
File - NorthStar Mental Wellness
... • As a stress hormone, norepinephrine affects parts of the brain, such as the amygdala, where attention and responses are controlled.2 Along with epinephrine, norepinephrine also underlies the fight-or-flight response, directly increasing heart rate, triggering the release of glucose from energy sto ...
... • As a stress hormone, norepinephrine affects parts of the brain, such as the amygdala, where attention and responses are controlled.2 Along with epinephrine, norepinephrine also underlies the fight-or-flight response, directly increasing heart rate, triggering the release of glucose from energy sto ...
Patrick chapter 19 part 2
... 3. Methacholine, carbachol, and bethanechol are acetylcholine agonists at the muscarinic receptor. Draw the structure of each and explain the rationale behind the structural modifications. Describe how each agonist is used clinically. 4. Atropine and scopolamine (hyocine) are cholinergic antagonists ...
... 3. Methacholine, carbachol, and bethanechol are acetylcholine agonists at the muscarinic receptor. Draw the structure of each and explain the rationale behind the structural modifications. Describe how each agonist is used clinically. 4. Atropine and scopolamine (hyocine) are cholinergic antagonists ...
5th Lecture 1433
... Drugs which bind through weak bonds to their receptors are generally more selective than drugs which bind through very strong bonds This is because weak bonds require a very precise fit of the drug to its receptor if an interaction is to occur Only a few receptor types are likely to provide su ...
... Drugs which bind through weak bonds to their receptors are generally more selective than drugs which bind through very strong bonds This is because weak bonds require a very precise fit of the drug to its receptor if an interaction is to occur Only a few receptor types are likely to provide su ...
Lecture 05 - binding quant - Cal State LA
... While the occupancy theory simulates actual dose-response curves, (theoretically, KD = EC50), it does not account for agonists that do not produce the maximum effect. Modified occupancy theory: modified to separate the binding affinity from the intrinsic activity () of the compound. That is, a comp ...
... While the occupancy theory simulates actual dose-response curves, (theoretically, KD = EC50), it does not account for agonists that do not produce the maximum effect. Modified occupancy theory: modified to separate the binding affinity from the intrinsic activity () of the compound. That is, a comp ...
Pharmacology
... Interaction of drugs with cellular proteins, such as receptors or enzymes, to control changes in physiological function of particular organs. • Drug-Receptor Interactions – Binding ...
... Interaction of drugs with cellular proteins, such as receptors or enzymes, to control changes in physiological function of particular organs. • Drug-Receptor Interactions – Binding ...
PPT
... • Drugs that block or reduce the action of an agonist are termed antagonists. • Antagonism most commonly results from competition with an agonist for the same or overlapping site on the receptor (a syntopic interaction) • Physical antagonist binds to the drug and prevents its absorption like charcoa ...
... • Drugs that block or reduce the action of an agonist are termed antagonists. • Antagonism most commonly results from competition with an agonist for the same or overlapping site on the receptor (a syntopic interaction) • Physical antagonist binds to the drug and prevents its absorption like charcoa ...
Chapter 4
... Some drugs can bind to postsynaptic receptors like NT Direct agonist – a drug that mimics the effects of a NT by binding with and acting on a receptor (Step 6) Receptor blocker – a drug that binds with a receptor but does not activate it; prevents the natural ligand from binding with the recep ...
... Some drugs can bind to postsynaptic receptors like NT Direct agonist – a drug that mimics the effects of a NT by binding with and acting on a receptor (Step 6) Receptor blocker – a drug that binds with a receptor but does not activate it; prevents the natural ligand from binding with the recep ...
Neurotransmitters
... Drugs that boost GABA’s effects have a calming or relaxing effect. Reduced levels of GABA may play a role in emotional disorders in which anxiety is a core feature. ...
... Drugs that boost GABA’s effects have a calming or relaxing effect. Reduced levels of GABA may play a role in emotional disorders in which anxiety is a core feature. ...
Abstract
... receptor antagonists that block both AT1 and AT2 receptor subtypes (eg saralasin). AT1-selective antagonists have also been studied in this model, at pharmacologically relevant doses. The AT1 blocker eprosartan reduced sympathetically-stimulated increases in blood pressure to a greater extent than c ...
... receptor antagonists that block both AT1 and AT2 receptor subtypes (eg saralasin). AT1-selective antagonists have also been studied in this model, at pharmacologically relevant doses. The AT1 blocker eprosartan reduced sympathetically-stimulated increases in blood pressure to a greater extent than c ...
Jeopardy
... receptor is an allosteric modulatory site, in addition to the benzodiazepine, this needs to be present to alter the function of the GABA A receptor ...
... receptor is an allosteric modulatory site, in addition to the benzodiazepine, this needs to be present to alter the function of the GABA A receptor ...
Drug Receptors
... Drugs act on the cell membrane by physical and/or chemical interactionsusually through specific drug receptor sites known to be located on the membrane. Some receptor sites have been identified with specific parts of proteins and nucleic acids. In most cases, the chemical nature of the receptor site ...
... Drugs act on the cell membrane by physical and/or chemical interactionsusually through specific drug receptor sites known to be located on the membrane. Some receptor sites have been identified with specific parts of proteins and nucleic acids. In most cases, the chemical nature of the receptor site ...
Document
... Side Effects: fatigue, dizziness, and sedation. Due to: the peripheral anticholinergic effects and the “interactions with a number of neurotransmitter systems in the CNS” ...
... Side Effects: fatigue, dizziness, and sedation. Due to: the peripheral anticholinergic effects and the “interactions with a number of neurotransmitter systems in the CNS” ...
THE UNIVERSITY OF AUCKLAND
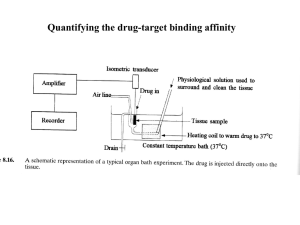
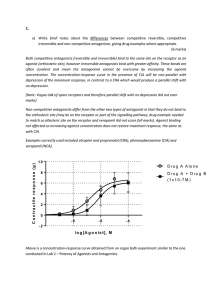
... a) Write brief notes about the differences between competitive reversible, competitive irreversible and non-competitive antagonism, giving drug examples where appropriate. (6 marks) Both competitive antagonists (reversible and irreversible) bind to the same site on the receptor as an agonist (orthos ...
... a) Write brief notes about the differences between competitive reversible, competitive irreversible and non-competitive antagonism, giving drug examples where appropriate. (6 marks) Both competitive antagonists (reversible and irreversible) bind to the same site on the receptor as an agonist (orthos ...
Pharmacology introduction Lecture three Dr. nahlah 21-10
... 2. Irreversible which is usually long-lasting for new enzyme synthesis, e.g., irreversible anticholinesterases. Action on specific receptors (Drug Receptor Interactions): receptors are macromolecular protein structures present on cell membrane or within the cell (cytoplasmic or nuclear) that react s ...
... 2. Irreversible which is usually long-lasting for new enzyme synthesis, e.g., irreversible anticholinesterases. Action on specific receptors (Drug Receptor Interactions): receptors are macromolecular protein structures present on cell membrane or within the cell (cytoplasmic or nuclear) that react s ...
2016 department of medicine research day
... due to ligand-dependent or –independent mechanisms. Another class of ERα antagonist- termed selective estrogen receptor downregulators (SERDs)- is represented by fulvestrant, a drug whose mechanism of action differs from that of SERMs. Treatment with fulvestrant causes ERα downregulation, an event t ...
... due to ligand-dependent or –independent mechanisms. Another class of ERα antagonist- termed selective estrogen receptor downregulators (SERDs)- is represented by fulvestrant, a drug whose mechanism of action differs from that of SERMs. Treatment with fulvestrant causes ERα downregulation, an event t ...
F.Neuroleptics
... component of neuroleptanesthesia, promethazine is not a good antipsychotic drug, but the agent is used in pruritus because of its antihistaminic properties. Adverse Effects: 1. Parkinsonian effects due to excess of cholinergic influence may be normalized by anticholinergics but often the symptoms pe ...
... component of neuroleptanesthesia, promethazine is not a good antipsychotic drug, but the agent is used in pruritus because of its antihistaminic properties. Adverse Effects: 1. Parkinsonian effects due to excess of cholinergic influence may be normalized by anticholinergics but often the symptoms pe ...
Haron Kirikiru Wk 10 discussion - PPI 1. What laboratory studies are
... the proton pump, significantly reducing the level of HCL produced, while H2 receptor antagonist only inhibit parietal cell stimulation attributed to H2 receptors activation, with reduced effect on ACh and gastrin receptors. 3.) Antacid are no longer the mainstay of acid related gastric ulcers and/or ...
... the proton pump, significantly reducing the level of HCL produced, while H2 receptor antagonist only inhibit parietal cell stimulation attributed to H2 receptors activation, with reduced effect on ACh and gastrin receptors. 3.) Antacid are no longer the mainstay of acid related gastric ulcers and/or ...
9.98 Neuropharmacology January
... There is a connection between the NE system and anxiety In general, the NE system is activated by alerting situations Some of the effects of anxiolytic drugs can be explained with the modulation of LC firing LC firing is activated by the corticotropin-releasing factor and it is inhibited by GABA and ...
... There is a connection between the NE system and anxiety In general, the NE system is activated by alerting situations Some of the effects of anxiolytic drugs can be explained with the modulation of LC firing LC firing is activated by the corticotropin-releasing factor and it is inhibited by GABA and ...
DOSE *RESPONSE CURVES
... maximal efficacy or ceiling effect (greatest attainable response) slope (change in response per unit dose). Biologic variation (variation in magnitude of response among test subjects in the same population given the same dose of drug) also occurs. Graphing dose-response curves of drugs studied under ...
... maximal efficacy or ceiling effect (greatest attainable response) slope (change in response per unit dose). Biologic variation (variation in magnitude of response among test subjects in the same population given the same dose of drug) also occurs. Graphing dose-response curves of drugs studied under ...
Quiz 1 Key - chem.uwec.edu
... 1. On a single graph, draw a typical dose/response curve for the new natural product drug, hartseloic acid. Also draw dose/response curve for the drug in the presence of (A) , a competitive antagonist and (B) a non-competitive antagonist. In addition, include a curve for a newly discovered similar d ...
... 1. On a single graph, draw a typical dose/response curve for the new natural product drug, hartseloic acid. Also draw dose/response curve for the drug in the presence of (A) , a competitive antagonist and (B) a non-competitive antagonist. In addition, include a curve for a newly discovered similar d ...
Direct cholinergic agonists
... These drugs [reversible cholinestrease inhibitors] can have effects on the cholinergic system in the CNS, if the drug can cross the blood-brain barrier. The effects range from tremor, anxiety, and restlessness to coma. The organophosphates, because of their lipid solubility, rapidly cross into the ...
... These drugs [reversible cholinestrease inhibitors] can have effects on the cholinergic system in the CNS, if the drug can cross the blood-brain barrier. The effects range from tremor, anxiety, and restlessness to coma. The organophosphates, because of their lipid solubility, rapidly cross into the ...
5-HT3 antagonist
The 5-HT3 antagonists, informally known as ""setrons"", are a class of drugs that act as receptor antagonists at the 5-HT3 receptor, a subtype of serotonin receptor found in terminals of the vagus nerve and in certain areas of the brain.With the notable exception of alosetron and cilansetron, which are used in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome, all 5-HT3 antagonists are antiemetics, used in the prevention and treatment of nausea and vomiting. They are particularly effective in controlling the nausea and vomiting produced by cancer chemotherapy and are considered the gold standard for this purpose.The 5-HT3 antagonists may be identified by the suffix –setron, and are classified under code A04AA of the WHO's Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System.