Homework
... 7. As the resistance in a circuit increases, the current flow will _______________________. 8. Electrical power is measured in _______________________. 9. Electrical force is measured in ________________________. 10. The resistance in a conductor ____________________ as the diameter gets larger 11. ...
... 7. As the resistance in a circuit increases, the current flow will _______________________. 8. Electrical power is measured in _______________________. 9. Electrical force is measured in ________________________. 10. The resistance in a conductor ____________________ as the diameter gets larger 11. ...
504e - İnfotek
... The new 50MHz analog oscilloscope HM504 is unsurpassed in its price range, convincing by high performance measurement characteristics and operation comfort. Other outstanding features are the integrated 100 MHz frequency counter, which also enables period time measurement and five automatic voltage ...
... The new 50MHz analog oscilloscope HM504 is unsurpassed in its price range, convincing by high performance measurement characteristics and operation comfort. Other outstanding features are the integrated 100 MHz frequency counter, which also enables period time measurement and five automatic voltage ...
Hw4-1
... Electrical Engineering is all about ‘what can you do to a voltage’ (or current, or resistance…). Op amp circuits let us do many different things to our voltages, currents, and resistance – such as amplifying (or reducing), comparing, adding, differencing, etc. In the next several homework assignment ...
... Electrical Engineering is all about ‘what can you do to a voltage’ (or current, or resistance…). Op amp circuits let us do many different things to our voltages, currents, and resistance – such as amplifying (or reducing), comparing, adding, differencing, etc. In the next several homework assignment ...
FIGURE 4.2-1 Circuit with an independent voltage source and an
... FIGURE 4.5-4 Mesh currents, i1 and i2, and element current, i1 – i2, of a (a) generic circuit element, (b) current source, and (c) resistor. ...
... FIGURE 4.5-4 Mesh currents, i1 and i2, and element current, i1 – i2, of a (a) generic circuit element, (b) current source, and (c) resistor. ...
Unleashing the LM386
... Dæliveien 1, NO 1383 Asker, Norway. The LM386 must be one of the most popular audio output amplifiers among radio amateurs, despite having been around for a long time. It can be obtained in both dual-in-line and surfacemount packages and outputs 325 mW in the standard version that runs from 4-12 Vol ...
... Dæliveien 1, NO 1383 Asker, Norway. The LM386 must be one of the most popular audio output amplifiers among radio amateurs, despite having been around for a long time. It can be obtained in both dual-in-line and surfacemount packages and outputs 325 mW in the standard version that runs from 4-12 Vol ...
Slide 1
... For the transistor, even though it has three basic configurations, they are all fourterminal configurations, and thus, the resulting equivalent circuit will have the same format. The h-parameter will however change with each configuration. To distinguish which parameter has been used or which is ava ...
... For the transistor, even though it has three basic configurations, they are all fourterminal configurations, and thus, the resulting equivalent circuit will have the same format. The h-parameter will however change with each configuration. To distinguish which parameter has been used or which is ava ...
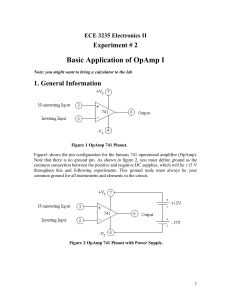
ECE 3235 Electronics II
... 1) Measure the voltage gain and the phase shift at that frequency. Limit the voltage at the input to 80 mV peak-to-peak maximum. 2) Measure accurately the –3 dB frequency fc (sometimes called corner or break frequency) and the phase shift there. 3) Additionally, measure the voltage gain and phase sh ...
... 1) Measure the voltage gain and the phase shift at that frequency. Limit the voltage at the input to 80 mV peak-to-peak maximum. 2) Measure accurately the –3 dB frequency fc (sometimes called corner or break frequency) and the phase shift there. 3) Additionally, measure the voltage gain and phase sh ...
Electronics Engineering - Dronacharya College of Engineering
... A cycle consists of two voltage polarity reversals, current reversals, or electromagnetic field oscillations. Frequency is measured in cycles per second (cps). The unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz). ...
... A cycle consists of two voltage polarity reversals, current reversals, or electromagnetic field oscillations. Frequency is measured in cycles per second (cps). The unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz). ...
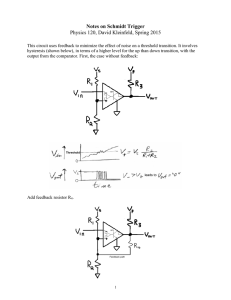
Notes on Schmidt Trigger Physics 120, David Kleinfeld, Spring 2015
... Notes on Schmidt Trigger Physics 120, David Kleinfeld, Spring 2015 This circuit uses feedback to minimize the effect of noise on a threshold transition. It involves hysteresis (shown below), in terms of a higher level for the up than down transition, with the output from the comparator. First, the c ...
... Notes on Schmidt Trigger Physics 120, David Kleinfeld, Spring 2015 This circuit uses feedback to minimize the effect of noise on a threshold transition. It involves hysteresis (shown below), in terms of a higher level for the up than down transition, with the output from the comparator. First, the c ...
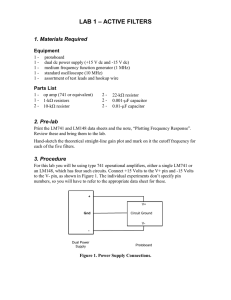
lab 1 – active filters
... 4. Apply the power and measure the Voltages at the two amplifier inputs and its output; all should be at 0 Volts. Correct the circuit if necessary. 5. Set the signal generator amplitude to 1 V peak-to-peak. (Note: the generator output level meter is calibrated only when the unit is driving 50 . The ...
... 4. Apply the power and measure the Voltages at the two amplifier inputs and its output; all should be at 0 Volts. Correct the circuit if necessary. 5. Set the signal generator amplitude to 1 V peak-to-peak. (Note: the generator output level meter is calibrated only when the unit is driving 50 . The ...
Study of Amplitude Modulation Transmitter
... geometries and specifications are possible. The optimumantenna type for a given situation depends on the communications frequency, thedistance to be covered, 3.4.2 Inductor L1 ...
... geometries and specifications are possible. The optimumantenna type for a given situation depends on the communications frequency, thedistance to be covered, 3.4.2 Inductor L1 ...
Wien Bridge Oscillator Automatic Gain Control (AGC)
... Op-amp U2 is configured as an inverting stage with gain = -51. This allows the output Vout to be reasonably large (of order 5V peak) while keeping the V1 output of op-amp U1 (and, more importantly, the drain-source voltage VDS on the MOSFET) small. RB1 and RB2 form a voltage divider that biases the ...
... Op-amp U2 is configured as an inverting stage with gain = -51. This allows the output Vout to be reasonably large (of order 5V peak) while keeping the V1 output of op-amp U1 (and, more importantly, the drain-source voltage VDS on the MOSFET) small. RB1 and RB2 form a voltage divider that biases the ...
Electronics EECE2412 — Spring 2016 Exam #1
... putting down everything you know and hoping I will find something correct in it. • Each question has a vertical black bar providing space for your work and a box for numerical answers. Please write your answer to each question clearly. If it happens to be correct, I give you points quickly and move ...
... putting down everything you know and hoping I will find something correct in it. • Each question has a vertical black bar providing space for your work and a box for numerical answers. Please write your answer to each question clearly. If it happens to be correct, I give you points quickly and move ...
Presentation on basic electricity
... If only gravity is causing the fluid to flow then water can flow out of the end of open pipe where as electrical charge will not flow out of an electrical socket. Gravity is always turned on where as the electrical potential is not turned on until the circuit makes a closed loop. ...
... If only gravity is causing the fluid to flow then water can flow out of the end of open pipe where as electrical charge will not flow out of an electrical socket. Gravity is always turned on where as the electrical potential is not turned on until the circuit makes a closed loop. ...
Expt. 5: Study of Operational Amplifiers Pin-Diagram of IC-741
... 4. Select R1 and Rf such that required pass band gain is obtained. Pass band gain = 1+(RF/R 1). Let R1= RF = 10 kΩ for a pass band gain of 2. 5. Final values of components: R1 = 10 kΩ, RF = 10 kΩ, R = 22 kΩ, C = 0.01 µF, fH=700 Hz. Experimental Procedure: 1. Apply sinusoidal inputs with different fr ...
... 4. Select R1 and Rf such that required pass band gain is obtained. Pass band gain = 1+(RF/R 1). Let R1= RF = 10 kΩ for a pass band gain of 2. 5. Final values of components: R1 = 10 kΩ, RF = 10 kΩ, R = 22 kΩ, C = 0.01 µF, fH=700 Hz. Experimental Procedure: 1. Apply sinusoidal inputs with different fr ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.