* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electromagnetic Induction
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
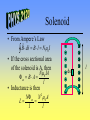
Faraday’s Law and Inductance Faraday’s Law • A moving magnet can exert a force on a stationary charge. Remember: • Faraday’s Law of Induction d m N dt m B dA • Induced emf is directly proportional to the change in the magnetic flux. Collapsing Field • Ex. What is the induced emf in a 100 turn coil with an area of 0.035 m² when the magnetic field decreases linearly from 2.5 T to 0 T in 10 seconds? B Moving Loop • Ex. For a rectangular loop moving through a magnetic field, plot the total flux, emf, and force on the loop with respect to time. v l w d B l = 20 cm w = 20 cm v = 5 m/s B = 0.75 T d = 60 cm R=1W Motional EMF • For a moving conductor in a magnetic field qE qvB or R V lvB With a resistor attached the current is lvB I R l v Lenz’s Law • Polarity of the induced emf is such that it produces a current that will create a magnetic flux to oppose the change in magnetic flux through the loop. As the loop enters the field the downward flux increases. Therefore, the current flows I in the loop to generate an upward flux to cancel the change. v Induced EMF • A changing magnetic field always generates an electric field. d m E ds dt • This electric field is non-conservative and time varying. Generators & Motors • AC Generator - A spinning loop in a magnetic field generates an AC voltage. m BA cost NBA sin t • Eddy Currents - Currents generated within a conductor due to changes in the magnetic field. Induced EMF • Self induced emf is due to a change in current. d m dI N L dt dt • Inductance, L N m L I • Units, henry (H) which is a V·s/A Solenoid • From Ampere’s Law B ds B l N0 I • If the cross sectional area of the solenoid is A, then N 0 IA m B A • Inductance is then l N m N 2 0 A L I l ds l Solenoid (cont.) • Ex. What is the inductance of a solenoid of 500 turns where the length is 0.05 m and the diameter of the coil is 0.04 m? A r (0.02m) 1.26 10 m 2 2 3 2 N 2 0 A (500) 2 4 107 N / A2 (1.26 103 m2 ) L l (0.05m) L 7.9 10 3 H RL Circuits • After the switch is closed, Kirchoff’s rules gives R dI IR L 0 dt • Solution is I (t ) 1 e R Rt / L I 1 e t / 0 • If power supply is shorted out, then I (t ) I 0 e t / L L R RL Circuit Current • How much current is flowing in a 10W 0.1H 1.0I0 RL circuit 15 ms after 0.5I0 it is hooked up to a 10V power supply? 0.1H 10ms 10W Current Flow 0 10V 15ms / 10 ms I (t ) 1 e 0.78 A 10W 2 3 4 Energy in the Magnetic Field • Power is voltage times current, but also the rate at which work is done. dI P I IL dt dU m dW P dt dt dU m dI IL dt dt • Energy Density of a solenoid: Um B2 um A l 2 0 U m LI 1 2 2 Important E & M Equations • Maxwell’s Equations Q E dA 0 B d A 0 • Lorentz Force d m E ds dt d e B ds 0 I 0 0 dt F qE qv B