WORKING OF scr….
... current IC2 flows through the base of transistor T1.So,the collector current IC1 increases. This is cumulative process. As a result a large current is conducted by the device in very short time, the resistance of the device decrease too much. So ,load can be control by very small positive pulse in S ...
... current IC2 flows through the base of transistor T1.So,the collector current IC1 increases. This is cumulative process. As a result a large current is conducted by the device in very short time, the resistance of the device decrease too much. So ,load can be control by very small positive pulse in S ...
Chapter_4_Lecture_PowerPoint
... a phase angle equal to the phase shift of the sinusoidal signal referenced to a cosine signal. 3. When one is using phasor notation, it is important to note the specific frequency ω of the sinusoidal signal, since this is not explicitly apparent in the phasor expression. ...
... a phase angle equal to the phase shift of the sinusoidal signal referenced to a cosine signal. 3. When one is using phasor notation, it is important to note the specific frequency ω of the sinusoidal signal, since this is not explicitly apparent in the phasor expression. ...
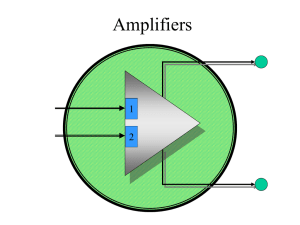
Amplifiers
... Note that even though impedance has dropped by factor of 2, power does not quite double. ...
... Note that even though impedance has dropped by factor of 2, power does not quite double. ...
Wireless Communications and Networks
... AM and FM modulators are therefore essentially different in design. FM can be produced by direct frequency modulation or by indirectly phase modulation. ...
... AM and FM modulators are therefore essentially different in design. FM can be produced by direct frequency modulation or by indirectly phase modulation. ...
Name - edl.io
... Nothing. The series is in parallel, so if they shut off, it doesn’t affect the rest of the circuit. c. Explain why household circuits are set up in parallel. ...
... Nothing. The series is in parallel, so if they shut off, it doesn’t affect the rest of the circuit. c. Explain why household circuits are set up in parallel. ...
Reducing Crosstalk in Vertically
... must have well-defined borders. Therefore, the problem is unique to VI-CMOS image sensors. ...
... must have well-defined borders. Therefore, the problem is unique to VI-CMOS image sensors. ...
DN-26 UC3842A Low-Cost Start-up and Fault Protection Circuit PDF
... high. This is fed to transistor Q1 which pulls the Rt/Ct input at pin 4 low, thus "freezing" the oscillator, while keeping the PWM output high. Once a valid fault (greater than 1 volt) is received at the current sense input (pin 3), the output at pin 6 will go low. Transistor Q1 is then turned off, ...
... high. This is fed to transistor Q1 which pulls the Rt/Ct input at pin 4 low, thus "freezing" the oscillator, while keeping the PWM output high. Once a valid fault (greater than 1 volt) is received at the current sense input (pin 3), the output at pin 6 will go low. Transistor Q1 is then turned off, ...
Transmission type rf single electron transistor operation of a
... conventional electron transport experiments, however, are restricted to dc or low-frequency current measurements through the device, since the high impedance of SET devices and the large capacitance of the cables determine the highest frequency, typically 10-100Hz or a few kHz at most. This is much ...
... conventional electron transport experiments, however, are restricted to dc or low-frequency current measurements through the device, since the high impedance of SET devices and the large capacitance of the cables determine the highest frequency, typically 10-100Hz or a few kHz at most. This is much ...
Tech Note 10 Microphone Amplifier Design, or, Why
... are mostly operated on internationally-standardized phantom power, which sets some hard limits on the amount of power available for such a circuit. Modern sound recording requires a very wide dynamic range – it’s not possible to preserve the lowest noise floor along with a high overload point to han ...
... are mostly operated on internationally-standardized phantom power, which sets some hard limits on the amount of power available for such a circuit. Modern sound recording requires a very wide dynamic range – it’s not possible to preserve the lowest noise floor along with a high overload point to han ...
16.3 Notes
... When devices are connected in __________________, the voltage across each device is the ______________. The __________________ in each device does not have to be the same. Instead the sum of all the devices equals the ____________ current. A _________________ in any one path in a parallel circuit do ...
... When devices are connected in __________________, the voltage across each device is the ______________. The __________________ in each device does not have to be the same. Instead the sum of all the devices equals the ____________ current. A _________________ in any one path in a parallel circuit do ...
radio communications: am and fm
... The noise added to the FM signal by the receiver will also be occupying the same band as the FM signal itself. Such bandpass noise will corrupt the instantaneous value of the FM signal, and thus corrupt the zero-crossings. It is the corruption of the zero-crossings that will affect the demodulated s ...
... The noise added to the FM signal by the receiver will also be occupying the same band as the FM signal itself. Such bandpass noise will corrupt the instantaneous value of the FM signal, and thus corrupt the zero-crossings. It is the corruption of the zero-crossings that will affect the demodulated s ...
Practice Electricity Questions
... You may want to color code the circuits to get a better idea of what’s going on… ...
... You may want to color code the circuits to get a better idea of what’s going on… ...
this document - Mutable Instruments
... not have enough room to implement a proper active filter for smoothing the resonance CV. We went cheap with a passive RC filter (22kΩ, 68nF , yielding a cutoff frequency of 106Hz), but there’s a big caveat here! From the SSM2164 datasheet, the CV inputs of the SSM2164 are connected to a 4.5kΩ / 500Ω ...
... not have enough room to implement a proper active filter for smoothing the resonance CV. We went cheap with a passive RC filter (22kΩ, 68nF , yielding a cutoff frequency of 106Hz), but there’s a big caveat here! From the SSM2164 datasheet, the CV inputs of the SSM2164 are connected to a 4.5kΩ / 500Ω ...
Homework 2 Solution Set
... The hidden assumptions in this problem are (1) that there is no mismatch between the line and load; if this condition is present, you may need much more signal to satisfy the receiver! (2) Everything in the system is at the same impedance level (otherwise using voltage decibels would be meaningless, ...
... The hidden assumptions in this problem are (1) that there is no mismatch between the line and load; if this condition is present, you may need much more signal to satisfy the receiver! (2) Everything in the system is at the same impedance level (otherwise using voltage decibels would be meaningless, ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.