Lab 3
... damping” is true for the circuit above. 2. Calculate the resonant frequency of the LC tank in Figure 1 (a) with L = 300 H and C = 100 pF. Verify your calculation with LTSpice simulations. You should do an ac sweep around f0, and also a transient run to observe the natural response. Suggestion: use ...
... damping” is true for the circuit above. 2. Calculate the resonant frequency of the LC tank in Figure 1 (a) with L = 300 H and C = 100 pF. Verify your calculation with LTSpice simulations. You should do an ac sweep around f0, and also a transient run to observe the natural response. Suggestion: use ...
O A RIGINAL RTICLE
... The objective of this project to design and develop a portable solar headphone amplifier system to transmit and receive audio signals is achieved. In this project, two circuits were constructed and tested. The circuits designed are also suitable to be integrated for small world communication system ...
... The objective of this project to design and develop a portable solar headphone amplifier system to transmit and receive audio signals is achieved. In this project, two circuits were constructed and tested. The circuits designed are also suitable to be integrated for small world communication system ...
File - oneNESS AND UNITY
... say A, then modulation factor is A/A = 1 or 100%. The modulation factor indicates the strength and quality of the transmitted signal. The greater the modulation factor, the stronger and clearer will be the signal. However, ...
... say A, then modulation factor is A/A = 1 or 100%. The modulation factor indicates the strength and quality of the transmitted signal. The greater the modulation factor, the stronger and clearer will be the signal. However, ...
Series Circuits - Athens Academy
... • The resistance in the circuit is the sum of the resistances in the series. • Current in the circuit is the same in all parts of the circuit. I = V/R • Different components use (or “drop”) different voltages based on their resistance. V = IR • If one element fails (creating an open circuit), no cur ...
... • The resistance in the circuit is the sum of the resistances in the series. • Current in the circuit is the same in all parts of the circuit. I = V/R • Different components use (or “drop”) different voltages based on their resistance. V = IR • If one element fails (creating an open circuit), no cur ...
THE INVENTION
... receiver gain and therefore effective range without exceeding the transmitter power required for conformance. Unlike any existing system, this increase in system range is equal to that afforded by the high gain antenna at the end of the link path with the least gain and not the more usual algebraic ...
... receiver gain and therefore effective range without exceeding the transmitter power required for conformance. Unlike any existing system, this increase in system range is equal to that afforded by the high gain antenna at the end of the link path with the least gain and not the more usual algebraic ...
There are 9 Multiple choice questions, 3 fill in the blank, and two
... (a) It is used to measure resistance of a single resistor in a network without removing the resistor II Fill in the blanks from the circuit (b) It is used to measure resistance in a circuit on;y 1. A solar cell with an e ciency of 12% drives a small of the circuit is powered by low-voltage batteries ...
... (a) It is used to measure resistance of a single resistor in a network without removing the resistor II Fill in the blanks from the circuit (b) It is used to measure resistance in a circuit on;y 1. A solar cell with an e ciency of 12% drives a small of the circuit is powered by low-voltage batteries ...
Physics 422 - Spring 2016 - Midterm Exam, March 10
... Answer all questions in the exam booklets provided. There are 6 questions - please answer any five of them. Explain your reasoning clearly but concisely. (but it is not expected to be at the same level as the homework) ((although some of the homework is really pretty bad...)) (((just not yours...))) ...
... Answer all questions in the exam booklets provided. There are 6 questions - please answer any five of them. Explain your reasoning clearly but concisely. (but it is not expected to be at the same level as the homework) ((although some of the homework is really pretty bad...)) (((just not yours...))) ...
In this method cross correlation is used to find the impedance of the
... Using another approach a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) generates an AC control voltage signal which is sent to the crystal by an Op-amp having it oscillate at a defined input. Using the Op-amp here will also be beneficial in allowing low output impedance, and flat frequency response. The outpu ...
... Using another approach a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) generates an AC control voltage signal which is sent to the crystal by an Op-amp having it oscillate at a defined input. Using the Op-amp here will also be beneficial in allowing low output impedance, and flat frequency response. The outpu ...
Plan - Duplin County Schools
... I will make sure the current only has one path. I will explain to my partner the electron path. I will trace the electron path of the circuit. ...
... I will make sure the current only has one path. I will explain to my partner the electron path. I will trace the electron path of the circuit. ...
resonance experiment
... and –1.5. The quality factor was 10.8 for R1 33 ohms and 2.3 for R1 330 ohms. The circuit behaved as expected. ...
... and –1.5. The quality factor was 10.8 for R1 33 ohms and 2.3 for R1 330 ohms. The circuit behaved as expected. ...
Freshman Science Study Guide
... 10. Ohm’s law states that as the _________________in a circuit _______________ the current will decrease. ...
... 10. Ohm’s law states that as the _________________in a circuit _______________ the current will decrease. ...
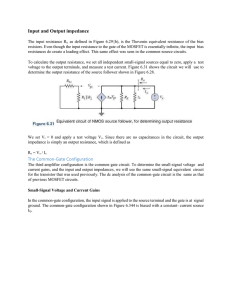
The Common-Gate Configuration
... We set Vi = 0 and apply a test voltage Vx. Since there are no capacitances in the circuit, the output impedance is simply an output resistance, which is defined as Ro = Vx / Ix ...
... We set Vi = 0 and apply a test voltage Vx. Since there are no capacitances in the circuit, the output impedance is simply an output resistance, which is defined as Ro = Vx / Ix ...
Lecture #1: Basic Op-Amp
... 1) The input impedance Ri is infinite - i.e. no current flows into either input. 2) The output impedance Ro is zero - i.e. the op-amp can drive any load impedance to any voltage. 3) The open-loop gain (A) is infinite. 4) The bandwidth is infinite. 5) The output voltage is zero when the input voltage ...
... 1) The input impedance Ri is infinite - i.e. no current flows into either input. 2) The output impedance Ro is zero - i.e. the op-amp can drive any load impedance to any voltage. 3) The open-loop gain (A) is infinite. 4) The bandwidth is infinite. 5) The output voltage is zero when the input voltage ...
Deriving Voltage and Current from HF RFID/NFC Reader Field
... • Vincent Chan (TI HK office) expressed that potential customer in his region would like to power display on transit card from High Frequency (HF, 13.56MHz) reader field using the existing tag coil and additional circuitry. • Simple circuit was designed and prototyped to demonstrate this capability. ...
... • Vincent Chan (TI HK office) expressed that potential customer in his region would like to power display on transit card from High Frequency (HF, 13.56MHz) reader field using the existing tag coil and additional circuitry. • Simple circuit was designed and prototyped to demonstrate this capability. ...
INTELLIGENT TRAIN ENGINES
... transmitting signals only when the red light is on. If there is green light no transmission. The engine has a receiver which catches these transmitted signals and takes desire actions. Both the transmitter and receiver are of RF type with minimum range of 2KM, so that train can get enough time to de ...
... transmitting signals only when the red light is on. If there is green light no transmission. The engine has a receiver which catches these transmitted signals and takes desire actions. Both the transmitter and receiver are of RF type with minimum range of 2KM, so that train can get enough time to de ...
A Simple Clock Phys 3610/6610 Lab 10 Student: TA:
... A Simple Clock Task: Using only parts from your lab kit: Design, build, and debug a circuit that will count and display seconds from 0 to 9 endlessly. Preliminaries: If the 60 Hz square wave does not look very good on the scope, use a LM 311 voltage comparator to clean it up with the circuit given i ...
... A Simple Clock Task: Using only parts from your lab kit: Design, build, and debug a circuit that will count and display seconds from 0 to 9 endlessly. Preliminaries: If the 60 Hz square wave does not look very good on the scope, use a LM 311 voltage comparator to clean it up with the circuit given i ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.