* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Click here to download
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
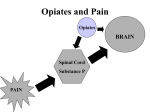
Medication Management of the Chronic Pain Patient Benjamin Meeks, CFNP Pain Medicine Associates Overview Overview of Pain Transmission Rational Poly-pharmacy NASIDS Antidepressants Anti-Seizure Medications Topical Medications Opiates Cannabinoids Transmission of Pain Peripheral Sensitization Peripheral Neurons Ascending Spinal Cord Brain Structures/Mechanisms Descending Spinal Cord Peripheral Sensatization Painful Stimuli Sodium and Calcium Channel Depolarization Glutamate Substance P Bradykinin Prostaglandin Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Glial Cells, Schwann Cells, Microglia, Astrocytes Nitric Oxide Arachidonic Acid Ascending Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn NMDA, AMPA G-Protein and Tyrosine Receptors Summation Response Spinothalamic Tract Brain Singnal from Spinothalamic Tract Concioius perception of pain Serotonin/Norepinephrine Endogenous Opioids in Periaqueductal Gray Descending Spinal Cord Norepinephrine (Inhibitory) Serotonin (Inhibitory and Excitatory) Dopamine (Inhibitory and Excitatory) Rational Poly-Pharmacy Norepinephrine Opiate Receptors – Peripheral and Central Afferents Peripheral Sensitization COX-2/Acid Sensitive Channels Subsbstance P Calium and Sodium Channels Prostaglandins “Multidrug analgesic approaches take advantage of complementary mechainisms of different drug classes to enhance analgesia” NSAIDS Inhibit Cyclooxygenase, prostaghaldins and acid-sensative ion channels GI, Kidney Risk, Coronary Risk Opiate Sparring Antidepressants TCA's Norepinephrine,Imipramine, Amitryptiline, Desipramine Anticholinergic Side Effects Cariovascular Toxicity SSRI's – Little data to support use in pain Venlafaxine – Pain data is mixed Milnacipran – Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor FDA approved fibromyalgia Duloxetine Inhibit serotonin and norephephrine uptake FDA approved for diabetic peripheral neuropathy, low Antiseizure Medications Stabilize Calcium and/or Sodium Channels Increases Spinal Norepinephrine Concentration Carbamaepine, Oxycarbamazepine, Gabapentin, Pregabalin, Topiramate, Lamotragine Extensively studied in peripheral neuropathic states Dizzyness, somnolence and peripheral edema Topical Medications Capsaicin – Substance P depletion Lidocaine – Sodium Channel Blockade OTC Ointment – prescription patch 3 – 10% Ointment or 5% patch Compounded Ointments/Gels Lidocaine, Baclofen, Ketoprofen, Amitrytyline, Gabapentin, Ketamine, Cyclobenzaprine Opioids – No controlled studies Topical Diclofenac Gel or patch Better tolerated than by mouth Opiates Immediate Release Extended Release Immediate Release Opiates May be associated with increased risk of tolerance and addiction compared to extended release opiates Analgesic Half-life 2 – 4 hours Onset by mouth 5 – 40 minutes Oxycodone, oxymorphone, codeine, morphine, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, tramadol, tapentadol Constipation, nausea, confusion, dizzyness, itching Indicated for as needed usage Immediate Release Opiates Buprenorphine – Mu agonist/antagonist long half life suitable for once daily dosing Methadone – Mu/NMDA agonist Unpredictable half-life Extended Release Opiates May be associated with low risk of tolerance and addiction Indicated to chronic pain in patients who require constant opiate dosing MS ER tabs, MS ER Capsules, Hyromorphone ER Tabs, Oxycodone ER Tabs, Oxymorphone ER Tabs, Tramadol ER tabs, Tapentadol ER Tabs, Fentanyl Patch, Buprenorphine Patch Cannabinoids Dronabinol FDA approved for chemotherapy induced nausea and AIDS wasting Smoked and Nebulized Cannabinoids activity at Mu and Delta receptors Does not alter opiate pharmacokinectics Little placebo controlled data for chronic pain Low dose nebulized canabinoid not assoctied with “high” Summary Cyclooxgenase Calcium/Sodium Channels Norephrine Re-Uptake Mu-Agonists NSAIDS Gabapentin Nortriptyline Codeine Diclofenac Patch Carbamazepine Amitryptline Hydrocodone Dicofenac Gel Oxcarbamazepine Desipramine Hydromorphone Compound Gels Pregabalin Imipramine Tramadol Zonisamide Tramadol Tapentadol Lamotrgine Tapentadol Morphine Topical Lidocaine Duloxetine Oxycodone Savella Oxymorphone Methadone Fentanyl Buprenorphine Questions? Questions?