* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.3 Plates Move Apart
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
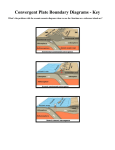
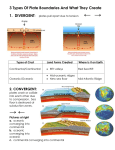
Plates Move Apart Learn about: Different plate boundaries What happens when plates move apart. How the direction and speed of plates can be measured. Plate Boundaries There are three kinds of plate boundaries Divergent Convergent Transform Both the kind of boundary and the kind of plate affects how plates interact Divergent Boundary Most divergent Boundaries occur on the ocean sea floor. Types of Divergent Boundaries (What happens there?) 1. Oceanic – Oceanic Divergence 2. Mid-Ocean Ridges Rift Valleys Continental – Continental Divergence Rift Valleys Oceanic-Oceanic Divergence This is where two oceanic plates were diverging forming new crust Oceanic-Oceanic Divergence (Continued) This is where oceanic plates are being ripped apart magma comes up from deep within the earth’s crust and forms pillow basalts and under water vents The Mid Atlantic Ridge The Mid Atlantic Ridge is an example of oceanicoceanic divergence Over millions of years the continents have moved enough to create an ocean The ridge also contains the longest mountain chain in the world (6214 miles long) (15 miles wide) (6 miles deep) http://www.wwnorton.com/college/geo/egeo/flash/2_5.swf Mid- Atlantic Ridge (continued) Review Oceanic-Oceanic Divergent Boundaries With your neighbor, review what happens at Divergent Oceanic-Oceanic Boundaries Remember to put these concepts into your own words. How can you best remember the information? (You have 2 minutes) Continent-Continent Divergence Boundary Continental plates diverge in the same way as Oceanic plates Cliffs and ridges are more easily visible in continental divergence Continental- Continental divergent Boundary Same as Oceanic – Oceanic Boundaries rift vallies will occur. What is different? In this case, rift valley’s happen on land. Two piece of land are pulled apart, revealing magma. (it will cool and harden) Creating what is called a continental rift valley (it could fill with water, making a lake.) Rift Valleys East African Rift Valley The East African Rift Valley formed when a three way split almost tore Africa apart Example of a Continental rift valley. East African Valley (On land Rift Valley) Review the difference! What is the difference between? Oceanic – Oceanic divergence and Continental – Contiental divergance (you have 1 minute) 3.4 Convergent Boundaries Learn: What happens when: two continental plates converge An oceanic plate converges with another plate One plate scrapes past another. Types of Convergent Boundaries Continental – Continental Collision Contiental – Oceanic Subduction Oceanic – Oceanic Convergent Continental-Continental Convergence When two continental crusts collide the pressure builds up and they form Mountains Since both plates are approximately equal density neither subducts and no volcanoes are formed Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence When oceanic plates collide a subduction zone occurs One plate goes under the other deep beneath the ocean floor (creating a deep ocean trench.) Island Arcs- can form when oceanic plates converge Japan Japan is part of an Island Arc formed by oceanic-oceanic convergence Continental – Oceanic Convergent Boundary Occurs when ocean crust and continental crust are pushed together What happens there? (Subduction Zone) Subduction – one plate is pushed under another. Which Plate always goes under? And why? Subduction Zone? What kinds of landforms are created at a Subduction Zone? •Deep Ocean Trenches •Volcanoes (after a long period of time.) •Coastal Mountain Ranges (Parallel to the Coast.) (see next slide for an illustration) Transform Faults Transform faults occur along divergent oceanic and continental plate boundaries Plates slide past each other building up tension until the tension is released during an earthquake San Andreas Fault The San Andreas fault is a surface fault line going through San Francisco In 1906 an Earthquake hit San Francisco setting breaking gas and water lines and causing fires that could not be stopped Hot Spots Another type of tectonic activity are areas called hot spots A hot spot is where magma rises to the earths crust melting the land and forming a line of volcanoes as the earth’s crust moves past it Hot Spots Hawaii In oceans hot spots form Island chains Since the hot spot is under mafic rocks the lava flows smoothly down the mountain creating shield volcanoes like Hawaii Yellowstone National Park Hotspots below continents are highly explosive and form craters called calderas The force required for Felsic rock is so great the eruption vaporizes the land and sends ash over large parts of continents